
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
All living things are divided into three domains: bacteria, archaea, and eukarya. They have several traits that are specific to each domain or shared across the domains.
Based on this information, what traits would the last universal common ancestor (LUCA) be expected to have?
A. Nuclear envelope, introns in genes, and peptidoglycan in cell walls.
B. Histones associated with DNA, circular chromosome, and peptidoglycan in cell walls.
C. Unbranched hydrocarbons in membrane lipids, histones associated with DNA, and introns in genes.
D. Circular chromosome, unbranched hydrocarbons in membrane lipids, and one kind of RNA polymerase.
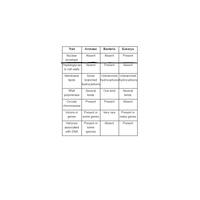
Transcribed Image Text:Trait
Archaea
Bacteria
Eukarya
Nuclear
Absent
Absent
Present
envelope
Peptidoglycan
in cell walls
Absent
Present
Absent
Membrane
Some
Unbranched Unbranched
branched hydrocarbons hydrocarbons
hydrocarbons
lipids
RNA
Several
One kind
Several
polymerase
kinds
kinds
Circular
Present
Present
Absent
chromosome
Introns in
Present in
Very rare
Present in
genes
some genes
many genes
Histones
Present in
Absent
Present
associated
some
with DNA
species
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following statements accurately describes what we learned about HIV evolution? a. HIV is more deadly in Northern Europe, but more transmissible in Africa. That is why there are more individuals infected with the illness in Africa. b. HIV shares a most recently common ancestor with Simian Immunodeficiency Virus (SIV) such that SIV evolved as it host-switched from chimpanzees and gorillas into humans multiple times. c. Drug development is exceedingly difficult because there are very few drug targets for HIV and AZT (a reverse transcriptase inhibitor) alone is the single most effective treatment for HIV. d. Evolution of HIV virions within a person is quite slow such that a blood draw after 1 year of infection would reveal that every single virion would have the exact same sequence.arrow_forwardWhich of the following schemes for molecular information flow never occurs in cellular life forms? a. DNA to rRNA b. mRNA to protein c. DNA to tRNA d. DNA to mRNA e. RNA to DNAarrow_forwardA scientist discovered a new group of unicellular organisms that lack mitochondria but possess an organelle related to the endoplasmic reticulum and is involved in energy production. The scientist hypothesizes that this organelle might be a missing link in the evolution of mitochondria. A) Do you agree with this hypothesis? Explain. B) Based on the available evidence, what is the most likely hypothesis for the origin of mitochondria? Provide four pieces of evidence to support this theory and justify why they are valid.arrow_forward
- According to Lynn Margulis's theory of endosymbiosis, bacteria entered large cells either as parasites or as undigested prey as illustrated. All the following are proof that mitochondria and chloroplast evolved from bacteria, except: Endosymbiosis in a nutshell: 1. Start with two 2. One bacterium engulfs the other. 3. One bacterium now lives inside the other. independent bacteria. 4. Both bacteria benefit from the arrangement. 5. The internal bacteria are passed on from generation to generation. O a they each have a double membrane they have chromosomes similar in shape to their host they are the size of bacteria their DNA is different from its hostarrow_forwardExplain antibiotic resistance observed in bacteria in light of Darwinianselection theory.arrow_forwardIf you found the same gene in all organisms you test, what could this suggest about the evolution of this gene in the history of life on earth? What if a gene is very similar in most species that you study, but quite different in a particular group? What if it’s present in nearly everything, but the specific sequences vary quite a bit?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education