
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780078807213
Author: Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
No Chatgpt please will upvote
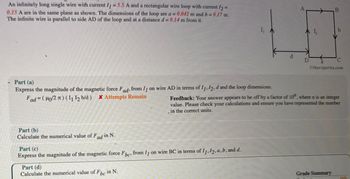
Transcribed Image Text:An infinitely long single wire with current 11 = 5.5 A and a rectangular wire loop with current 12 =
0.15 A are in the same plane as shown. The dimensions of the loop are a = 0.042 m and b = 0.17 m.
The infinite wire is parallel to side AD of the loop and at a distance d= 0.14 m from it.
I₁
A
B
AL
b
D
C
Otheexpertta.com
Part (a)
Express the magnitude of the magnetic force Fad, from I on wire AD in terms of 11, 12, d and the loop dimensions.
Fad=(μo/2л) (11 12 b/d) x Attempts Remain
Feedback: Your answer appears to be off by a factor of 10", where n is an integer
value. Please check your calculations and ensure you have represented the number
in the correct units.
Part (b)
Calculate the numerical value of Fd in N.
Part (c)
adi
Express the magnitude of the magnetic force Fbe, from I1 on wire BC in terms of 11, 12, a, b, and d.
Part (d)
Calculate the numerical value of Fbc in N.
Grade Summary
AC

Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Can you please answer g & h?arrow_forward.………………. In the figure below, the current in the long, straight wire is I₁ = 9.00 A and the wire lies in the plane of the rectangular loop, which carries a current I₂ = 10.0 A. The dimensions in the figure are c = 0.100 m, a = 0.150 m, and l = 0.600 m. Find the magnitude and direction of the net force exerted on the loop by the magnetic field created by the wire. UN magnitude direction ---Select--- 1.0arrow_forwardA circular loop of wire of radius 16.0 cm is in a magnetic field of 4.50 · 10−3 T directedout of the page. The loop is stretched to make it long and thin, with no area betweenthe wires. The stretching takes 0.850 s. What are the magnitude and direction of theinduced emf in the loop while the loop is being stretched? Explain how you found thedirection, briefly giving all the steps of your thinking.arrow_forward
- PLEASE SHOW UNITS WHEN SOLVING THE WORK PROBLEM ALSO. PLEASE LET ME KNOW THE PHYSIC CONCEPT OF THE PROBLEMarrow_forwardAs a model of the physics of the aurora, consider a proton emitted by the Sun that encounters the magnetic field of the Earth while traveling at 3.3 × 10³ m/s. Figure Z V Vparallel B Vperpendicular 700 < 1 of 1 Part A The proton arrives at an angle of 33" from the direction of B (refer to (Figure 1)). What is the radius of the circular portion of its path if B Express your answer to two significant figures and include appropriate units. LO Value Submit Part B Value Submit Part C Calculate the time required for the proton to complete one circular orbit in the magnetic field. Express your answer to two significant figures and include appropriate units. 6 A Value Submit Request Answer Units 6 A Request Answer ← Units C How far parallel to the magnetic field does the proton travel during the time to complete a circular orbit? This is called the pitch of its helical motion. Express your answer to two significant figures and include appropriate units. BI? C Units Request Answer ? 2.8 x 10-5…arrow_forwardA loop of wire with a radius of 0.16 m and resistance, 47.4 Ohms is in a region with a changing magnetic field that is oriented perpendicular to the loop. If the magnetic field increases linearly from 0.011 T to 0.05 T, over 5.59 x 10-3 s, what is the current in the loop? Please give your answer in Amps.arrow_forward
- An infinitely long single wire with current I1 = 5.5 A and a rectangular wire loop with current I2 = 0.25 A are in the same plane as shown. The dimensions of the loop are a = 0.033 m and b = 0.145 m. The infinite wire is parallel to side AD of the loop and at a distance d = 0.19 m from it. Part a) Calculate the numerical value of Fad in N. Part b) Calculate the numerical value of Fbc in N. part c) Calculate the numerical value of the sum of the forces F = Fad - Fbc on the infinite wire in N.arrow_forwardA metal cube with sides of length a is moving at velocity v=voj across a uniform magnetic field B = Bok. The cube is oriented so that four of its edges are parallel to its direction of motion (i.e., the normal vector of two faces are parallel to the direction of motion). (Figure 1) Figure Bo N 1 of 1 Vo Part A Find E, the electric field inside the cube. Express the electric field in terms of vo, Bo, and unit vectors (i, j, and/or k). E = Submit Part B V ΑΣΦ -î Request Answer Now, instead of electrons, suppose that the free charges have positive charge q. Examples include "holes" in semiconductors and positive ions in liquids, each of which act as "conductors" for their free charges. www. J? If one replaces the conducting cube with one that has positive charge carriers, in what direction does the induced electric field point? Submit Request Answerarrow_forwardSuppose you wish to measure the current in a wire. You have a device that can measure the strength of the magnetic field produced by the wire, but the device does not directly measure the current. If the device is place 0.98m away from the wire, and the magnetic field strength is 1.72µT, what is the current running through the wire in Amps? Note: It is understood that the unit of your answer is in A, however do not explicitly include units in your answer. Enter only a number. If you do enter a unit, your answer will be counted wrong.arrow_forward
- In the figure (Figure 1) the top wire is 1.2 mm -diameter copper wire and is suspended in air due to the two magnetic forces from the bottom two wires. The current flow through the two bottom wires is 79 A in each. Figure 1 of 1 N -3.8 cm -3.8 cm -3.8 cm Part A Calculate the required current flow in the suspended wire. Express your answer using two significant figures. —| ΑΣΦ ? Icu = Submit Provide Feedback Request Answer A Next >arrow_forwardA circular closed, conducting loop of radius r is in the presence of a uniform magnetic field that points into the page, shown in the figure below. The strength of the magnetic field changes as a function of time, which is described by the following expression: B(t) = B1t? + Bo. You may assume that B1 and Bo are both positive numbers. The direction of the magnetic field stays constant. The total resistance of the conducting loop is R. Use this information to solve parts (a) - (d). Write your answers in terms of known quantities such as: r, R, B1, Bo, and t. B(t) = B,t? + Bo %3D R r (a) Write an expression for the magnetic flux through the loop, assuming that the area vector of the loop points out of the page. Is the flux increasing or decreasing over time? (b) Determine the magnitude of the induced electromotive force driven through the loop. (c) Determine the magnitude of the induced current driven through the loop. (d) In which direction does the induced current flow (clockwise or…arrow_forwarddB = The vector 7 points from the source (the current, or location S) to the location of interest (P). What is the y component of the "unit vector", in meters? Ho Idlxf 4T p2 This problem checks your understanding of the term in the equation for the magnetic field due to a small "segment" of current, Consider a small "piece" of current (perhaps in a wire) at a location $ whose coordinates are (6 m, 6 m, 7 m). We would like to find the magnetic field at a location P whose coordinates are (4 m, 2 m, 9 m).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
