
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
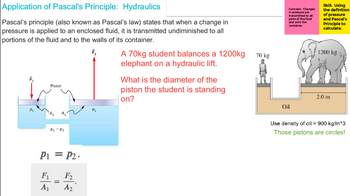
Transcribed Image Text:Application of Pascal's Principle: Hydraulics
Pascal's principle (also known as Pascal's law) states that when a change in
pressure is applied to an enclosed fluid, it is transmitted undiminished to all
portions of the fluid and to the walls of its container.
F₂
F₁
P₁
Piston
P₁ P₂
P1 = P2.
F₁ F₂
A₁
A₂
=
P₂
A 70kg student balances a 1200kg
elephant on a hydraulic lift.
What is the diameter of the
piston the student is standing
on?
70 kg
Concept: Changes
in pressure are
transmitted to all
parts of the fluid
and onto the
container.
Oil
Skill: Using
the definition
of pressure
and Pascal's
Principle to
calculate.
1200 kg
2.0 m
Use density of oil = 900 kg/m^3
Those pistons are circles!
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1

Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An object hangs from a spring balance.The balance registers 32 N in air, 22 N when this object is immersed in water, and 27 N when the object is immersed in another liquid of unknown density. What is the density of that other liquid? Number i Units Varrow_forwardWater flows from the pipe shown in (Figure 1) with a speed of 4.0 m/s. Figure 1 of 1 Part A What is the water pressure as it exits into the air? Express your answer using four significant figures. P� = kPakPa SubmitRequest Answer Part B What is the height hℎ of the standing column of water?arrow_forward* Question Co mpi The container shown is filled with a mystery liquid with density 33.5 x103 kg/m³. It is open to atmosphere on the left and closed on the right. What is the pressure at point A, in kPa (kiloPascal)? 1.0 atm = 1.00 x 105 Pa = 100 kPa, and g = 10.0 m/s². Your answer needs to have 3 significant figures, including the negative sign in your answer if needed. Do not include the positive sign if the answer is positive. No unit is needed in your answer, it is already given in the question statement. y (cm) 100 % 75- 50 25- f5 0 5 C T f6 < 6 B Y f7 & 4- lip U fg * 4+ K 8 fg KAA 9 f10 ▶11 f11 P 12arrow_forward
- Q16arrow_forwardWhich liquid has the larger surface tension? A. Liquid A because it supports a greater weight per unit length B. Liquid B because it supports the same weight over a larger length C. The liquids have the same surface tension because they support the same weight D. It is impossible to compare the surface tensions of the liquids based on the given infoarrow_forwardA 60 kg hot-air balloon carrie a person of 50 kg. The balloon and the person move at an upward acceleration of 1.75 m/s^2. What is the buoyant force on the system in SI base units? Other 588 O 110 O 1078 O 1270.5 As a balloon designer, what is the minimum volume of the hot-air balloon you need to make that possible? Use SI base units Other O 90 O 106 O 74arrow_forward
- Question 3 (1 point) 1.00 L (0.00100 m*3) of water is poured into a large container. 100 g of ice is added to the container. The ice floats freely and does not touch the bottom of the container. The densigy of ice is 917 kg/m. When the ice melts, what happens to the level of the water in the container? The water level rises. The water level stays the same. The water level falls. There is not enough information to tell.arrow_forward2. Gravitational acceleration on Earth is 9.8 m/s?, while on the Moon it is 1.6 m/s?. Scientists on Earth observe that when a wooden block is placed in a bucket of water, 60% of the block's volume is submerged under water. Suppose the same experiment is repeated on the Moon, with the same block and the same bucket of water. What fraction of the block's volume is submerged under water on the Moon? Explain your answer and support it with calculations.arrow_forwardThe same fluid (density unknown) fills three depressions on an alien planet. Depression #1 is a small pond. Depression #2 is a large lake. Depression #3 is a very large ocean. All of these depressions have the same depth. Gravity g is the same at all three locations. However the value of gravity is unknown. How do the gauge pressures at the bottoms of the three depressions compare? A. P3 > P2 > P1 B. They are the same C. P1 > P2 > P3 D. Can't tell without knowing the dimensions of the depressions.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON