
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
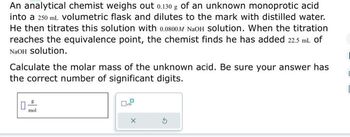
Transcribed Image Text:An analytical chemist weighs out 0.130 g of an unknown monoprotic acid
into a 250 mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water.
He then titrates this solution with 0.0800M NaOH Solution. When the titration
reaches the equivalence point, the chemist finds he has added 22.5 mL of
NaOH Solution.
Calculate the molar mass of the unknown acid. Be sure your answer has
the correct number of significant digits.
0
mol
X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An analytical chemist weighs out 0.066 g of an unknown monoprotic acid into a 250 mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. She then titrates this solution with 0.1700M NaOH solution. When the titration reaches the equivalence point, the chemist finds she has added 8.4 mL of NaOH solution. Calculate the molar mass of the unknown acid. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. g mol x10 X Sarrow_forwardA technician would like to standardize an unknown Ca(OH)2 solution. It takes 18.53 mL of a 0.174 M solution of HCI to titrate 25.00 mL the unknown Ca(OH)2 solution. Calculate the molarity of the Ca(OH)2 solution. Tip: Don't forget to consider the mole ratio between HCl and Ca(OH)2. 2 HCI (aq) + Ca(OH), (aq) CaCl2 (aq) + 2 H2O (1)arrow_forwardA 30.00 ml sample of phosphoric acid is titrated with a 0.050 M magneisim hydroxide solution. The initial buret reading is 4.71 mL; the final buret reading is 31.09 mL. What is the concentration of the unknown phosphoric acid solution? 2.64 M 0.100 M 0.0293 M 0.0879 M 0.0310 Marrow_forward
- A chemistry student needs to standardize a fresh solution of sodium hydroxide. He carefully weighs out 30. mg of oxalic acid (H,C,0,), a diprotic acid that can be purchased inexpensively in high purity, and dissolves it in 250. mL of distilled water. The student then titrates the oxalic acid solution with his sodium hydroxide solution. When the titration reaches the equivalence point, the student finds he has used 62.3 mL of sodium hydroxide solution. Calculate the molarity of the student's sodium hydroxide solution. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. x10arrow_forwardAn analytical chemist weighs out 0.406 g of an unknown diprotic acid into a 250 mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. She then titrates this solution with 0.1400M NaOH solution. When the titration reaches the equivalence point, the chemist finds she has added 34.9 mL of NaOH solution. Calculate the molar mass of the unknown acid. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. C mol Explanation Recheck JAHE B! F2 # 3 80 F3 X $ 4 888 F4 S % LO 5 F5 MacBook Air A 2 F6 & 7 F7 Ⓒ2023 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Acc * ∞ DII F8 9 FO A F10 4 F11arrow_forwardA chemistry student weighs out 0.159 g of ascorbic acid (H,C,H,0), a diprotic acid, into a 250. mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. He plans to titrate the acid with 0.0800M NaOH solution. Calculate the volume of NaOH solution the student will need to add to reach the final equivalence point. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. mLarrow_forward
- A chemistry student needs to standardize a fresh solution of sodium hydroxide. He carefully weighs out 54. mg of oxalic acid (H₂C₂O4), a diprotic acid that can be purchased inexpensively in high purity, and dissolves it in 250. mL of distilled water. The student then titrates the oxalic acid solution with his sodium hydroxide solution. When the titration reaches the equivalence point, the student finds he has used 92.3 mL of sodium hydroxide solution. Calculate the molarity of the student's sodium hydroxide solution. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. do O Ar M X ?arrow_forwardCalculate the molar mass of the unknown acid from the information below.arrow_forwardAn analytical chemist weighs out 0.026 g of an unknown monoprotic acid into a 250 mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. She then titrates this solution with 0.0700 M NaOH solution. When the titration reaches the equivalence point, the chemist finds she has added 3.8 mL of NaOH solution. Calculate the molar mass of the unknown acid. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. g x10 molarrow_forward
- Calculate the molar mass of the unknown acid. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forwardAn analytical chemist weighs out 0.318 g of an unknown triprotic acid into a 250 mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. He then titrates this solution with 0.0600 M NaOH solution. When the titration reaches the equivalence point, the chemist finds he has added 82.8 mL of NaOH solution. Calculate the molar mass of the unknown acid. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. mol x10 x 3arrow_forwardAn analytical chemist weighs out 0.203 g of an unknown diprotic acid into a 250 mL volumetric flask and dilutes to the mark with distilled water. He then titrates this solution with 0.1500M NaOH solution. When the titration reaches the equivalence point, the chemist finds he has added 18.0 mL of NaOH solution. Calculate the molar mass of the unknown acid. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. mol Explanation Check 0.9 X 4 S MacBook Air © 2023 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Iarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY