
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
An underwater gate 8 m wide is held closed by a force, F, as shown in the figure. If the force is applied at the middle of the gate, what is the minimum value required to keep the gate closed? take density of water= 996kg/m3
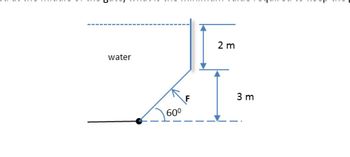
Transcribed Image Text:2 m
4
3 m
60⁰
water
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A reservoir is filled with water of density ρ. The depth of the water is ℎ. A gate is used to block the water on the right side as shown in the figure. The gate is hinged at the free surface level (z = 0), and a cable is attached to the gate ℎ/2 above the hinge. Compute how much pulling force F is needed to keep the gate closed. The atmospheric pressure is a constant p=p0 in case needed. The width (horizontal length) of the gate is W.arrow_forwardA 0.5-m diameter helium (Density of He = 0.18 kg/m3) balloon is attached by a rope to the bottom of a 10-m deep freshwater lake (Fig. 1). Given that the rope can sustain a maximum tensile force of 300 N, would it be able to secure the balloon? Please clearly illustrate your free-body diagram.arrow_forwardQuestion 2 In the schematic demonstrated in the figure, a spherical gate is used to regulate the height of water in a tank. The sphere radius is 50 cm and when the water height in the tank reaches 6 m, the gate opens by turning around hinge A. Determine the total hydrostatic force applied on the sphere and its angle of action at the moment that the gate is about to open. h=6 m R=50cmarrow_forward
- A semicircular, hinged gate separates two fluids on either side of a partition. Part (a) of the figure shows the geometry of the gate, and part (b) of the figure shows the whole system in side view. The radius of the gate (4 m) is equal to the height of the fluid on the right side of the gate (fluid 2), and the specific weight ratio of the fluids is γ2/γ1 = 1.5. At what height, h, will thegate just start to open?arrow_forwardRectangle Gate AB has length L and width b into the paper is hinged at B and has negligible weight. The liquid level, water, h does not reach the top of the gate for an angle theta. Find an equation for the force P, required to keep the gate in equilibrium. Solve for width, b. In the figure. (hint: draw a free-body diagram for the left and right side of the gate separately)arrow_forwardAn open manometer, shown in the figure, is installed to measure the pressure in a pipe carrying an oil (SG = 0.82). If the manometer liquid is carbon tetrachloride (SG = 1.60) determine the pressure in the pipe (in N/m2). Find the pressure head in meters of water column height.arrow_forward
- The 2-m wide gate ab depicted on the right retains water 3 m deep. Determine the horizontal and vertical forces on the gate, then calculate magnitude and direction of the resultant force on the gate.arrow_forwardProblem: Use a unit length for the gate, determine the height h (m) in fluid 2 in the figure below if the weightless triangular hinged gate is in equilibrium in the position shown. Assume y₂ = 1.5 ₁ Triangular Gate 1m Fluid 1 45° Hinge Fluid 2arrow_forwardPlease answer with a good explantion so I can understand the problemarrow_forward
- Consider the pressure and force acting on the pool retaining a reservoir of water. Suppose the pool is 50m wide and the water is 8m deep, as illustrated below. (a) What is the Gauge pressure on the dam due to the water? (b) What is the absolute pressure at10m depth of the dam? (C) Calculate the force exerted against the dam. Density of water is 1000kg/m3.arrow_forwardA vat contains a mixture of oil and water. The water forms a lower layer which is 0.8 m deep, and above it there is an oil layer 0.3 m thick. The density of water is 1000 kg/m³, and the density of oil is 800 kg/m³. Find the force on a flat door at the bottom of the vessel that has a cross-sectional area of 0.5 m². The acceleration due to gravity is 9.81 m/s². Oil, P. = 800 kg/m³ h, = 0.3 m %D Water, pw= 1000 kg/m3 h, = 0.8 m A = 0.5 m² O a. 5.1 kN O b. 5.4 kN Ос. 1.28 kN O d. 4.32 kN е. 10.2 kNarrow_forwardAn underwater pipeline must be laid 40 meters deep. The density of sea water is 1 025 kg/m³. The pipe has a mass of 40 kg per meter and an outside diameter of 300 mm. The pipe must be anchored every 5 m to the bottom of the sea. (a) What will the vertical force be on each anchor if the 4.3 pipe is empty. (b) What external pressure must the pipe be able to withstand if it is not to be crushed. [1 592 N, 402,2 kPa]arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY