
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
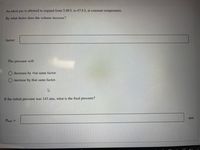
Transcribed Image Text:An ideal gas is allowed to expand from 5.60 L to 47.6 L at constant temperature.
By what factor does the volume increase?
factor:
The pressure will
O decrease by that same factor.
O increase by that same factor.
If the initial pressure was 143 atm, what is the final pressure?
atm
Prinal =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following should be done to reduce the pressure of 1 mole of an ideal gas in a 22.4 L container to zero torr? O Double the temperature of the gas. O Cool the gas to absolute zero. Halve the volume of the container. O Cool the gas to zero Celsius. Double the amount of gas.arrow_forwardA flexible container at an initial volume of 7.14 L contains 9.51 mol of gas. More gas is then added to the container until it reaches a final volume of 12.1 L. Assuming the pressure and temperature of the gas remain constant, calculate the number of moles of gas added to the container. number of moles of gas: molarrow_forwardA sample of oxygen gas at 301 K and 2.02 atm occupies a volume of 1.82 L. If the gas is allowed to expand to a larger volume, while at the same time it is cooled to a lower temperature, the final gas pressure will be lower than 2.02 atm. O will be higher than 2.02 atm. could be higher or lower than 2.02 atm depending on the final volume and temperature.arrow_forward
- a) SO₂ gas at a pressure of 7.50 atm is heated from 0.0°C to 481 °C and is simultaneously compressed to one-quarter of its original volume. Determine the final pressure (in atm). Pressure: atm b) If the SO₂ has a mass of 14.6 g, determine the final volume of the system described in part a) (in L). Volume: Larrow_forwardAn ideal sample of carbon dioxide gas at 303 K and 0.457 atm occupies a volume of 3.10 L. If the gas is compressed into a smaller volume, while at the same time it is heated to a higher temperature, the final gas pressure: Could be higher or lower than 0.457atm, depending on the final temperature and volume O Will be higher than 0.457atm O Will be lower than 0.457atmarrow_forwardA sample containing 4.70 gg of O2O2 gas has an initial volume of 11.0 LL . What is the final volume, in liters, when each of the following changes occurs in the quantity of the gas at constant pressure and temperature? A. A sample of 0.650 mole of O2O2 is added to the 4.70 gg of O2O2 in the container. B. A sample of 1.65 gg of O2O2 is removed from the 4.70 gg of O2O2 in the container. C.A sample of 4.80 gg of O2O2 is added to the 4.70 gg of O2O2 gas in the container.arrow_forward
- 13. A barometer is used to measure the total pressure of a mixture of gases A, B, and C. The total pressure is measured to be 750 torr. Assume the partial pressure of gas A is 203 torr and the partial pressure of gas B is 167 torr. What is the pressure of gas C? Do not include units with your answer.arrow_forwardAn ideal gas is allowed to expand from 6.60 L to 62.7 L at constant temperature. By what factor does the volume increase? factor: The pressure will increase by that same factor. decrease by that same factor. If the initial pressure was 117 atm, what is the final pressure? Pinal atmarrow_forwardUse the Refereices to acc ant values A sample of argon gas occupies a volume of 9.38 L at 58.0°C and 1.01 atm. If it is desired to increase the volume of the gas sample to 12.1 L, while decreasing its pressure to 0.643 atm, the temperature of the gas sample at the new volume and pressure must be °C.arrow_forward
- Doubling the initial pressure, from 1.0 atm to 2.0 atm, while keeping the temperature constant causes the volume of a gas to go from 1000 mL to a final volume ofarrow_forwardAn ideal gas is allowed to expand from 6.40 L to 48.0 L at constant temperature. By what factor does the volume increase? factor: The pressure will increase by that same factor. decrease by that same factor. If the initial pressure was 145 atm, what is the final pressure? atm Pfinal =arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY