
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:ter
answ
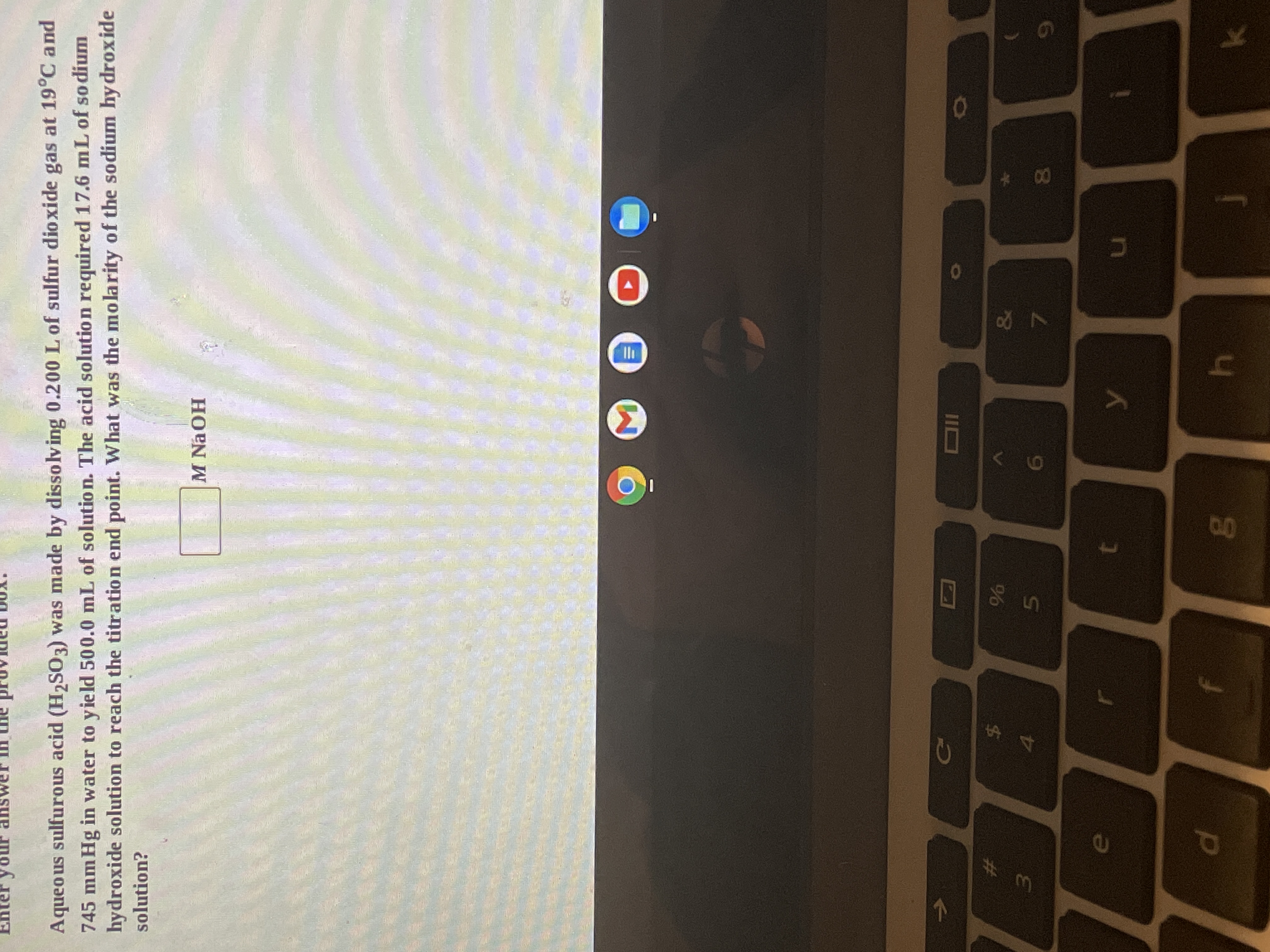
Aqueo us sulfurous acid (H2S03) was made by dissolving 0.200 L of sulfur dioxide gas at 19°C and
745 mm Hg in water to yield 500.0 mL of solutio n. The acid solution required 17.6 mL of so dium
hydroxide solution to reach the titration end point. What was the molarity of the sodium hy droxide
solution?
M NaOH
IID
$4
7.
CO
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What volume of 1.050 M hydrochloric acid is needed to completely dissolve a 5 51 g piece of chalk? Assume reacts with HC1 as written below CACO3(s) + 2 HCI(aq) --> CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H20(1)arrow_forwardA titration of 29.2 mL of a solution of the weak base aniline, C@HNH, ( K 4.0 x 10-10), requires 21.61 mL of 0.155 M HCl to reach the equivalence point. CH_NHz(aq) + HyO* (aq) + C,H,NH, (aq)+H,O(l) a What was the concentration of aniline in the original solution? Concentration 0115 ✔ M The equivalence point for a reaction is the point at which one reactant has been completely consumed by addition of another reactant. Thus, [C,HNH] [H₂O+] [OH-]- = 0.155 mol HC1 1.00 L 1 29.2 mL b What are the concentrations of H₂O¹, OH, and C6H5NHs at the equivalence point? M C = 0.115 M x 21.61 ml x M Correct 1 mol C, H, NH, 1 mol HCl Show Hintarrow_forwardA student used 26.28 mL of hydrochloric acid to titrate a 0.1166 gram sample of primary standard sodium carbonated (FW=105.99) What is the molarity of the HCl?arrow_forward
- What volume of 0.100 M H3PO4 is required to completely neutralize 15.0 mL of 0.200 M NaOH? H3PO4 + 3NAOH→ 3H20 + Na3PO4 O 10.0 mL O 7.50 mL 30.0 mL 90.0 mL 5.00mLarrow_forwardGiven the reaction: __NaHCO3(aq)+__H2SO4(aq)--> __NaSO4(aq)+__CO2(g)+__H2O(l) You mix 100.0 mL of 0.25 M NaHCO3 with 75.00 mL of 0.20 M H2SO4. a. What is the limiting reagent? b. What is the theoretical yield in grams of CO2? c. If the percentage yield of the reaction is 95%, what is the actual yield?arrow_forward13. The reaction of HCl with NaOH is represented by the equation: HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(ag) + Hz0(1) What volume of 0.252 MHC1 is required to titrate 54.1 mL of 0.424 M NAOH? [ Select ]arrow_forward
- To 0.340 L of 0.150 M NH3 is added 0.150 L of 0.120 M MgCl. Part A How many grams of (NH4)2SO4 should be present to prevent precipitation of Mg(OH)2(8)? Express your answer using two significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ m = 2.38 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect: Try Again; 3 attempts remaining ? garrow_forwardWhat volume of 0.120 M HCl is needed to neutralize 2.65 g of Mg(OH)2? V = M= 177) ΑΣΦ VE ΑΣΦ If 25.6 mL of AgNO3 is needed to precipitate all the CI ions in a 0.795-mg sample of KCl (forming AgCl), what is the molarity of the AgNO3 solution? V = M 15. ΑΣΦ O What volume of 0.105 M HClO4 solution is needed to neutralize 58.00 mL of 8.50x10-2 M NaOH? www. www. ? ? mLarrow_forward(4) - 25.00 ml of the phosphorus acid solution above was titrated with 0.350 M NaOH titrant using the following chemical equation: H) + NaOH( I (aq) → H₂O + Nag) (1) (aq) If 19.4 ml of 0.350 M NaOH titrant were needed to complete the reaction, how many moles of acidic protons (H+ ions) are present in the solution? (Remember to include the stoichiometric ratio from the chemical equation in your calculations!!!)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY