
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
-
Among the two stress strain curves generated from tensile tests up to the material failure, which curve, A or B represents that generated from a brittle material?
A
B
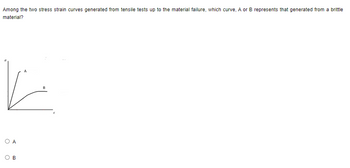
Transcribed Image Text:**Title: Understanding Stress-Strain Curves in Materials**
**Content:**
Among the two stress-strain curves generated from tensile tests up to the material failure, which curve, A or B, represents that generated from a brittle material?
**Diagram Explanation:**
The image contains a graph with two stress-strain curves labeled A and B. The graph has vertical and horizontal axes representing stress (σ) and strain (ε), respectively.
- **Curve A**: This curve rises steeply and ends abruptly, indicating a sudden failure. It suggests minimal plastic deformation before fracture, characteristic of brittle materials.
- **Curve B**: This curve rises gradually and has a noticeable plateau before failing, indicating significant plastic deformation. This behavior is typically associated with ductile materials.
**Question Options:**
- ○ A
- ○ B
**Educational Insight:**
In material science, understanding the difference between brittle and ductile behaviors is crucial. Brittle materials tend to fracture suddenly without significant deformation, whereas ductile materials exhibit noticeable stretching or deforming before breaking. Curve A is an example of brittle material behavior.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- H pleasearrow_forwardThis steel alloy specimen had an original diameter of 12.8 mm and a gauge length of 50.80 mm: i) If it were subjected to a load of 120 kN and then released, what would have been its permanent elongation? Be thorough. ii) If it were subjected to a load of 230 kN and then released, what would have been its permanent elongation? Be thorough.arrow_forwardHello, the stress and cycles required for this question is Stress 1 = 420MPa at 7 cycles, Stress 2 = 360MPa at 65 cycles and Stress 3 = 130MPa at 325 cycles. Use the first three cycles (which shows how many cycles at that stress level to failure) to calculate when the specimen will fail if it underwent test of 7 cycles at 420MPa, then undergoes 360MPa for 65 cycles and finally 130MPa at 325 cycles. Will the specimen fail? Please show calculations of failurearrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY