
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
all parts of the same question
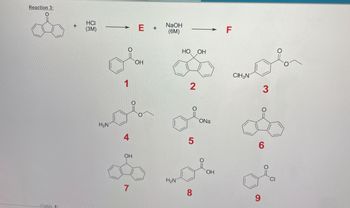
Transcribed Image Text:### Reaction 3:
In this chemical reaction, the starting compound is reacted with hydrochloric acid (HCl, 3M concentration) to form an intermediate product E. Subsequently, E is reacted with sodium hydroxide (NaOH, 6M concentration) to produce the final product F.
#### Chemical Structures:
- **Starting Compound**: A bicyclic structure with a carbonyl group (C=O).
- **Reagents**:
- **HCl (3M)**: Hydrochloric Acid in 3 molar concentration.
- **NaOH (6M)**: Sodium Hydroxide in 6 molar concentration.
#### Possible Products Illustrated:
1. **Compound 1**:
- Structure: A bicyclic structure with an additional carboxyl group (C=O) and hydroxyl group (OH).
2. **Compound 2**:
- Structure: A bicyclic structure with two hydroxyl groups (dihydroxy).
3. **Compound 3**:
- Structure: A bicyclic ketone with a side chain containing an ethyl ester group.
4. **Compound 4**:
- Structure: A bicyclic structure with an amino group (NH2) attached to the aromatic ring.
5. **Compound 5**:
- Structure: A sodium salt (ONa) of a bicyclic carboxylate.
6. **Compound 6**:
- Structure: A simple bicyclic ketone.
7. **Compound 7**:
- Structure: A bicyclic structure with a single hydroxyl group (OH).
8. **Compound 8**:
- Structure: A bicyclic structure with an amino group (NH2) and a hydroxyl group (OH).
9. **Compound 9**:
- Structure: A chlorinated derivative with a carbonyl group.
These structures represent possible outcomes of the reaction sequence leading to product F.
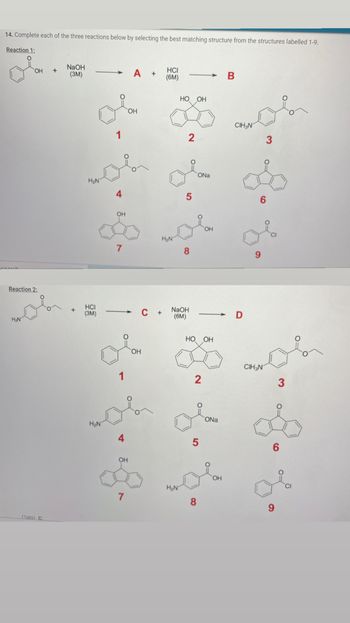
Transcribed Image Text:**Educational Content: Organic Chemistry Reactions**
**Task 14:**
Complete each of the following reactions by selecting the best matching structure from the structures labeled 1-9.
---
**Reaction 1:**
Starting Materials:
- Reactant: A compound depicted with a benzene ring attached to a hydroxyl group (phenol).
- Reagent: NaOH (3M)
Process:
- A compound is labeled as "A" is formed.
- Following, HCl (6M) is added to give compound "B".
Options for A and B:
1. A phenol structure.
2. A bicyclic compound with two hydroxyl groups.
3. An ethoxybenzene compound.
4. A benzene ring with an aminomethyl group.
5. A sodium phenoxide ion.
6. A naphthalene structure.
7. A naphthol structure.
8. An aminophenol compound.
9. A chloro-benzoyl chloride compound.
---
**Reaction 2:**
Starting Materials:
- Reactant: A compound with an aniline derivative (ethyl attached).
- Reagent: HCl (3M)
Process:
- Formation of compound "C".
- Subsequently, NaOH (6M) is applied to yield compound "D".
Options for C and D:
The same options listed in Reaction 1.
**Diagrams Explanation:**
- The diagrams depict different organic structures with functional groups such as hydroxyl, amino, and acyl groups. They represent potential products or intermediates in chemical reactions involving substitutions or ion formations.
Explore the relation between reactants, reagents, and possible products based on the functional groups and reactivity patterns common in organic chemistry!
**Notes:**
- Consider acidity and basicity when predicting the outcomes.
- Examine any possible structural changes or stable ions that could be formed with the given reagents.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Mass is.... which if the following ? (See picture)this question kinda confused mearrow_forward[answer with correct answer] Water exists as a solid (ice), a liquid and a gas (steam). Which state of matter will water be when it is easiest to compress?arrow_forwardShow ALL your steps and details in your calculations, by using GRASPS: Given, Required, Analysis, Solution, and Paraphrase. Answer in complete sentences and therefore statements. Show All of your work, in full solutionsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY