
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
answer all parts and i will rate really highly! *28

Transcribed Image Text:1. An elevator shown below filled with passengers has a mass of 1.7 10³ kg. The elevator does motions
(a) through (c) in succession.
T
y
L.
X
meg
For each of the parts below draw a free body diagram of the elevator in your notebook for each of
the parts (a) to (c). Draw the acceleration and velocity vectors in the boxes. For each part, are the
vectors for tension in the string and weight of the elevator of equal lengths or unequal lengths.
Owe back...
m₁
E
5 A
V
(a) The elevator accelerates upward from rest at a rate of 1.4
quantities are correct to 3 significant figures.
(i) Newton's Second Law in the y-direction can be written as:
Instruction: If a is the magnitude of the acceleration, pick "1" if the acceleration is upwards,
pick "-1" if the acceleration is downwards, and pick "0" if there is no acceleration.
✓x mea
ΣF=T-m₂g=
(ii) Calculate the tension in the cable supporting the elevator.
Enter to 3 significant figures
T=
N
(iii) How high has the elevator moved during this time?
Enter to 3 significant figures
Ay=
(iv) Calculate the velocity of the elevator after this time.
Enter to 3 significant figures
v(t = 1.5 s) =
m
m
S
for 1.5 s. Assume that all
(b) The elevator continues upward at constant velocity for 8.15 s. Assume that all quantities are
correct to 3 significant figures.
(i) Newton's Law in the y-direction can be written as:
Instruction: If a is the magnitude of the acceleration, pick "1" if the acceleration is upwards,
pick "-1" if the acceleration is downwards, and pick "0" if there is no acceleration.
x mea
ΣF₁=T-meg=
y
(ii) Calculate the tension in the cable supporting the elevator.
Enter to 3 significant figures
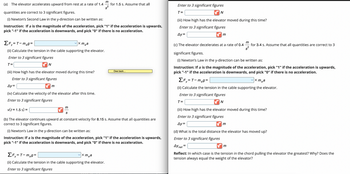
Transcribed Image Text:(a) The elevator accelerates upward from rest at a rate of 1.4
ΣF₁=T-meg=
(ii) Calculate the tension in the cable supporting the elevator.
Enter to 3 significant figures
T=
✔N
quantities are correct to 3 significant figures.
(i) Newton's Second Law in the y-direction can be written as:
Instruction: If a is the magnitude of the acceleration, pick "1" if the acceleration is upwards,
pick "-1" if the acceleration is downwards, and pick "0" if there is no acceleration.
(iii) How high has the elevator moved during this time?
Enter to 3 significant figures
Ay=
(iv) Calculate the velocity of the elevator after this time.
Enter to 3 significant figures
v(t = 1.5 s) =
m
vxmea
m
S
m
for 1.5 s. Assume that all
x mea
ΣF₁=T-m₂g=
(ii) Calculate the tension in the cable supporting the elevator.
Enter to 3 significant figures
Owe back...
(b) The elevator continues upward at constant velocity for 8.15 s. Assume that all quantities are
correct to 3 significant figures.
(i) Newton's Law in the y-direction can be written as:
Instruction: If a is the magnitude of the acceleration, pick "1" if the acceleration is upwards,
pick "-1" if the acceleration is downwards, and pick "0" if there is no acceleration.
Enter to 3 significant figures
T=
N
(iii) How high has the elevator moved during this time?
Enter to 3 significant figures
Ay=
✔m
m
(c) The elevator decelerates at a rate of 0.4 for 3.4 s. Assume that all quantities are correct to 3
s²
significant figures.
(i) Newton's Law in the y-direction can be written as:
Instruction: If a is the magnitude of the acceleration, pick "1" if the acceleration is upwards,
pick "-1" if the acceleration is downwards, and pick "0" if there is no acceleration.
vxmea
ΣF₁=T-meg=
(ii) Calculate the tension in the cable supporting the elevator.
Enter to 3 significant figures
T=
N
(iii) How high has the elevator moved during this time?
Enter to 3 significant figures
Ay=
✔m
(d) What is the total distance the elevator has moved up?
Enter to 3 significant figures
Ay net
=
m
Reflect: In which case is the tension in the chord pulling the elevator the greatest? Why? Does the
tension always equal the weight of the elevator?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How many significant figures are in the following number: 2.5x10(power of 2)arrow_forwardWhere did you get the first part of b) from? Before multiplying it by e- landaBtarrow_forwardIf a radar unit measures that speed of an object 3 times and the results of 300km/hr, 297 km/hr, 302 km/hr, then what is the percent difference of the device? Answer: 100 xarrow_forward
- Convert 180 miles per hour to feet per second. I keep getting 303 (when rounded) but the correct answer is 264 so I am unsure as to where I am messing up my conversionsarrow_forwardA common unit for speed used in sailing is the knot (nautical miles per hour). A nautical mile is about 1.15 regular miles. Calculate how much further (in feet) a boat moving at 22 knots will travel in 5 minutes compared to a car moving at 22 mph during the same time.arrow_forwardA 66 kg man pushes off from the 87kg block on ice and slides away at a speed of 3 m/s What is the speed of the block Calculate answer to one decimal.arrow_forward
- If the cost to do business for a particular company is $4,000 for the startup fee plus $250 per day thereafter, write a graph linear equation that could represent the cost over time. How much cost will there be after 1 month (assume that there are 30 days in that month's time)?arrow_forwardA car travels at 43 km/hr for 1 hour. It in travels in addition of distance of 20 KM in four hours. The average speed of the car for the entire trip is (in, km, hr)arrow_forwardIf one mile is equivalent to 1,609 m, what would it in cm? (round it off to the nearest integer)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON