
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
An incompressible viscous flow is contained between two parallel plates separated from each other by distance b. as shown in Figure 1. The flow is caused by the movement of the upper plate which has a velocity U, while the bottom plate is fixed. If U =7 m/s and b= 1 cm, and there is no pressure gradient in the flow direction. A.) Start with Navier-Stokes equations and determine the velocity at the point x = 3 cm and y= 0.41 cm. The value of the velocity is.B.) Calculate the magnitude of the vorticity at the same point. The magnitude value of vorticity. C.) Calculate the rate of angular deformation at the same point. The angular deformation value
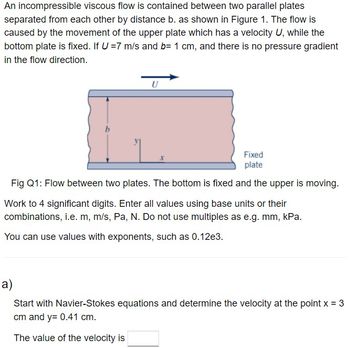
Transcribed Image Text:An incompressible viscous flow is contained between two parallel plates
separated from each other by distance b. as shown in Figure 1. The flow is
caused by the movement of the upper plate which has a velocity U, while the
bottom plate is fixed. If U = 7 m/s and b= 1 cm, and there is no pressure gradient
in the flow direction.
U
Fixed
plate
Fig Q1: Flow between two plates. The bottom is fixed and the upper is moving.
Work to 4 significant digits. Enter all values using base units or their
combinations, i.e. m, m/s, Pa, N. Do not use multiples as e.g. mm, kPa.
You can use values with exponents, such as 0.12e3.
a)
Start with Navier-Stokes equations and determine the velocity at the point x = 3
cm and y= 0.41 cm.
The value of the velocity is

Transcribed Image Text:b)
C)
Calculate the magnitude of the vorticity at the same point.
The magnitude value of vorticity
Calculate the rate of angular deformation at the same point.
The angular deformation value
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A Newtonian fluid is flowing in the narrow gap between two infinite parallel horizontal plates due to the movement of the top plate (see the figure below). The top plate is moving at a speed U from left to right, and the bottom plate is stationary. Consider the flow is steady, incompressible, and laminar. The distance between two plate is H, and the gravity acts in negative z-direction (which is perpendicular into the page). There is an applied constant pressure gradient of apJəx in the x-direction. Calculate the velocity and pressure fields. Plot typical velocity profiles in dimensionless form for a pressure gradient value of 0 and -15. In your solution show the conceptual diagram of the problem; write all relevant assumptions and boundary conditions; show the detailed steps of the problem solutions including equations and detailed processing of those equations. Moving plate Fluid: p.H Fixed plate P2-P1arrow_forwardThe fluid particles do not rotate about their own axis in an irrotational fluid flow. Select one: True Falsearrow_forwardThe equation shown is the continuity equation for steady, compressible flow. P1Q1=P2Q2 TRUE FALSEarrow_forward
- (a) A wing section with a chord of c and a span of b is mounted at zero angle of attack in a wind tunnel. A pitot probe is used to measure the velocity profile in the viscous region downstream of the wing section as shown in the figure. The measured velocity profile is u(z) = U∞ - (U/2) cos[TZ/(2w)] for -w ≤ z ≤w. Here, w = 0.02c. Assuming a constant pressure p = po along the streamlines (dashed lines in the figure) and across the wake where the velocity was measured, calculate the friction drag coefficient Cp, of the wing section. U Streamlines u = U_ -- cos 22 2W² +w Viscous wake = -W (b) Consider a thin flat plate at zero angle of attack in an airflow at P∞ = 1.225 kg/m³, T∞ = 288 K and μ∞ 1.7894 x 10-5 kg/m/s. The length of the plate is 2 m and the span is 0.5 m. Assume the boundary layers on the plate are laminar throughout (on the upper and lower surfaces both) where LBL(x)/x = 0.664/√√/Rex applies. The freestream velocity is 100 m/s. Calculate the friction drag (Df) of the first…arrow_forwardConsider a two-dimensional flow which varies in time and is defined by the velocity field, u = 1 and v = 2yt. Do the fluid elements experience angular rotation? Thus, state whether the flow field is rotational or irrotational.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY