
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780078807213
Author: Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
PLEASE REPLY ASAP!!!!!!!
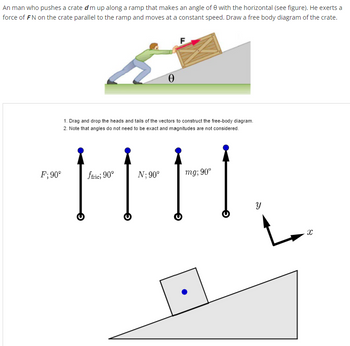
Transcribed Image Text:**Physics of Motion on an Inclined Plane**
An individual pushes a crate of mass \(m\) up along a ramp inclined at an angle \(\theta\) to the horizontal. He applies a force of \(F \, N\) on the crate, parallel to the plane, maintaining a constant speed. The task is to illustrate a free body diagram for the crate.
### Instructions for Free-Body Diagram:
1. **Drag and Drop**: Manipulate the vectors by moving their heads and tails in order to construct the free-body diagram.
2. **Guidelines**: Exact angles aren't necessary, and the magnitudes of the vectors aren't considered.
### Forces and Vectors:
- **\(F; 90^\circ\)**: Represents the applied force by the man.
- **\(f_{fric}; 90^\circ\)**: Symbolizes the frictional force opposing motion.
- **\(N; 90^\circ\)**: Denotes the normal force perpendicular to the surface.
- **\(mg; 90^\circ\)**: Indicates the gravitational force acting downwards.
### Free Body Diagram Setup:
Below the instructions, there is a depiction of the crate placed on an inclined plane. Next to it, coordinate axes (\(x\),\(y\)) are aligned such that \(x\) is along the plane.
This educational material guides students in understanding the dynamics of forces acting on objects on inclined planes by constructing accurate free-body diagrams.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A person holds a ball in her hand. (a) Identify all the external forces acting on the ball and the Newtons third-law reaction force to each one. (b) If the ball is dropped, what force is exerted on it while it is falling? Identify the reaction force in this case. (Ignore air resistance.)arrow_forwardA car is moving forward slowly and is speeding up. A student claims that the car exerts a force on itself or that the cars engine exerts a force on the car. (a) Argue that this idea cannot be accurate and that friction exerted by the road is the propulsive force on the car. Make your evidence and reasoning as persuasive as possible. (b) Is it static or kinetic friction? Suggestions: Consider a road covered with light gravel. Consider a sharp print of the tire tread on an asphalt road, obtained by coating the tread with dust.arrow_forwardReview. A student, along with her backpack on the floor next to her, is in an elevator that is accelerating upward with acceleration a. The student gives her backpack a quick kick at t = 0, imparting to it speed v and causing it to slide across the elevator floor. At time t, the backpack hits the opposite wall a distance L away from the student. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction k between the backpack and the elevator floor.arrow_forward
- In Figure P1.84, the pulleys and the cord are light, all surfaces are frictionless, and the cord does not stretch. (a) How does the acceleration of block 1 compare with the acceleration of block 2? Explain your reasoning. (b) The mass of block 2 is m2 = 1.30 kg. Derive an expression for the acceleration of the block having mass m2 as a function of the mass of block 1, m1. (c) What does the result of part (b) predict if m1 is very much less than 1.30 kg? (d) What does the result of part (b) predict if m1 approaches infinity? (e) In this last case, what is the tension in the cord? (f) Could you anticipate the answers to parts (c), (d), and (e) without first doing part (b)? Explain. Figure P1.84arrow_forward*PLEASE SOLVE #6* Make a sketch of a wood block sliding down the inclined track. Draw and label vectors to indicate the direction of the velocity and the direction of the acceleration. Also assign a symbol to the mass of the block and label it on the drawing. Draw a free-body diagram of the forces on the block as it slides down the ramp. Draw the acceleration vector for the block near the free-body diagram. Choose a coordinate system, and draw the force vectors on your coordinate system (a force diagram). What angles between your force vectors and your coordinate axes are the same as the angle between the ramp and the table? Determine all of the angles between the force vectors and the coordinate axes. Write down Newton's 2nd law in both the x and y directions. For any forces that are at an angle to your coordinate system, be sure to consider the components along the x and y axes. It is also important to make sure that all of your signs are correct. For example, is the…arrow_forwardA 3 kg object is sliding down an incline of 40° with respect to the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the incline and object is 0.4. The initial velocity of the object is 2.0 m/s. a.) Draw a free body diagram for the situation labeling all forces present. b.) Write the Newton’s Second Law equation for the forces acting on the object perpendicular to the incline. c.) Write the Newton’s Second Law equations for the forces acting on the object parallel to the incline. d.) Calculate the normal force acting on the object. e.) Calculate the acceleration of the object.arrow_forward
- Please Answer Question 7arrow_forwardHello, please answer the following Physics question correctly. *If you solve the question CORRECTLY and I will 100% leave a thumbs up for you. Thank you. Physics Question: 3) An object with mass 75 kg is pulled on a horizontal surface by a horizontal pull of 50 N to the right. The friction force on this object is 30 N to the left. What is the acceleration of the object?arrow_forwardA motion sensor and a force sensor record the motion of a cart along a track, as shown above. The cart is given a push so that it moves toward the force sensor and then collides with it. The two sensors record the values shown in the following graphs. a. Determine the cart’s average acceleration between t = 0.33 s and t = 0.37 s.arrow_forward
- * Untitled Question A box weighing 100 N is at rest on a horizontal floor. The coefficient of the static friction Fsin e between the box and the floor is 0.4. What is the - Mr smallest foree exerted castward and upward at an angle of 30" with the horizontal that can start the F cos 6 box in motion? Q2: Use dimensional analysis to determine which of the following equation is certainly wrong: Where i. and h are the lengths and | F] = [MLTJ. The other symbols have their usual meaning? Q3: What is the sum å + b if å (-4.0 m) i+(3.0 m) jand b ( -11.0 m) i+ (7.0m)j? What are the (b) magnitude and (c) direction of a + b Q4: Figure shows three forces applied to a trunk that moves leftward by 3.00 m over a frictionless floor. The force magnitudes are F1 = 7.00 Ib, F2 = 10.00 Ibs and F3= 3.00N, and the indi le O g ne unspeeent, (a) what is the net work done on the trunk by the three fortes and (b) does the kinetic energy of the trunk increase or decrease?arrow_forward* (1) A person is dragging a 15kg box along the ground by a rope 30° to the horizontal with a force of 58N, at a constant velocity. a) Draw the free - body diagram. b) Determine the normal force. c) Determine the frictional force. d) Determine the coefficient of friction. C. * (2) Trolley is set move on a smooth track that is banked at angle of 30°. For a trolley moving with a speed of 8m /s to round the curve. a) Draw the free - body diagram b) what is the radius of the banked surface? * (3) Two billiard balls of equal mass undergo a perfectly elastic head – on collision. If the speed of one ball was initially 2.00m/s, and of the other 3.00m/s in the opposite direction, what will be their speeds after the collision? 11' 1. ologtically with a second billiardarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements about friction is not true? * A. An object of large mass is pulled down onto a surface with a greater force than an object of low mass and, as a consequence, experiences a greater friction B. The direction of friction is always opposite to the direction of motion C. Friction is a force D. The direction of friction is always the same as the direction of motionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning