
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780470458365
Author: Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
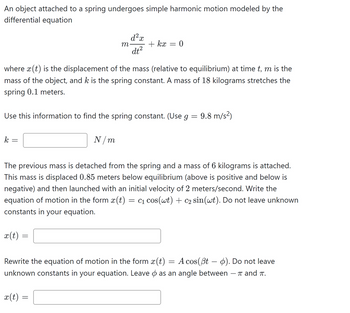
Transcribed Image Text:An object attached to a spring undergoes simple harmonic motion modeled by the
differential equation
k =
x(t)
m
where x(t) is the displacement of the mass (relative to equilibrium) at time t, m is the
mass of the object, and k is the spring constant. A mass of 18 kilograms stretches the
spring 0.1 meters.
=
x (t)
d² x
Use this information to find the spring constant. (Use g
=
N/m
dt²
=
+ kx
=
= 0
The previous mass is detached from the spring and a mass of 6 kilograms is attached.
This mass is displaced 0.85 meters below equilibrium (above is positive and below is
negative) and then launched with an initial velocity of 2 meters/second. Write the
equation of motion in the form (t) = C₁ cos(wt) + C₂ sin(wt). Do not leave unknown
constants in your equation.
9.8 m/s²)
Rewrite the equation of motion in the form x(t) = A cos(Bt - ). Do not leave
unknown constants in your equation. Leave as an angle between - and T.
π
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A piece of chicken is boiled until its internal temperature reaches 165 °F. The chicken is then transferred to a refrigerator held at 49 °F to cool down. The internal temperature of the chicken at time t is given by T(t), and the temperature obeys Newton's law dT = -k(T - Tm) where Tm is the temperature of the refrigerator and k > 0 is a constant. After 5 minutes in the refrigerator, the internal temperature of the chicken is 155 °F. How long will it take for the temperature of the chicken to reach 70 °F?arrow_forwardA comet passing by a star, with initial velocity (30, 60), experiences a force which causes it to accelerate according to a(t) = (-25e – 25e-t, 25e – 25e-t) (in m/sec?). Find a formula for its velocity at time t.arrow_forwardA metal bar of initial temperature 15 degrees C is placed in a a vat of boiling water (100 degrees C). Assuming Newton's Law of warming, this equation describes the temperature of the bar at time t > 0. Oy 100 (1 - e kt) O y= 15 + .85kt 100 85e kt -kt y 85e + 15arrow_forward
- A force of 720 newtons stretches a spring 4 meters. A mass of 45 kilograms is attached to the end of the spring and is initially released from the equilibrium position with an upward velocity of 6 m/s. Give the initial conditions. x(0) = x'(0) = Find the equation of motion. x(t) = Need Help? m m/s Read It Watch Itarrow_forwardPlease walk me through this problem. Thank you!arrow_forwardA model rocket is fired vertically upward from rest. Its acceleration for the first three seconds is a(t) = 90t, at which time the fuel is exhausted and it becomes a freely "falling" body. Eighteen seconds later, the rocket's parachute opens, and the (downward) velocity slows linearly to -11 ft/s in 5 seconds. The rocket then "floats" to the ground at that rate. (a) Determine the position function s and the velocity function v (for all times t). 4512 if 0 sts 3 405 if 3 26 15r3 if 0 sts 3 405 if 3 26arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY
Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,


Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780073397924
Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781118141809
Author:Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781337798310
Author:Peterson, John.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

