
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Handwritten answers only pls. I need asap!
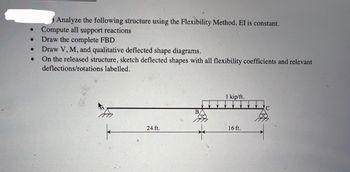
Transcribed Image Text:### Structural Analysis Using Flexibility Method
#### Task Description:
Analyze the following structure using the Flexibility Method. The constant EI is assumed for the structure.
#### Steps to Follow:
1. **Compute all support reactions:**
- Determine the reactions at each support point, ensuring equilibrium is maintained throughout the structure.
2. **Draw the complete FBD (Free Body Diagram):**
- Create a detailed Free Body Diagram illustrating all forces, moments, and support reactions.
3. **Draw V, M, and qualitative deflected shape diagrams:**
- **V (Shear Force Diagram):** Show how shear forces vary along the length of the structure.
- **M (Bending Moment Diagram):** Indicate the bending moments experienced by the structure at various points.
- **Deflected Shape Diagram:** Provide a qualitative sketch of how the structure would deform under the applied loads.
4. **On the released structure, sketch deflected shapes with all flexibility coefficients and relevant deflections/rotations labeled:**
- Illustrate the deflected shapes, ensuring all flexibility coefficients (related to structural stiffness and displacement) are indicated and labeled with corresponding figures.
#### Structure Analysis Diagram:
- **Support Configuration:**
- Left support (at the left-most side of the beam) is a fixed support.
- Right support (at point C on the far-right end) is pinned.
- Middle support (at point B) is a roller support.
- **Load Applied:**
- A uniform distributed load of \(1 \text{ kip/ft}\) is applied along the segment BC.
- **Dimensions:**
- Distance from the left support to point B is \(24 \text{ ft}\).
- Distance from point B to point C (span of uniform load) is \(16 \text{ ft}\).
By following these steps and using the provided data, a comprehensive analysis of the structural behavior under the described load can be achieved.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I need a literature review on the topic (Enhancing indoor air quality and safe entertainment in sports halls) consisting of several paragraphs... Introduction with determine 5 to 7 line with reference(https link to the reference 6 reference pls) and conclusion 7 line Pls veryy urgent thank youarrow_forwardI need a quick solution within 15 minutesarrow_forwardWhat is stop notice?When can be it used?arrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning