
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
An archer pulls her bowstring back 0.360 m by exerting a force that increases uniformly from zero to 232 N.
(a) What is the equivalent spring constant of the bow?
N/m
(b) How much work does the archer do in pulling the bow?
J
N/m
(b) How much work does the archer do in pulling the bow?
J
Expert Solution
arrow_forward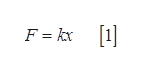

Step 1
(a) The force exerting on the spring is
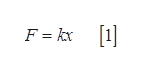
arrow_forward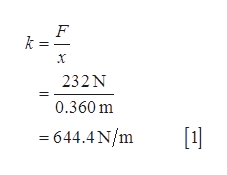

Step 2
Use equation (1) to find the spring constant of the bow.
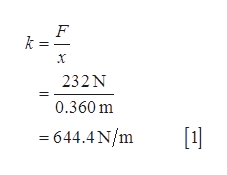
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Ā C. ETIVATS, JOCES, TO m Completion Status: QUESTION 14 Which of the five graphs correctly shows the potential energy of a spring (spring obeys Hooke's law) as a function of its elongation X? U кк ка IV Ο.Α.Ι OB. II OC. III OD.IV OEV of three particles on which external Cove All Answsarrow_forward2. A block of mass m approaches the foot of a hill with a speed of vo. It heads up the frictionless hill of height h and reaches the top. The top is rough with coefficient of kinetic friction μk over a distance d. After the rough patch, there is a spring of spring constant k. Ignore air resistance. a) Assume that the block does not make it through the rough patch. Determine the length L that it travels through the rough patch before coming to rest. b) For the situation in (a), what is the work done by non-conservative forces? c) Now assume that the block does make it through the rough patch. Determine the maximum compression of the spring.arrow_forwardAn archer pulls her bowstring back 0.398 m by exerting a force that increases uniformly from zero to 231 N. (a) What is the equivalent spring constant of the bow? N/m (b) How much work does the archer do on the string in drawing the bow?arrow_forward
- 26. ao The drawing shows three situations in which a block is attached to a spring. The position labeled “O m" represents the unstrained position of the spring. The block is moved from an initial position x, to a final position x, the magnitude of the displacement being denoted by the sym- bol s. Suppose the spring has a spring constant of k = 46.0 N/m. Using the data provided in the drawing, determine the total work done by the restoring force of the spring for each situation. Position of box when (a) spring is unstrained Om +1.00 m +3.00 m (b) -3.00 m Om +1.00 m -3.00 m Om +3.00 marrow_forwardA compressed spring has the potential energy of 20 J and its spring constant is 200 N/m. Calculate the displacement or extension of the spring.arrow_forwardAfter the first snow of the year, you decide to go sledding. You find a hill that is 39 m high to slide down. After a couple trips, you want to go faster, so you rig up a bungee cord to give you a head start N at the top of the hill. The bungee cord can be treated as a spring with a spring constant of 160 You have a mass of 90 kg and you compress your "spring" by a distance of 1.9 m before beginning your ride. There is no friction at the top of the hill or on the hill. Bungee/spring Conservation of Energy Straw-covered portion What is your speed at the top of the hill after you leave the "spring"? m Vtop = What is your speed after sliding to the bottom of the hill? Vbottom = S At the bottom of the hill, you reach a horizontal section where the ground is covered in straw. This straw adds friction to slow the sled down. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the ground and the sled is 0.68. How far do you slide along the straw until you come to a complete stop? d =arrow_forward
- A 0.90 kg brick compresses a spring 0.35 meters at point A and the spring has a spring constant of 75 N/m. How much elastic potential energy does the brick possess? A В hA = 0 he = 0 VA = 0 Vв > 0 A 3.20 Joules 984 Joules 4.59 Joules 675 Joules O O O Oarrow_forwardAn archer pulls her bowstring back 0.408 m by exerting a force that increases uniformly from zero to 215 N. (a) What is the equivalent spring constant of the bow? N/m (b) How much work does the archer do on the string in drawing the bow?arrow_forward1.The work required to stretch a certain spring from an elongation of 4.00 cm to an elongation of 5.00 cm is 30.5 J. (a) Is the work required to increase the elongation of the spring from 5.00cm to 6.00 cm greater than, less than, or equal to 30.5 J?Draw and Explain. (b)Verify your answer to part (a) by calculating the required work.arrow_forward
- Nadia's parents have just bought her a trampoline. She can already reach a height of 1.2 m. If Nadia's mass is 50 kg, determine: a. With the conservation of energy, the speed at which it is thrown through the air to reach the height of 1.2m. b. The elasticity constant of the trampoline if it compresses like a spring, over 0.4 m after Nadia has jumped on it.arrow_forwardQUESTION 9 When a spring is compressed or stretched, the elastic potential energy (U=1/2kx²) of the spring: Oa. Stays constant Ob. Decreases Oc Increases Od. Either positive or negativearrow_forwardThe spring constant of a spring is 100 N/m. A force of 10 N stretches the spring by 10 cm. How much potential energy is stored in the spring? а. О.3] b. 0.2J c. 0.4J d. 0.5Jarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON