
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
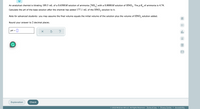
Transcribed Image Text:An analytical chemist is titrating 189.5 mL of a 0.6500M solution of ammonia (NH, ) with a 0.8000M solution of HNO,. The p K, of ammonia is 4.74.
Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 177.1 mL of the HNO, solution to it.
Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HNO, solution added.
Round your answer to 2 decimal places.
pH = 0
alo
Ar
G
Explanation
Check
© 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The p?a of hypochlorous acid is 7.530 . A 58.0 mL solution of 0.130 M sodium hypochlorite ( NaOCl ) is titrated with 0.299 M HCl . Calculate the pH of the solution after the addition of 9.78 mL of 0.299 M HCl . (please type answer not write by hend)arrow_forwardA chemist titrates 130.0 mL of a 0.6533 M cyanic acid (HCNO) solution with 0.5467 M KOH solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. The pK, of cyanic acid is 3.46. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of KOH solution added. pH = Uarrow_forwardA chemist titrates 110.0 mL of a 0.3453 M methylamine (CH3NH₂) solution with 0.7011 MHCl solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. The pK, of methylamine is 3.36. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of HCl solution added. pH = X S ?arrow_forward
- An analytical chemist is titrating 111.5 mL of a 0.2600M solution of acetic acid (HCH,CO,) with a 0.5100M solution of NaOH. The p K, of acetic acid is 4.70. Calculate the pH of the acid solution after the chemist has added 10.45 mL of the NaOH solution to it. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of NaOH solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pH = |arrow_forwardAn analytical chemist is titrating 231.8 mL of a 0.9900M solution of acetic acid (HCH, CO,) with a 1.200M solution of NaOH. The p K, of acetic acid is 4.70. Calculate the pH of the acid solution after the chemist has added 131.2 mL of the NaOH solution to it. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of NaOH solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. alo pH %3| Ar Explanation Check © 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center | Accessibility CAarrow_forwardA chemist titrates 210.0 mL of a 0.3206M ammonia (NH3) solution with 0.3768 M HCl solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. The pK, of ammonia is 4.75. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of HCl solution added. pH = 0 Xarrow_forward
- An analytical chemist is titrating 111.3 mL of a 0.2800 M solution of ammonia (NH, with a 0.3500 M solution of HIO,. The p K, of ammonia is 4.74. Calculate 3' the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 99.0 mL of the HIO, solution to it. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HIO, solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.arrow_forwardAn analytical chemist is titrating 147.3 mL of a 0.3200M solution of ammonia (NH,) with a 0.8200M solution of HNO,. The p K, of ammonia is 4.74. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 64.7 mL of the HNO, solution to it. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume the solution plus the volume of HNO, solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.arrow_forwardA chemist titrates 160.0 mL of a 0.3445 M pyridine (C-H5N) solution with 0.8552M HNO3 solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. The pK, of pyridine is 8.77. 6 Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of HNO3 solution added. E pH = 0 X 5 OL 9 Larrow_forward
- A chemist titrates 240.0 mL of a 0.0890M aniline (C,H,NH,) solution with 0.6621M HNO, solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. The p K, of aniline is 4.87. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of HNO, solution added. pH =arrow_forwardAn analytical chemist is titrating 219.9 mL of a 0.5100 M solution of aniline (CH,NH,) with a 0.1800 M solution of HNO,. The p K, of aniline is 9.37. 3 Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 360.5 mL of the HNO, solution to it. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HNO, solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.arrow_forwardFor each of the salts (assume at this point completely soluble), write the equation for dissociation and label the ions as acidic, basic or neutral.Each salt listed will 100% dissociate NH4C2H3O2 Al2(CO3)3 Na2HPO4 NaI For each of the following salts, determine the pH of a 2.50M solution of the salt.You will need the Ka and Kb tables to complete this problem. NaBrO CH3NH3Cl NaClO2 C6H5OK CsNO3 C6H5NH3Brarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY