
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Note the margin of error that they calculated. You will use that value in another context.
As another election cycle begins this fall, you will likely hear newscasters state poll data and then mention the margin of error. For example:
"Polls show that among likely voters in the Make-Believetown Governor’s race, Bad Wolf is currently leading with 43% of expected votes, Little Pig has 41%, and 16% are undecided. The poll has a margin of error of 4%.”
- Instead of the 4% margin of error currently in the example, use the margin of error from your classmate as the new margin of error% for the poll.
- Write a brief paragraph explaining who you believe will be the next imaginary governor of Make Believetown and why. Use the information you know about the margin of error to make your case.
- I chose to use random numbers to represent the weight of middle schoolers' backpacks.
My margin of error is 2.65
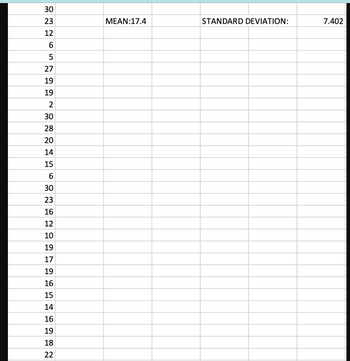
Transcribed Image Text:### Educational Statistics Spreadsheet
**Data Records:**
The following dataset consists of a series of numerical values:
- 30
- 23
- 12
- 6
- 5
- 27
- 19
- 19
- 2
- 30
- 28
- 20
- 14
- 15
- 6
- 30
- 23
- 16
- 12
- 10
- 19
- 17
- 19
- 16
- 15
- 14
- 16
- 19
- 18
- 22
**Statistical Analysis:**
1. **Mean (Average):** 17.4
2. **Standard Deviation:** 7.402
These statistical values provide insights into the central tendency and variability of the dataset.
- The **Mean** is calculated as the average of all the numerical values present in the dataset.
- The **Standard Deviation** quantifies the amount of variation or dispersion in the dataset from the mean.
### Explanation of Statistical Terms:
- **Mean (Average):** This is the sum of all values divided by the number of values. It provides the central value for the dataset.
- **Standard Deviation:** This measures the dispersion of the dataset relative to its mean. A higher standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range, while a lower standard deviation indicates that the values are closer to the mean.
Understanding these statistical measures is crucial for analyzing data trends and making informed decisions based on data.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A survey by the Arthur Andersen Enterprise attempted to determine what the leading challenges are for the growth and survival of small businesses. Although the economy and finding qualified workers were the leading challenges, several others were listed in the results of the study, including regulations, listed by 30% of the companies, and the tax burden, listed by 35%. Suppose that 71% of the companies listing regulations as a challenge also listed the tax burden as a challenge. Assume these percentages hold for all small businesses. 1. If a small business is randomly selected, find the following probabilities: (a) The small business lists either the tax burden or regulations as a challenge. (b) The small business lists either the tax burden or regulations but not both as a challenge. (c) The small business does not list regulations as a challenge given that it lists the tax burden as a challenge. (d) The small business does not list regulations as a challenge given that it does not…arrow_forwardIn a statistics activity, students are asked to spin a penny and a dime and determine the proportion of times that each lands with tails up. The students believe that since a dime is lighter, it will have a lower proportion of times landing tails up compared to the penny. The students are instructed to spin the penny and the dime 30 times and record the number of times each lands tails up. For one student, the penny lands tails side up 18 times, and the dime lands tails side up 20 times. Let PD = the true proportion of times a dime will land tails up and pp = the true proportion of times a penny will land tails up. Which of the following is the correct standardized test statistic and P-value for the hypotheses, Ho: Po-Pp= 0 and H₂: Po-Pp<0?arrow_forwardIn politics, marketing, etc. we often want to estimate a percentage or proportion p. One calculation in statistical polling is the margin of error - the largest (reasonble) error that the poll could have. For example, a poll result of 72% with a margin of error of 4% indicates that p is most likely to be between 68% and 76% (72% minus 4% to 72% plus 4%). In a (made-up) poll, the proportion of people who like dark chocolate more than milk chocolate was 37% with a margin of error of 2.5%. Describe the conclusion about p using an absolute value inequality. . That lets you type in a vertical bar | to represent absolute values. Also, when you type in < and then =, the symbolic entry option will automatically convert that to ≤ . In the same way, if you type in > and then =, the symbolic entry option will automatically convert that to ≥. Be sure to use decimal numbers in your answer (such as using 0.40 for 40%).arrow_forward
- A business magazine mailed a questionnaire to the treasurers of all of the Top 400 most profitable companies, and received responses from 22% of them. Those responding reported that they did not find that such surveys intruded significantly on their workday. What is the population and sample? The sample is The population is 1. the 22% (88) of the treasurers who responded 2. the 78% (412) of the treasurers who did not respond 3. all treasurers of all companies 4. treasurers of the Top 400 most profitable companies 5. all profitable companies 6. The business magazine 7. all people 8. the proportion of those responding that said they did not find that such surveys intruded significantly on their workday.arrow_forwardThe Party of Nonvoters From past elections, nonvoters are those who are either not registered to vote or are considered unlikely to vote in an upcoming election. Nonvoters are very different demographically from likely voters.Nonvoters are more racially and ethnically diverse. 43% of those who are not likely to cast a ballot are Hispanic, African or other racial and ethnic minorities, roughly double the percentage amoung likely voters(22%) (Source: Pew Research Center, October, 2014, "The Party of Nonvoters"). Suppose you interview 10 people who are considered nonvoters. Round answers to 4 decimal places.a.) What is the probability that 5 of them are an ethnic minority? b.) What is the probability that more than 8 are an ethnic minority? c.) What is the probability that at least 8 are not an ethnic minority? d.) What is the probability that fewer than 5 are not an ethnic minority?arrow_forward1. Use the results of simulation to appropriate the margin of error for hackers estimate of the proportion of students at his school that can roll their tongue 1b . Interpret the margin of errorarrow_forward
- PLEASE USE THE TABLE PROVIDED TO ANSWER THE QUESTION: A movie theater will be replaying old movies for a film festival and considering those with the highest public opinion back when the movie came out. Did movies with high public opinion explain a high revenue according to the dataset? Give a formal statistical conclusion to explain your answer. Construct any plot(s)/graph(s) to support your answer.arrow_forwardOpinions are split about a coffee company's pumpkin-flavored coffee (PFC). Yet every year over the last five years the consumption of pumpkin-flavored goods has increased. If we look at the numbers, it also becomes clear why a leading coffee company keeps offering the PFC earlier and earlier every year. According to a magazine, the amount spent by PFC buyers at the coffee company is about 17% higher than non-PFC buyers. The accompanying table shows a random sample of eight consumers, the amount they spend per week, and the number of PFCs purchased per week. PFC Spending 2 13.88 7 39.11 4 19.79 1 9.84 3 15.43 1 21.52 5 37.39 3 13.85 Calculate the slope and y-intercept for the regression formula. The slope is b1=4.465 The y-intercept is b0=6.840 Provide an interpretation for the value of the slope. Because the slope is positive, it can be…arrow_forwardTo get from Berkeley to the San Francisco airport (SFO) one can either take a shuttle van or drive. Either way, one must cross the San Francisco Bay Bridge. The shuttle van drops its passengers at the airport departure terminal. If one drives, he or she must park in a lot near the airport, then take a parking shuttle from the parking lot to the airport departure terminal. There is a 40% chance that the Bay Bridge will be congested with traffic. If it is, it takes 1.1 hours to drive to the parking lot. If not, it takes 40 minutes to drive to the parking lot. The parking shuttle runs every 10 minutes and takes 10 minutes to get to the airport departure terminal from the parking lot. Suppose it is equally likely that one must wait 0, 1, or 9 minutes for the parking shuttle once getting to the parking lot, and that the amount of time one must wait is independent of the amount of time it takes to drive to the parking lot from Berkeley. 2, If one takes the shuttle van from Berkeley directly…arrow_forward
- When you hear thw words “population” and “sample,” what comes first in your mind?arrow_forwardIn politics, marketing, etc. we often want to estimate a percentage or proportion p. One calculation in statistical polling is the margin of error - the largest (reasonble) error that the poll could have. For example, a poll result of 72% with a margin of error of 4% indicates that p is most likely to be between 68% and 76% (72% minus 4% to 72% plus 4%). In a (made-up) poll, the proportion of people who like dark chocolate more than milk chocolate was 44% with a margin of error of 2.2%. Describe the conclusion about p using an absolute value inequality. The answer field below uses the symbolic entry option in Mobius. That lets you type in a vertical bar | to represent absolute values. Also, when you type in and then =, the symbolic entry option will automatically convert that to >.arrow_forwardA sports equipment manufacturer has developed a new reasonably priced golf ball that it hopes will allow average golfers to hit the ball straighter. A concern is that this new technology might impact on the distance that the ball travels. To compare distances, Sarah, a company researcher, conducts an experiment where 20 current balls and 20 new balls are subjected to distance tests, using a mechanical hitting device for consistency. The results of the tests, with distances given to the nearest metre, are given in Table 1. Table 1 Distances travelled by golf balls Current golf ball New golf ball 299 292 292 291 293 285 295 288 283 273 280 305 280 286 311 308 292 291 283 296 292 294 309 281 311 286 302 302 294 296 297 303 287 298 282 293 300 290 297 284arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman