
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
An orbiting satellite has a mass of 5000 kg and is travelling at a constant velocity of V0. To
alter its orbit, an attached rocket discharges 100 kg of gases from the reaction of solid fuel
at a speed of 3000 m/s relative to the satellite in a direction opposite V0. The fuel discharge
rate is constant for 2 s. Determine
(a) The thrust exerted on the satellite.
(b) The acceleration of the satellite during this 2 s period.
(c) The change of velocity of the satellite during this time period.

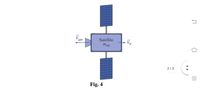
Transcribed Image Text:4. An orbiting satellite has a mass of 5000 kg and is travelling at a constant velocity of Vo. To
alter its orbit, an attached rocket discharges 100 kg of gases from the reaction of solid fuel
at a speed of 3000 m/s relative to the satellite in a direction opposite Vo. The fuel discharge
rate is constant for 2 s. Determine
(a) The thrust exerted on the satellite.
(b) The acceleration of the satellite during this 2 s period.
(c) The change of velocity of the satellite during this time period.
gas
Satellite
Msat
2/3
Fig. 4
Transcribed Image Text:gas
Satellite
Vo
Msat
2/3
Fig. 4
II
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q4. As shown in the image below, the freight cars A and B are approaching each other, and they have a mass of mA = 23 Mg and mB = 15 Mg, respectively. The directions of their initial velocities are shown in the image, and the speeds are VÃ,1 · 2.5 m/s and VB,1 = 2.1 m/s. If the two cars collide and get stuck together, then move with the same velocity, determine their common velocity after the collision. Right is considered the positive direction and negative sign must be included if they move to the left after the collision. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 3 places after the decimal point, and proper Sl unit. A Your Answer: VA,1 Answer units B VB.1arrow_forwardDuring terrible weather at a ski-flying world championship, a ski jumper tried to adjust for bad conditions midway down the ramp but completely lost control and tumbled wildly off the side at its bottom into a scattering crowd. The 73-kg jumper left the ramp about 45 m lower than his starting position. If the ski jumper had simply fallen straight down 45-m rather than skiing down a ramp, would his kinetic energy increase?arrow_forwardDuring an Olympic 100-m sprint race, Usain Bolt, the world record holder in that race, quickly accelerates to his top speed of 12.4 m/s. Analysis of his technique has shown that each of his feet make contact with the ground for 0.0800 s, exerting a force of magnitude 2.80 x 10° N during this contact. This allows the 94.0 kg Bolt to leap forward and remain airborne for 0.120 s until the next foot touches the ground. (Ignore air resistance.) (a) What are the magnitudes of the horizontal and vertical components of the force (in N) Bolt's feet exert on the ground? (Round your answers to at least three significant figures.) horizontal N vertical (b) Assuming that the sprinter accelerates at a constant rate while his feet are in contact with the ground and does not slow down when he is airborne, by what amount does Bolt's horizontal speed (in m/s) increase with each step? (Round your answer to at least three significant figures.) m/s (c) Assuming that the sprinter's speed increases at a…arrow_forward
- A 0.430-kg soccer ball is kicked at an initial speed of 34.0 m/s at an angle of 35 degrees to the horizontal. What is the kinetic energy at the apex of its trajectory?arrow_forwardQ5. As shown in the image below, the freight cars A and B are approaching each other, and they have a mass of mà = 19 Mg and må 16 Mg, respectively. The directions of their initial velocities are shown in the image, and the speeds are VA,1 2.0 m/s and VB,1 = 1.7 m/s. If the two cars collide and get stuck together, determine the loss of their combined kinetic energy (in kJ) during the collision. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 1 place after the decimal point, and proper SI unit. A Your Answer: VA,1 Answer B VB,1 =arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY