
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
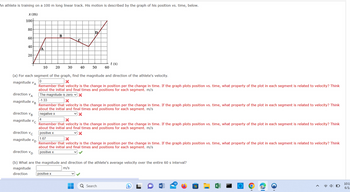
Transcribed Image Text:An athlete is training on a 100 m long linear track. His motion is described by the graph of his position vs. time, below.
x (m)
100-
80
60
40
20
direction VA
magnitude VB
direction VB
magnitude v
с
تو سفر
direction VC
magnitude VD
A
10
B
C
4
20 30 40
(a) For each segment of the graph, find the magnitude and direction of the athlete's velocity.
0
magnitude VA
X
D
50
positive x
60
Remember that velocity is the change in position per the change in time. If the graph plots position vs. time, what property of the plot in each segment is related to velocity? Think
about the initial and final times and positions for each segment. m/s
The magnitude is zero. ✓ X
-1.33
X
t (s)
Remember that velocity is the change in position per the change in time. If the graph plots position vs. time, what property of the plot in each segment is related to velocity? Think
about the initial and final times and positions for each segment. m/s
negative x
X
Remember that velocity is the change in position per the change in time. If the graph plots position vs. time, what property of the plot in each segment is related to velocity? Think
about the initial and final times and positions for each segment. m/s
positive x
1.67
X
Remember that velocity is the change in position per the change in time. If the graph plots position vs. time, what property of the plot in each segment is related to velocity? Think
about the initial and final times and positions for each segment. m/s
positive x
direction VD
(b) What are the magnitude and direction of the athlete's average velocity over the entire 60 s interval?
magnitude
m/s
direction
Q Search
D
18
H
<
(((
Ų
10:1
6/1/
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Step 1: Given:
VIEW Step 2: a) Calculation for the magnitude and direction of the athlete's velocity:
VIEW Step 3: a) Calculation for the magnitude and direction of the athlete's velocity:
VIEW Step 4: b) Calculation for the magnitude and direction of the athlete's average velocity:
VIEW Solution
VIEW Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 20 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An athlete is training on a 100 m long linear track. His motion is described by the graph of his position vs. time, below. For each segment of the graph, find the magnitude and direction of the athlete's velocity. magnitude vA _______ m/s direction vA(Pick from the following choices)- Positive x- Negative x- The magnitude is zero magnitude vB _______ m/s direction vB(Pick from the following choices)- Positive x- Negative x- The magnitude is zero magnitude vC _______ m/s direction vC(Pick from the following choices)- Positive x- Negative x- The magnitude is zero magnitude vD _______ m/s direction vD(Pick from the following choices)- Positive x- Negative x- The magnitude is zeroarrow_forwardAn athlete is training on a 100 m long linear track. His motion is described by the graph of his position vs. time, be x (m) 100 80 60 40 20 A magnitude VB direction VB magnitude vc direction VC magnitude VD direction VD 10 ---Select--- ---Select--- 20 30 40 50 60 (a) For each segment of the graph, find the magnitude and direction of the athlete's velocity. magnitude VA m/s direction v ---Select--- B ---Select--- ---Select--- m/s с m/s D m/s t (s) (b) What are the magnitude and direction of the athlete's average velocity over the entire 60 s interval? magnitude m/s directionarrow_forwardA particle r = (2t3+ 3t) i + (4 - 5t2) j - t4 k Position depending on time given positionmoves with the vector. Here r is in meters and t is in seconds.a) How far has it traveled at the end of the first 3 seconds?b) What is the angle between the instantaneous vector t = 2 s and the position vector?arrow_forward
- The velocity of an object as a function of time is given by v(t) = b + ct - et², where v and t are in Sl units. The other variables are given as b = 3.9 m/s, c = 4.3 m/s², and e = 2.2 m/s³. Determine the instantaneous acceleration of the object at time t = 0.63 s. a = m/s²arrow_forwardThe position vector of a particle is given as r = (t^2-6t+8)i + (t^2-9)j Find the magnitude and direction of the particle’s position, velocity, and acceleration at ? = 2?. Find the magnitude and direction of the particle’s displacement, average velocity and average acceleration for the time period ? = 2? to ? = 3?.arrow_forwardI need help with the part that has the red X. Thank you.arrow_forward
- A toy car can move to the right or left along a horizontal line (the positive portion of the distance axis). The positive direction is to the right. 0 + Choose the correct velocity-time graph (A - H) for each of the following questions. You may use a graph more than once or not at all. If you think that none is correct, answer choice J. A B D V e e 1 e + 0 0 0 e 0 1 0 Time Time Time Time E G H V 1 V + 0 e 0 1 0 0 None of these graphs is correct. Time Time Time Time Which velocity graph shows the car moving toward the left (toward the origin) at a steady (constant) velocity?arrow_forwardA pilot of mass 70 kg pulls out of a dive following a circular path of 900 m from the middle of the turn. His velocity is measured at a constant 250 m/sec. What is the acceleration around the turn in meters per seconds squared? v^2/rarrow_forwardAn object traveling at velocity v0 breaks into two objects, as shown in the diagram. What are the velocities of the 2 objects, in relation to v0 if Θ1 = 64 degrees and Θ2 = 25 degrees?arrow_forward
- The figure here shows the speed v versus height y of a ball tossed directly upward, along a y axis. Distance d is 0.37 m. The speed at height yA is vA. The speed at height yB is vA/3. What is speed vA?arrow_forwardAfter driving around and undergoing a displacement of Ar, = 21.5 km and Ar, = -14.7 km, a driver finds herself at position r2x = -38.1 km and r2y = 19.5 km. What were the components of the driver's initial position vector, r1x and riy, in kilometers? Pix = km rly kmarrow_forwardThe coordinates of a bee flying in the xy-plane are given by x(t) = At and y(t) = C - Bt², where A = 3.2 m/s, B = 1.4 m/s², and C= 2.5 m. Calculate the velocity and acceleration vectors of the bee as a function of time. Write your answers in unit vector notation.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON