
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
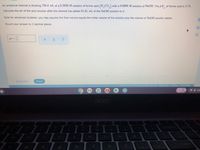
Transcribed Image Text:An analytical chemist is titrating 156.4 mL of a 0.3600 M solution of formic acid (H,CO,) with a 0.6800 M solution of NaOH, The p K of formic acid is 3.74.
Calculate the pH of the acid solution after the chemist has added 91.45 mL of the NaOH solution to it.
Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of NaOH solution added.
Round your answer to 2 decimal places.
alo
pH =||
Explanation
Check
2021 McGraw-Hill Education. Al Rights Reserved.
Terms of Use I Privacy Accessibility
O 1:0
acer
S Fa
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Jj.138.arrow_forwardAn analytical chemist is titrating 83.7 mL of a 0.3300M solution of isopropylamine ((CH,) CHNH, with a 0.5300M 2 solution of HNO3. The p K, of isopropylamine is 3.33. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 42.4 mL of the HNO, solution to it. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HNO, solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pH = | ?arrow_forwardAn analytical chemist is titrating 151.8 mL of a 0.1600M solution of piperidine (C,HNH) with a 0.5500M solution of HIO. The p K, of piperidine is 2.89. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 47.8 mL of the HIO, solution to it. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HIO, solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pH=arrow_forward
- An analytical chemist is titrating 179.6 mL of a 0.8400M solution of cyanic acid (HCNO) with a 1.200M solution of KOH. The p K, of cyanic acid is 3.46. Calculate the pH of the acid solution after the chemist has added 144.3 mL of the KOH solution to it. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of KOH solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pH = |arrow_forwardA chemist titrates 110.0 mL of a 0.1235M butanoic acid (HC,H,CO,) solution with 0.0643 M KOH solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. The pK, of butanoic acid is 4.82. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of KOH solution added. pH = ] ? %3Darrow_forwardThe pK, of hypochlorous acid is 7.530. A 52.0 mL solution of 0.148 M sodium hypochlorite (NaOCI) is titrated with 0.293 M HCI. Calculate the pH of the solution after the addition of 10.3 mL of 0.293 M HCI. pH = Calculate the pH of the solution after the addition of 27.9 mL of 0.293 M HCI. pH = Calculate the pH of the solution at the equivalence point with 0.293 M HCI. pH =arrow_forward
- A student wishes to make a buffer that has a pH of 4.65. The student has HNO2 and NaNO2. Nitrous Acid (HNO2) has a pKa of 3.40 The student makes 100.0 mL of a 0.100 M solution of HNO2. What mass (in grams) of NaNO2 should the student add to the solution to make a buffer that buffers at a pH of 4.25. (Hint: use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to find the molarity, then find the number of moles required to achieve that concentration in 100.0 mL of solution.)arrow_forwardAn analytical chemist is titrating 161.4 mL of a 0.8000M solution of trimethylamine ((CH,) N) with a 0.8900M solution of HIO3. The p K, of trimethylamine 3 is 4.19. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 161.5 mL of the HIO, solution to it. 3. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HIO, solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.arrow_forward1. A buffer solution contains 0.419 M of ammonium chloride and 0.221 M of ammonia.If 0.0293 moles of sodium hydroxide are added to 150 mL of this buffer, what is the pH of the resulting solution? (Assume that the volume does not change upon adding sodium hydroxide.) 2. A buffer solution contains 0.286 M of ammonium chloride and 0.472 M of ammonia. If 0.0620 moles of nitric acid are added to 250 mL of this buffer, what is the pH of the resulting solution? (Assume that the volume does not change upon adding nitric acid.)arrow_forward
- A chemist titrates 220.0 mL of a 0.6204 M butanoic acid (HC₂H,CO₂) solution with 0.2746 M KOH solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. The PK of butanoic acid is 4.82. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of KOH solution added. pH = 0 X Śarrow_forwardA formic acid buffer is prepared with 0.010 M each of formic acid (HCOOH) and Sodium formate (NaCOOH). The Ka for formic acid is 1.8 x 10-4. What is the pH of the solution? What is the pH if 0.0020 M of solid sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is added to a liter of buffer? What would be the pH of the sodium hydroxide solution without the buffer? What would the pH have been after adding sodium hydroxide if the buffer concentrations had been 0.10 M instead of 0.010 M?arrow_forwardAn analytical chemist is titrating 143.6 mL of a 0.7000M solution of piperidine (C,H10NH) with a 0.4000M solution of HNO3. The p K, of piperidine is 2.89. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 267.7 mL of the HNO, solution to it. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HNO, solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pHarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY