
Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337399425
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
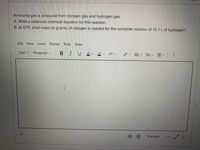
Transcribed Image Text:Ammonia gas is produced from nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas.
A. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
B. At STP, what mass (in grams) of nitrogen is needed for the complete reaction of 15.1 L of hydrogen?
Edit View Insert Format Tools Table
12pt v
Paragraph v
B IUAV2V ぴく
O words
</> レ7 …
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- At elevated temperatures, sodium chlorate decomposes to produce sodium chloride and oxygen gas. A 0.8765-g sample of impure sodium chlorate was heated until the production of oxygen gas ceased. The oxygen gas collected over water occupied 57.2 mL at a temperature of 22C and a pressure of 734 torr. Calculate the mass percent of NaClO3 in the original sample. (At 22C the vapor pressure of water is 19.8 torr.)arrow_forwardAs weather balloons rise from the earths surface, the pressure of the atmosphere becomes less, tending to cause the volume of the balloons to expand. However, the temperatura is much lower in the upper atmosphere than at sea level. Would this temperatura effect tend to make such a balloon expand or contract? Weather balloons do, in fact, expand as they rise. What does this tell you?arrow_forwardMethanol (CH3OH) can be produced by the following reaction: CO(g)+2H2(g)CH3OH(g) Hydrogen at STP flows into a reactor at a rate of 16.0 L/min. Carbon monoxide at STP flows into the reactor at a rate of 25.0 L/min. If 5.30 g methanol is produced per minute, what is the percent yield of the reaction?arrow_forward
- Gold is produced electrochemically from an aqueous solution of Au(CN)2 containing an excess of CN. Gold metal and oxygen gas are produced at the electrodes. What amount (moles) of O2 will be produced during the production of 1.00 mole of gold?arrow_forwardYou have a gas, one of the three known phosphorus-fluorine compounds (PF3, PF3, and P2F4). To find out which, you have decided to measure its molar mass. (a) First, yon determine that the density of the gas is 5.60 g/L at a pressure of 0.971 atm and a temperature of 18.2 C. Calculate the molar mass and identify the compound. (b) To check the results from part (a), you decide to measure the molar mass based on the relative rales of effusion of the unknown gas and CO2. You find that CO2 effuses at a rate of 0.050 mol/min, whereas the unknown phosphorus fluoride effuses at a rate of 0.028 mol/min. Calculate the molar mass of the unknown gas based on these results.arrow_forward95 Some engineering designs call for the use of compressed air for underground work. If water containing iron(II) ions is present, oxygen in the compressed air may react according to the following unbalanced net ionic equation: Fe2++H++O2Fe3++H2O (a) Write the balanced net ionic equation. Remember that the amounts of each substance and the charges must balance. (b) Assume all of the oxygen from 650 L of compressed air at 15°C and 6.5 atm is lost by this reaction. What mass of water would be produced? (The mole fraction of oxygen in air is about 0.21.) (c) What will be the final pressure after the loss of the oxygen?arrow_forward
- A 230-L sample of a colorless gas at STP decomposed to give 230 L of N2 and 1.25 L of O2 at STP. What is the colorless gas?arrow_forward105 The decomposition of mercury(II) thiocyanate produces an odd brown snake-like mass that is so unusual the process was once used in fireworks displays. There are actually several reactions that take place when the solid Hg(SCN)2 is ignited: 2Hg(SCN)2(s)2HgS(s)+CS2(s)+C3N4(s)CS2(s)+3O2(g)CO2(g)+2SO2(g)2C3N4(s)3(CN)2(g)+N2(g)HgS(s)+O2(g)Hg(l)+SO2(g) A 42.4-g sample of Hg(SCN)2 is placed into a 2.4-L vessel at 21°C. The vessel also contains air at a pressure of 758 torr. The container is sealed and the mixture is ignited, causing the reaction sequence above to occur. Once the reaction is complete, the container is cooled back to the original temperature of 21°C. (a) Without doing numerical calculations, predict whether the final pressure in the vessel will be greater than, less than, or equal to the initial pressure. Explain your answer. (b) Calculate the final pressure and compare your result with your prediction. (Assume that the mole fraction of O2 in air is 0.21.)arrow_forwardThe nitrogen content of organic compounds can be determined by the Dumas method. The compound in question is first reacted by passage over hot CuO(s): CompoundCuO(s)HotN2(g)+CO2(g)+H2O(g) The product gas is then passed through a concentrated solution of KOH to remove the CO2. After passage through the KOH solution, the gas contains N2 and is saturated with water vapor. In a given experiment a 0.253-g sample of a compound produced 31.8 mL N2 saturated with water vapor at 25C and 726 torr. What is the mass percent of nitrogen in the compound? (The vapor pressure of water at 25C is 23.8 torr.)arrow_forward
- perform stoichiometric ca1cu1uions for reactions involving gases as reactants or products.arrow_forwardExplain why the plot of PV for CO2 differs from that of an ideal gas.arrow_forward62 Ammonium dinitramide (ADN), NH4N(NO2)2, was considered as a possible replacement for aluminium chloride as the oxidizer in the solid fuel booster rockets used to launch the space shuttle. When detonated by a spark, AND rapidly decomposes to produce a gaseous mixture of N2,O2, and H2O. (This is not a combustion reaction. The ADN is the only reactant.) The reaction releases a lot of heat, so the gases are initially formed at high temperature and pressure. The thrust of the rocket results mainly from the expansion of this gas mixture. Suppose a 2.3-kg sample of ADN is denoted and decomposes completely to give N2,O2, and H2O. If the resulting gas mixture expands until it reaches a temperature of 100°C and a pressure of 1.00 atm, what volume will it occupy? Is your answer consistent with the proposed use of ADN as a rocket fuel?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning