
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
An elevator car has a mass of 1600 kg and is carrying passengers having a combined mass of 200 kg. A constant friction force of 4000 N retards its motion upward, as shown in Figure 7(a). (A) What power delivered by the motor is required to lift the elevator car at a constant speed of 3.0 m/s? (B) What power must the motor deliver at the instant the speed of the elevator is v if the motor is designed to provide the elevator car with an upward acceleration of 1.0 m/s® 3 - Fig. 7. (a) The motor exerts an upward force T on the Elevator ca. b) The free-body diagram for th elevator car
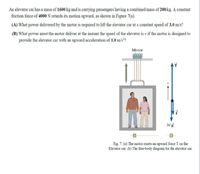
Transcribed Image Text:An elevator car has a mass of 1600 kg and is carrying passengers having a combined mass of 200 kg. A constant
friction force of 4000 N retards its motion upward, as shown in Figure 7(a).
(A) What power delivered by the motor is required to lift the elevator car at a constant speed of 3.0 m/s?
(B) What power must the motor deliver at the instant the speed of the elevator is v if the motor is designed to
provide the elevator car with an upward acceleration of 1.0 m/s?
Motor
Mg
Fig. 7: (a) The motor exerts an upward force T on the
Elevator car. (b) The free-body diagram for the elevator car.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A block of mass 2.40 kg is placed against a horizontal spring of constant k = 825 N/m and pushed so the spring compresses by 0.0750 m. HINT (a) What is the elastic potential energy of the block-spring system (in J)? (b) If the block is now released and the surface is frictionless, calculate the block's speed (in m/s) after leaving the spring. m/sarrow_forwardA block of mass m:=4 kg is placed on an inclined plane with angle a-35°, connected to a second hanging block of mass m_2 by a cord passing over a small frictionless pulley. The static and kinetic friction coefficients are \mu_s=0.5 and \mu_k=0.3, respectively. a.- Determine the mass m_2 such that the block m_1 rises along the plane with constant speed once set in motion. 1.35 kg B: 1.31 kg 1.52 kg B: C: 0.65 kg 1.17 kg b.- Determine the mass m1 such that the block mi moves down the plane with constant speed once set in motion. D: 0.92 kg 1.61 kg D: E: 1.54 kg E: 3.28 kg 2.15 kg c. In what range of values of m2 do the blocks remain at rest, if they are released from rest? A 0.25 kgs my s1.36 B: 0.65 kg smis 3.93 C 0.13 kgs mas 1.87 D: 0.43 kg smis 2.23 E: 0.35 kg s mis 3.87 kg kg kg kgarrow_forwardPlease answer with full solutionsarrow_forward
- Two blocks with masses m1 = 5.0 kg and m2 = 7.0 kg are attached by a string as shown in the figure below, over a pulley with mass M = 2.0 kg. The blocks are released from rest. The pulley, which turns on a frictionless axle, is a hollow cylinder with radius 0.050 m over which the string moves without slipping. The horizontal surface is frictionless. Find the speed of the system when the block of mass m2 has dropped 2 m.arrow_forwardPlease explain answers and include work. Please write the explanations and work out to make them easy to follow and understand.arrow_forwardProblem 3: A 75-kg box at rest is pulled by a force of 350 N acting parallel to the ground. Using the work and energy principle, determine the distance travelled by the box by the time its speed reaches 10 m/s. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the ground is 0.25.arrow_forward
- When Crates A and B of mass ma = 31 kg and mB = 78 kg are released from rest, Crate A moves to the right on a rough surface (u = 0.4 ). The force P = 20 Newtons is always acting on Crate B. The linear spring has a stiffness of k = 490 N and is initially stretched 0.4 meters before the system is released from rest. Neglect the mass of the pulleys and cables and neglect friction in the pulley bearings. Determine the work done by the weight of Crate B (in Joules) when Crate A has moved a distance of 0.8 meters to the right. Consider g = 10 m. 82 Barrow_forwardA 24 kg box is being pushed across the floor by a constant force <111, 0, 0> N. The coefficient of kinetic friction for the table and box is 0.18. At t= 8 s the box is at location <16, 5, -6> m, traveling with velocity <3, 0, 0> m/s. What is its position and velocity at t= 9.2 s? What is the new velocity and new position?arrow_forwardConsider the following arrangement of masses: Mass 1 is connected to mass 2 by a very light string and moves over a frictionless pulley so that both masses move with the same speed and move the same distances (?2 to the right a distance ? and ?1 down a distance ?).Assume ?1 = 15 ??, ?2 = 15 ??, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between ?2 and the table is ?? = 0.73. Let the masses start with an initial speed of 1.00 m/s. What is their speed after moving 1.00 cm (? = 0.0100 ?)?arrow_forward
- A 100 lb force exerted against a 1000-lb block causes the block to slide with constant velocity. The friction force on the block must bearrow_forwardTwo objects with masses of 2.55 kg and 4.15 kg are connected by a light string that passes over a light frictionless pulley to form an Atwood machine. (a) Determine the tension in the string. (b) Determine the acceleration of each object. (c) Determine the distance each object will move in the first second of motion if they start from rest.arrow_forwardThe mB = 8 kg block is moving to the right with a velocity of vo = 0.96 mls on a horizontal surface when a force P is applied to it at time t = 0 as shown in the following figure. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface is Hk = 0.27. Use P = 38, P2 = 72, t1 = 0.15, t2 = 0.35. %3D Р, N P2 P mB P1 t, s t1 t1 Calculate the velocity v in m/s of the block when t = 0.35 s. Insert your answer correct up to at least a third decimal place.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY