
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
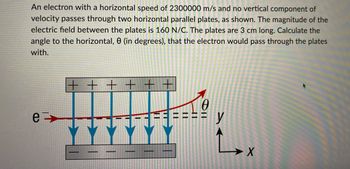
Transcribed Image Text:An electron with a horizontal speed of 2300000 m/s and no vertical component of
velocity passes through two horizontal parallel plates, as shown. The magnitude of the
electric field between the plates is 160 N/C. The plates are 3 cm long. Calculate the
angle to the horizontal, 0 (in degrees), that the electron would pass through the plates
with.
e-
+ + + + + +
II
||
||
0
||
y
X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- a) Calculate the acceleration in meters per second squared of the electron if the field strength is 2.50 ✕ 104 N/C.arrow_forwardA simple and common technique for accelerating electrons is shown in the figure below, where a uniform electric field is created between two plates. Electrons are released, usually from a hot filament, near the negative plate, and there is a small hole in the positive plate that allows the electrons to continue moving. (a) Calculate the acceleration of the electron if the field strength is 3.45 x 104 N/C. m/s² (b) Why will the electron not be pulled back to the positive plate once it moves through the hole? O The force of gravity is too strong. O There is no field outside the plates. O The other side of the positive plate also has a negative charge.arrow_forwardHelp me answer this question please. An electron is projected horizontally at a speed of 2.5 x 10*6 m/s between two plates. metal parallel I = 7.5 cm in length as shown in the figure below. The greatness of electric field is 130 N/C. Determined : a) Acceleration of the electron b) The time it takes to escape from the metal plates c) The final vector velocity of the electron as it escapes from the platesarrow_forward
- 3. A particle (q = 3.0 µC, m = 10 g) has a speed of 40 m/s when it enters a region where the electric field that has a constant magnitude of 100 N/C and the direction of the velocity with the electric field is 30 degree . What is the speed of the particle 5 s after it enters this region?arrow_forwardAn oil droplet of mass 1.00 × 10–14 kg loses an electron while it is in an electric field of 1.00 × 106 N/C. The resulting change in the acceleration of the oil droplet is approximately Group of answer choices 16.0 m/s2 1.76 × 1017 m/s2 1.60 m/s2 1.76 × 1018 m/s2 176 m/s2arrow_forwardA merry-go-round turns at a constant rate of 6 complete rotations per minute. What is its angular speed in radians per second? A. 6л rad/s B. π/10 rad/s С. π/5 rad/s D. 6.0 rad/s O A OBarrow_forward
- A 10-cm-long thin glass rod uniformly charged to 6.00 nC and a 10-cm-long thin plastic rod uniformly charged to -6.00 nC are placed side by side, 4.30 cm apart. What are the electric field strengths E₁ to E3 at distances 1.0 cm, 2.0 cm, and 3.0 cm, from the glass rod along the line connecting the midpoints of the two rods? Specify the electric field strength E2- Express your answer with the appropriate units. ▸ View Available Hint(s) ? E2= Value Units Submit Part C Specify the electric field strength E3- Express your answer with the appropriate units. ▸ View Available Hint(s) E3 = Submit Value НА ? Unitsarrow_forwardA 10-cm-long thin glass rod uniformly charged to 15.0 nC and a 10-cm-long thin plastic rod uniformly charged to -15.0 nC are placed side by side, 4.30 cm apart. What are the electric field strengths E1to E3 at distances 1.0 cm 2.0 cm, and 3.0 cm, from the glass rod along the line connecting the midpoints of the two rods? Specify the electric field strength E1 ,E2and E3arrow_forwardAn electron is projected into a uniform electric field that has a magnitude of 500 N/C. The direction of the electric field is vertically upward. The initial velocity of the electron has a magnitude of 6.00x10^6 m/s, and its direction is at an angle of 30°above the horizontal. Find:I. The maximum distance the electron rises vertically above its initial elevation.II. After what horizontal distance does the electron return to its original elevation.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON