
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
![As shown, a member is fixed at the origin, point \( O \), and has an applied force \( \mathbf{F} \), the tension in the rope, applied at the free end, point \( B \).
The force is given by \( \mathbf{F} = 130 \, \text{N} \, \mathbf{i} - 125 \, \text{N} \, \mathbf{j} + 70 \, \text{N} \, \mathbf{k} \). The dimensions are \( x_1 = 1.35 \, \text{m} \), \( y_1 = 1.70 \, \text{m} \), and \( z_1 = 1.15 \, \text{m} \).
What is the moment about the origin due to the applied force \( \mathbf{F} \)?
**Express the individual components of the Cartesian vector to three significant figures, separated by commas.**
\[ \mathbf{M}_O = [ \, ] \, \text{N} \cdot \text{m} \]](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/bc8e0844-b7a6-4b83-bdd7-070e35b4aff9/99e31d71-e854-44e1-9d3e-1a6bafd21570/fr961x2_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:As shown, a member is fixed at the origin, point \( O \), and has an applied force \( \mathbf{F} \), the tension in the rope, applied at the free end, point \( B \).
The force is given by \( \mathbf{F} = 130 \, \text{N} \, \mathbf{i} - 125 \, \text{N} \, \mathbf{j} + 70 \, \text{N} \, \mathbf{k} \). The dimensions are \( x_1 = 1.35 \, \text{m} \), \( y_1 = 1.70 \, \text{m} \), and \( z_1 = 1.15 \, \text{m} \).
What is the moment about the origin due to the applied force \( \mathbf{F} \)?
**Express the individual components of the Cartesian vector to three significant figures, separated by commas.**
\[ \mathbf{M}_O = [ \, ] \, \text{N} \cdot \text{m} \]
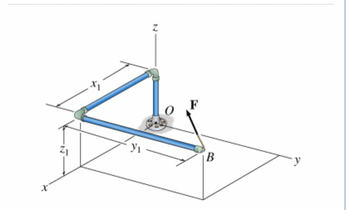
Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts a three-dimensional diagram commonly used in engineering mechanics to illustrate vector forces in a structure. Here is a detailed description of the diagram:
- The diagram features a structure composed of several pipes connected with joints, forming an L-shape.
- There are three main coordinate axes labeled as \( x \), \( y \), and \( z \), intersecting at the origin point \( O \). Each axis helps define the spatial orientation of the structure.
- The structure connects at different points along the axes, with lengths indicated by \( x_1 \), \( y_1 \), and \( z_1 \). These lengths help determine the position and dimensions of the structure.
- The point \( B \) is marked on the right end of the horizontal arm of the structure.
- At point \( B \), a force vector \( \mathbf{F} \) is shown, indicating that an external force is applied in a specific direction.
- The force vector illustrates both the magnitude and direction of the force acting on the structure.
This setup is typically used in educational materials to analyze how external forces influence the equilibrium and stability of mechanical structures.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A circular cylinder is being rotate as shown in the figure below with an axis of rotation going through point O perpendicular to the plane shown. The cylinder has dimensions of h = 17 cm, r = 3.1 cm and d = 16 cm. The cylinder has a density of \rhoρ = 7276 kg/m3. What is the object mass moment of inertia? (Enter your answer to the nearest thousandth kg·m2.)arrow_forwardThe force F = 12i − 8j + 6k N is applied to the gripper of the holding device shown. Determine the momentof F about (a) the a-axis; and (b) the z-axis.arrow_forwardAn ice figure skater is doing a spin with her hands on bar bells weighing 10 pounds a piece, clutched directly to her center of gravity for the spin. She has started to spin at 120 rpm(12.57 rad/sec) and suddenly extends her hands with the bar bells straight out radially from her body. Her arms are 2.5 feet long, her lo=8 lb-ft²(before extension). How much did she increase her mass moment of inertia by after she extended her arms? Answer in Ibm-ft².arrow_forward
- The particle has a mass of 0.45 kg and is confined to move along the smooth vertical slot due to the rotation of the arm OA. The rod is Part A rotating with a constant angular velocity 0 = 2 rad/s. Assume the particle contacts only one side of the slot at any instant. (Figure 1) Determine the magnitude of the force of the rod on the particle when 0 = 30°. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. HA ? F = Value Units Figure 1 of 1 > Submit Request Answer Part B A Determine the magnitude of the normal force of the slot on the particle when 0 0°. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. HA ? e = 2 rad/s N = Value Units 0.5 marrow_forwardThe body in the figure is pivoted at O. Three forces act on it in the directions shown: FA = 12.0 N at point A, 7.70 m from O; FB = 15.0 N at point B, 2.60 m from O; and Fc = 25.0 N at point C, 3.50 m from O. Taking the clockwise direction to be negative, what is the net torque about O? Number i -56.26 Units 160° N•m 90°/ B 135%arrow_forward2 sin t, y = 2cos t,z = 3t; 0arrow_forwardcould you explain why we choose dm=p(2pir)dr? circular disk or cyllinder has a volume so shouldn`t dm be p(2pir)dr * thickness ? ( i attached an expression). Why we choose a dm of a ring (without volume)?arrow_forwardAn engineer estimates that under the most adverse expected weather conditions, the total force on the highway sign in the figure (Figure 1) will be F→=(±2.1i^−4.2j^)kN, acting at the cm. What is the magnitude of the torque this force exert about the base O? Express your answer using two significant figures.arrow_forwardThe 0.61×1.00-m lid ABCD of a storage bin is hinged alongside AB and is held open by looping cord DEC over a frictionless hook at E. If the tension in the cord is 70 N, determine the moment about each of the coordinate axes of the force exerted by the cord at D.arrow_forwardASAParrow_forwardFor F = 51 lb, compute the combined moment of the two forces about (a) point O, (b) point C, (c) point D. The moments are positive if counterclockwise, negative if clockwise.arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution. Three identical full spheres of mass 3.1kg and Radius R=2.9m are welded together in such a way that the centres of each of them are at (R,0,0), (3R,0,0) and (5R,0,0). The whole system rotates in +XY plane about the axis parallel to z axis and passing through point (6R,0,0). Find the moment of inertia of the whole system. State your answer to the nearest tenth of kgm2.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON