
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
17.16
Transcribed Image Text:AQUEOUS EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANTS
APPENDIX
TABLE D. 1 Dissociation Constants for Acids at 25 °C
Кл
K2
Formula
1.8 x 10 5
Name
CH,COOH (or HC,H,O2)
5.6 x 10 3
1.0 X 10-7
Acetic acid
30X 1012
Arsenic acid
H3ASO4
5.1 x 10 10
H3ASO3
8.0 x 10 5
1.6 x 10 12
Arsenous acid
Ascorbic acid
H2C,H,O6
6.3 x 10-5
Benzoic acid
CHSCOOH (or HC,H5O2)
5.8 x 10-10
Boric acid
HаВОЗ
1.5 X 10-5
TA
Butanoic acid
C3H,COOH (or HC4H,O2)
4.3 x 10-7
5.6 X 10-11
Carbonic acid
Н.СОЗ
1.4 X 10 3
Chloroacetic acid
CH2CICOOH (or HC2H2O2CI)
1.1 X 10-2
Chlorous acid
HCIO2
7.4 X 10-4
1.7 X 10-5
Citric acid
HOOCC(OH)(CH2COOH)2 (or H3C,H5O7)
4.0 x 107
3.5 x 10 4
Cyanic acid
HCNO
НСООН (or НСНО2)
1.8 X 10-4
Formic acid
Hydroazoic acid
HN3
1.9 x 10-5
Hydrocyanic acid
4.9 x 10-10
HCN
Hydrofluoric acid
6.8 X 10-4
HF
Hydrogen chromate ion
HCRO4
3.0 x 10-7
Hydrogen peroxide
H2O2
2.4 X 10-12
Hydrogen selenate ion
HSEO4
2.2 X 10-2
Hydrogen sulfide
H2S
9.5 x 10-8
1 x 10-19
Hypobromous acid
HBRO
2.5 x 10-9
Hypochlorous acid
HCIO
3.0 x 10-8
Hypoiodous acid
HIO
2.3 x 10-11
Iodic acid
HIO3
1.7 x 10-1
Lactic acid
CH3CH(OH)COOH (or HC3H;O3)
1.4 X 10-4
Malonic acid
CH2(COOH)2 (or H2C3H2O4)
1.5 X 10-3
2.0 x 10-6
Nitrous acid
HNO2
4.5 X 10-4
Oxalic acid
(CООН)2 (or HС,О)
5.9 x 10-2
6.4 x 10-5
Paraperiodic acid
H;IO6
2.8 x 10-2
5.3 x 10-9
Phenol
C,H3OH (or HC,H;O)
1.3 x 10-10
Phosphoric acid
HЭРОД
7.5 x 10-3
6.2 x 10-8
4.2 x 10
Propionic acid
CЭН,СООН (or НС3H,02)
1.3 x 10-5
Pyrophosphoric acid
НАР.О,
3.0 x 10-2
4.4 x 10-3
2.1 x 10
Selenous acid
H,SeO3
2.3 X 10-3
5.3 x 10-9
Sulfuric acid
H2SO4
Strong acid
1.2 x 10-2
Sulfurous acid
H,SO3
1.7 x 10-2
6.4 x 10-8
Tartaric acid
HOOC(CHOH),СООН (or H,C,Н,О6)
1.0 X 10-3
1092

Transcribed Image Text:(C,H5COOH) and an
ate (C,H5COONA).
solution prior to ad.
grams of sodium be
buffer? Neglect the
the sodium benzoa
CHAPTER 17 Additional Aspects of Aqueous Equilibria
760
trimethylamine, (CH3)3N, and 0.10 M in trimethylammo-
nium chloride, (CH3)3NHƠI; (c) a solution that is made by
mixing 50.0 mL of 0.15 M acetic acid and 50.0 mnL of 0.20 M
sodium acetate.
17.27 A buffer contains
sodium acetate in
(a) a solution that is 0.250 M in sodium formate (HCOONA)
and 0.100 M in formic acid (HCOOH), (b) a solution that is
0.510 M in pyridine (C,H,N) and 0.450 M in pyridinium
chloride (CsH;NHCI), (c) a solution that is made by com-
bining 55 mL of 0.050 M hydrofluoric acid with 125 mL of
0.10 M sodium fluoride.
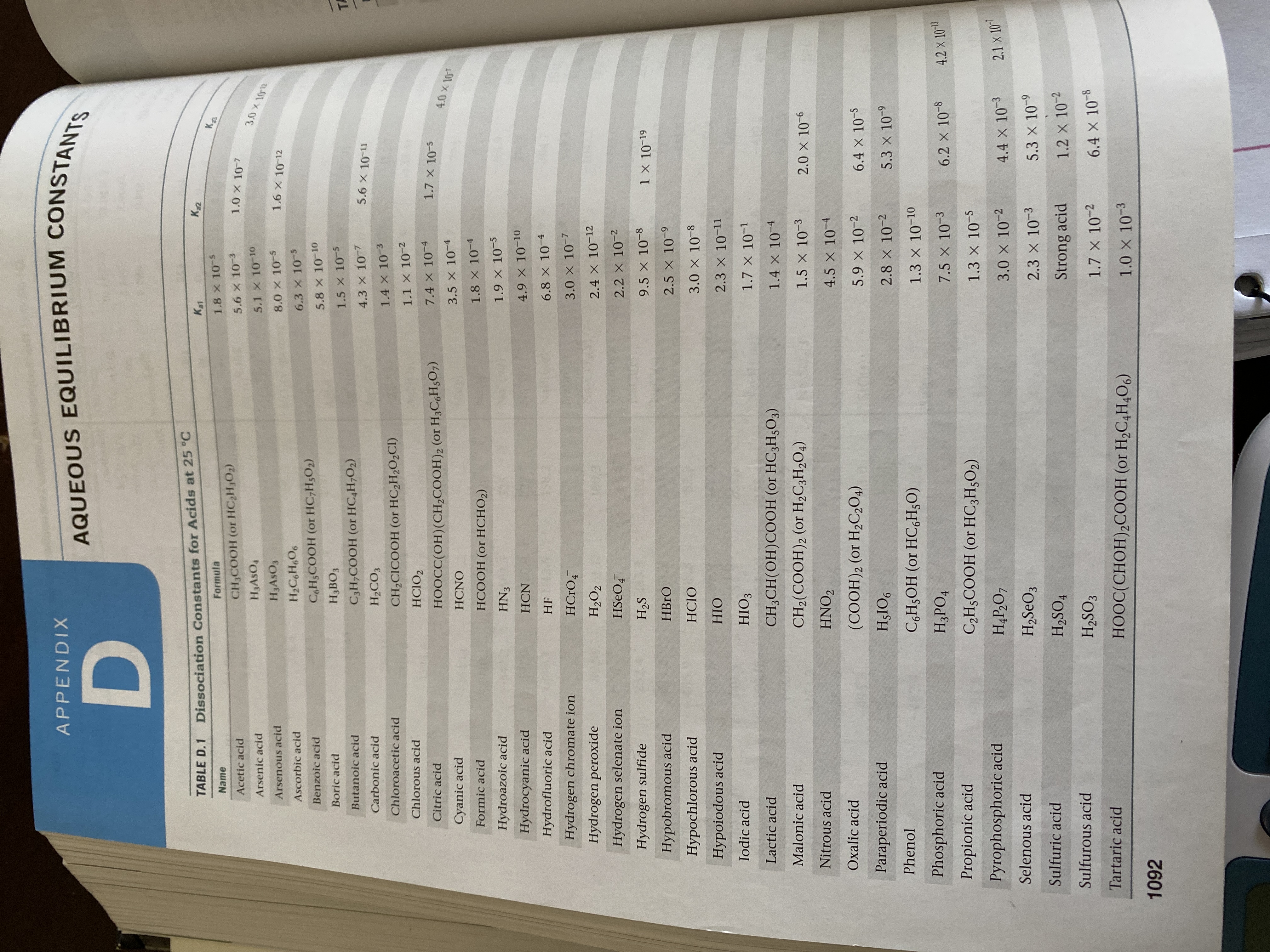
17.16 Use information from Appendix D to calculate the pH of
(b) What is the pH
mol of KOH? (c) W
tion of 0.02 mol o
17.28 A buffer contains
and 0.10 mol of so
17.17 (a) Calculate the percent ionization of 0.0075 M butanoic
1.5 x 10-5). (b) Calculate the percent ioniza-
(a) What is the p
buffer after the a
acid (Ka
tion of 0.0075 M butanoic acid in a solution containing
0.085 M sodium butanoate.
%3D
the pH of the bu
17.29 (a) What is the r:
(b) What is the
marathon runn
17.18 (a) Calculate the percent ionization of 0.125 M lactic acia
= 1.4 × 10¬4). (b) Calculate the percent ionization of
0.125 M lactic acid in a solution containing 0.0075 M so-
dium lactate.
(Ka
%3D
17.30 A buffer, consis
the pH of physi
Buffers (Section 17.2)
also use this bu
in which the m
and 8.0 g of Na
17.19 Which of the following solutions is a buffer? (a) 0.10 M
ixG
CH3COOH and 0.10 MCH3COONA, (b) 0.10 M CH3COOH,
(c) 0.10 M HCl and 0.10 M NaCI, (d) both a and c, (e) all of a,
b, and c.
17.20 Which of the following solutions is a buffer? (a) A solu-
tion made by mixing 100 mL of 0.100 M CH3COOH and 50
mL of 0.100 M NaOH, (b) a solution made by mixing 100
mL of 0.100 M CH;COOH and 500 mL of 0.100 M NaOH,
(c) A solution made by mixing 100 mL of 0.100 M CH3COOH
and 50 mL of 0.100 M HCI, (d) A solution made by mixing
100 mL of 0.100 M CH3COOK and 50 mL of 0.100 M KCI.
17.31 You have to pi
following 0.10
H3PO4, HCOC
tions would y
would you us
17.32 You have to p
following 0.1
CH,COОН,
tions would
17.21 (a) Calculate the pH of a buffer that is 0.12 M in lactic acid
and 0.11 M in sodium lactate. (b) Calculate the pH of a buf-
fer formed by mixing 85 mL of 0.13 M lactic acid with 95
mL of 0.15 M sodium lactate.
would you u
Acid-Base Titra
17.22 (a) Calculate the pH of a buffer that is 0.105 M in NaHCO3
and 0.125 M in Na2CO3. (b) Calculate the pH of a solution
formed by mixing 65 mL of 0.20 M NaHCO3 with 75 mL of
0.15 M Na CO3.
17.23 A buffer is prepared by adding 20.0 g of sodium ace-
tate (CH3COONA) to 500 mL of a 0.150 M acetic acid
(CH;COOH) solution. (a) Determine the pH of the buffer.
(b) Write the complete ionic equation for the reaction that
17.33 The accomp
monoproti
(b) What i
of each titr
a 0.100 M
mate the p
Occurs when a few drops of hydroghl
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 7 steps with 10 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A slightly soluble salt has the formula A B1 and a Ksp of 6.1E-25. What is pB in a solution of this salt? Answer: (12.11)arrow_forwardWhat is the correct reading of the volume in the pictured buret? Make sure to report your reading with the appropriate significant figures. 16 17 18 19arrow_forwardPlease. I want step by step and explain everything.arrow_forward
- What is the molality of a 13.6 mol/L solution of sulfuric acid in water, which has a density of 1.7043 g/mL? Answer: * (36.1)arrow_forward4.1.3.15. How many grams of sodium acetate trihydrate (m. wt. 136) and how many ml of 1 M acetic acid solution are necessary for preparing 3 liter 0.2 M, pH6.4 acetate buffer? pk, = 4.7 4.1.3.16. 0.03 g-eq. [H*] is formed during an enzymatic reaction carried out in 0.2 M TrisHCI buffer (pH=7.8). Calculate the pH at the end of reaction (pK,= 8.1). Calculate the pH if water were used instead of the buffer! Why is necessary to use the buffer in this reaction?arrow_forwardA 250.00 mL solution of 0.00215 M AB4 is added to a 230.00 mL solution of 0.00380 M C3D2. What is pQsp for A3D4? Answer: (18.607)arrow_forward
- How many grams of solid of LiCl (MW 42.471 g/mol) would be left behind if 28.807 mL of 0.550 M KCl solution was evaporated to dryness? (2 SF)arrow_forwardRun 2 Run 1 Molarity of KMNO4 solution (M) from 0.0010 0.0010 bottle Final reading of buret (KMNO4) (mL) 14.91 7.77 Initial reading of buret (KMNO4) (mL) 0,30 7.81 Volume of KMN04 solution (mL) Moles of MnO, used for titration (mL) Moles of C2042- in 100.0 mL of solution (mol) Molarity of C2042 (M) Molarity of Cd2+ (M) Ksp of CdC204arrow_forwardExtended matching For each description listed below select the correct drug from the list provided Description 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. gingival enlargement antiseizure medicine seizures or chronic orofacial pain sodium channel blocker migraine prophylaxis Drug a. valproic acid (Depakote) b. phenytoin (Dilantin) c. levetiracetam (Keppra) d. gabapentin (Neurontin) e. lamotrigine (Lamictal) Iarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY