Question
thumb_up100%
An astronaut and his gear
(mA = 80.0 kg)
are at rest with respect to his shuttlecraft
(mS = 15,000 kg).
The astronaut and the shuttlecraft are initially separated by a distance of 15.0 m. If the astronaut moves farther away from the shuttlecraft to a distance of 30.0 m, what is the change in gravitational potential energy for the astronaut–shuttlecraft system?
Hint:
Write an expression for the gravitational force between the astronaut and the shuttle using the equation
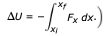
Transcribed Image Text:AU
Fx dx.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- What is the gravitational potential energy of a 4.0 kg block that is raised 2.50 m from the ground? 40 J 980 J 100 J 250 Jarrow_forwardA 6.50 kg ball hangs from the end of a 1.75 m rope. The ball is pulled back until the rope makes a 45 degrees angle with the vertical. What is the gravitational potential energy of the system? 32.49 J 52 J 78.82 J 111.48 J 16. A 16500 kg car travels at a speed of 12.5 m/s. What is its kinetic energy? 130000 J 1289062.50 J 1003125 J 206250 J 16000 Jarrow_forwardThe Elf on the Shelf has mass 0.500 kg and is sitting on a shelf some height y above the ground. If the gravitational potential energy is 49.0 J, what is y?arrow_forward
- A system consists of six particles. How many terms appear in the expression for the total gravitational potential energy of the system? O 15 O 6 O 5 О 36 О 30arrow_forwardThe figure shows four particles, each of mass 40.0 g, that form a square with an edge length of d = 0.900 m. If d is reduced to 0.300 m, what is the change in the gravitational potential energy of the four-particle system? Number i Units d d îarrow_forwardassume the object has a mass of 0.55kg. calculate the gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy of the object. add the values to get the total energy. don't forget to label the units. time (s) 0.05 height (m) 4.99 speed (M/s) 0.5arrow_forward
- A 150g book is initially at rest on a table that has no friction. A force of 3.2 N is applied to the book which moves over a distance of 1.2 m. The table is 1.4m high. What is the gravitational potential energy of the book relative to the table?arrow_forwardCould you help with questions 2 and 3?arrow_forwardQ10 The planet Saturn has a mass of 5.70 x 1026 kg and a diameter of 139820 km. A satellite in orbit around Saturn has a mass of 400 kg and is in orbit 1600 km above the surface of the planet. What is the gravitational potential energy of the satellite? (A) -1.98 x 10'l J (C) -2.13 x 10l J (B) -2.07 x 10!" j (D) 2.13 x 10"Jarrow_forward
- an applied force of 40.0 N j lifts an object straight up a distance of 1.20 m. If the object has a mass of 2.50 kg and is initially at rest what is the objects change in gravitational potential energy?arrow_forwardIn deep space, sphere A of mass 30 kg is located at the origin of an x axis and sphere B of mass 10 kg is located on the axis at x = 0.85 m. Sphere B is released from rest while sphere A is held at the origin. (a) What is the gravitational potential energy of the two-sphere system just as B is released? (b) What is the kinetic energy of B when it has moved 0.25 m toward A? Additional Materials eBook Powers of Tenarrow_forwardDuring a rockslide, a 390 kg rock slides from rest down a hillside that is 460 m long and 300 m high. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the rock and the hill surface is 0.24. If the gravitational potential energy U of the rock-Earth system is set to zero at the bottom of the hill, what is the value of U just before the slide?1.15×106 J How much mechanical energy is dissipated by frictional forces during the slide? What is its speed then? What is the kinetic energy of the rock as it reaches the bottom of the hill?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios