
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
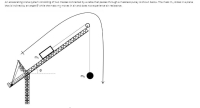
Transcribed Image Text:An accelerating crane system consisting of two masses connected by a cable that passes through a massless pulley is shown below. The mass m, slides in a plane
that is inclined by an angle e while the mass m2 moves in air and does not experience air resistance.
m2
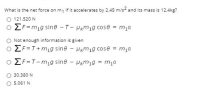
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please asaparrow_forwardA force of 40.0N is applied in the positive x-direction to a block of mass 7.15 kg, at rest on a frictionless surface. HINT (a) What is the block's acceleration (in m/s2)? (Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) m/s2 (b) How fast is it going (in m/s) after 5.50 s? m/sarrow_forwardA(n) 94 kg clock initially at rest on a hor- izontal floor requires a(n) 652 N horizontal force to set it in motion. After the clock is in motion, a horizontal force of 538 N keeps it moving with a constant velocity. The acceleration of gravity is 9.81 m/s a) Find us between the clock and the floor. b) Find д between the clock and the floor.arrow_forward
- Q4.:Block A in Fig 2 weighs 50 N and block B weighs 35 N. The blocks are connected by a flexible inextensible cord which passes over a smooth pully at C. The coefficient of friction between the plane and the block A is 0.3. The blocks are initially at rest. Determine the tension in the cord and the velocity of A after it has travelled 5 m. B C Fig. 2 A 3 25 N 4arrow_forwardNeed help right awayarrow_forward= 60°. When released from rest, m1 accelerates downward at Two objects are connected by a light string that passes over a frictionless pulley as shown in the figure below. m1 = 6.00 kg, m2 = 6.00 kg, and o than 0.57 and to even begin sliding in the first place the coefficient of static friction must be less 1.421 m/s2. For this to happen, the coefficient of kinetic friction must be . Use g=9.8 m/s2. m2arrow_forward
- Answer Pleasearrow_forwardOn earth, a block sitting on a frictionless, horizontal table accelerates at 7.11 m/s² when a 40-N horizontal force is applied to it. The block and table are then moved to the moon where the acceleration due to gravity is 1.65 m/s². Find the magnitude of the block's weight wm on the moon. Wm = Narrow_forwardAn object rests on a horizontal frictionless surface. A horizontal force of magnitude F is applied. This force produces an acceleration: O only if F is larger than the weight of the object. O only while the object suddenly changes from rest to motion. O always. O only if the inertia of the object decreases. Onone of the given choicesarrow_forward
- 8. Consider the system shown in figure. Block A weighs 45.0 N and block B weighs 25.0 N. Once block B is set into downward motion, it descends at a constant speed. (a) Calculate the coefficient of kinetic friction between block A and the tabletop. (b) A cat, also of weight 45.0 N, falls asleep on top of block A. If block B is now set into downward motion, what is its acceleration (magnitude and direction)? O -2.13 m/s^2 -4.56 m/s^2 -6.78 m/s^2 O -8.45 m/s^2 O No Answer A Farrow_forwardA force F1 is applied to a mass M1. If the same force F1 is applied to a mass M2 = 4M1 the acceleration of mass M1 is: one-half the acceleration of the mass M2. twice the acceleration of the mass M2. the same as for the mass M2. four times the acceleration of the mass M2. one-fourth the acceleration of the mass M2.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON