Course:
An electric dipole is located at (1, 1, 0). If the voltage at
(5, 6, 0) is 9V analyze the dipole for dipole moment in azdirection.
Electric Dipole
If two charges of equal magnitude and opposite signs are placed at a very small distance from one another, then the system is known as an electric dipole. The strength of an electric dipole is measured by its dipole moment vector. If the magnitude of the charge is and the separation between the charges is then the dipole moment is given by
The direction of the dipole moment is from the negative to the positive charge.
Let us consider two charges and be placed at a distance of . Let be the distance between the center of the dipole and the point of interest . Let and be the distance between the point P and and respectively.
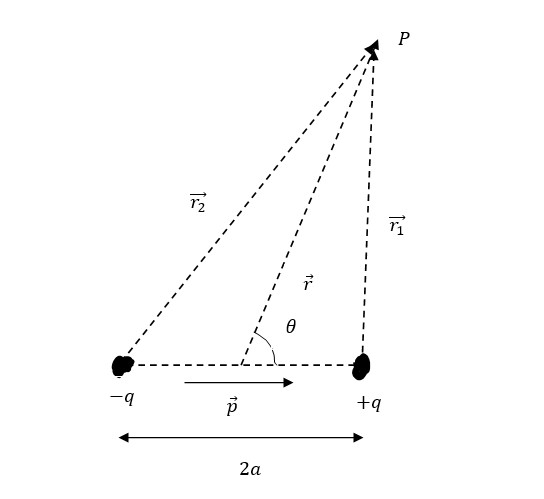
Potential due to charge at P
Potential due to charge at P
The total potential at P is
Applying cosine law of vector we have
Now for a short dipole, we have
Similarly, we can see that
Therefore the potential
In the question given, the dipole is located at the position and the position of the observation point is . Therefore
Therefore
and
Let the dipole moment is given by
Therefore we have
Thus we wee that there is no component of the dipole moment in the z-direction, that is, .
Considering the dipole is kept on the x axis. Therefore
Therefore the magnitude of the dipole moment
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

- Part2arrow_forwardplease type out your solution so that it is easy to read I have bad eyesight and cant read handriting wellarrow_forward3 Charge Deflector E beam An experiment to look for a charge imbalance between the proton and electron is constructed as shown. A beam of particles moving at speed vo = 1.0 x 106 m/s is prepared in an accelerator. Before striking the detector, the beam passes through a region of length L = 10 m that contains a uniform electric field of strength & = 100 N/C perpendicular to the beam. (a) Where would a proton from the beam be expected to strike the detector? (L.e., how many meters above or below the beam line would it strike?) (b) Where would an electron from the beam be expected to strike the detector? (L.e., how many meters above or below the beam line would it strike?) (c) We do not believe a hydrogen atom has any charge, but an experiment can only put an upper limit on the net charge - not prove that it is zero. Suppose the detector in this experiment is unable to detect a deflection less than 1 nm. I.c., if the deflection is 1 nm or less, the detector will register "0" deflection.…arrow_forward
- Current Attempt in Progress An Electrostatic Positioner. You and your team are designing a device that can be used to position a small, plastic object in the region between the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor. A small plastic sphere of mass m = 1.10 × 10-2 kg carries a charge q = +0.190 μC and hangs vertically (along the y direction) from a massless, insulating thread (length/ = 10.0 cm) between two vertical capacitor plates. When there is no electric field, the object resides at the midpoint between the plates (at x = 0). However, when there is a field between plates (in the +x direction) the object moves to a new equilibrium position. (a) To what value should you set the field if you want the object to be located at x = 2.10 cm? (b) To what value should you set the field if you want the object to be located at x = -3.15 cm? (a) Number i Units (b) Number i Unitsarrow_forwardUsing the symmetry of the arrangement, determine the direction of the force on +q in the figure below, given that: Case I. qa=qb= +6.5 μC and qc = qd = +6.5 μC. (a) In your notebook, draw the forces on q due to qar qb²9c² (b) Due to symmetry the direction of the net force is F O qc net ✔N O qd Hint: For each force draw the x and y components. Some will add and some will cancel. (c) Calculate the magnitude of the force on the charge q, given that the square is 10.0 cm on a side and q = 2.3 μC. and 9d- Xarrow_forward