
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
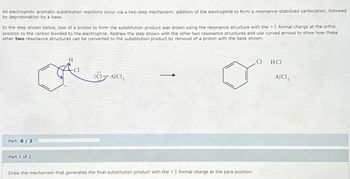
Transcribed Image Text:All electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions occur via a two-step mechanism: addition of the electrophile to form a resonance-stabilized carbocation, followed
by deprotonation by a base.
In the step shown below, loss of a proton to form the substitution product was drawn using the resonance structure with the + 1 formal charge at the ortho
position to the carbon bonded to the electrophile. Redraw the step shown with the other two resonance structures and use curved arrows to show how these
other two resonance structures can be converted to the substitution product by removal of a proton with the base shown.
Part: 0/2
Part 1 of 2
H
:CI-AICI,
Draw the mechanism that generates the final substitution product with the +1 formal charge at the para position.
Cl
HC1
AICI3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Complete the equation for the following proton-transfer reaction by using curved arrows to show the flow of electron pairs and drawing the products of the reaction. • Draw all atoms, including hydrogen atoms. Apply formal charges where appropriate. Assign lone pairs and radical electrons where appropriate. • Use the "starting points" menu to revert to the original molecule(s) shown. • Draw the appropriate electron-flow arrows. • Omit + signs between structures. ● ● H-O: == starting points == ↑ TAYY H T H-C-H H-N-H T H در ? ChemDoodlearrow_forwardThe compound below is treated with chlorine in the presence of light. H₂C CH3 H₂C CH3 Draw the structure for the organic radical species produced by reaction of the compound with a chlorine atom. Assume reaction occurs at the weakest C-H bond. You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. Undoarrow_forwardDraw a structural formula of an alkene or alkenes (if more than one) that undergo acid-catalyzed hydration and without rearrangement give 1-methylcyclohexanol as the major product. You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. ● If more than one structure fits the description, draw them all. • Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner. Separate structures with + signs from the drop-down menu. ● ● ✓ ? ChemDoodleⓇ n [ ]#arrow_forward
- Provide 2 additional resonance structures for the following molecule and draw the electron pushing arrows to arrive at each new structure.arrow_forwardKetones and aldehydes are hydrated under acidic or basic conditions. An example of the acid-catalyzed hydration is shown. Complete the first step of this mechanism. Include all lone pairs of electrons, curved arrows, and nonzero formal charges in your mechanism.arrow_forwardPQ-2. This reaction is classified as (A) a nucleophilic addition. (C) a nucleophilic substitution. NaCN H3C CH3 H₂O (B) an electrophilic addition. (D) an electrophilic substitution. HO H3C CN CH3arrow_forward
- Draw the major organic product(s) of the following reactions including stereochemistry when it is appropriate. H20/ H,SO, / HgSO4 CH,CH2-CEC-CH, • Use the wedge/hash bond tools to indicate stereochemistry where it exists. • If no reaction occurs, draw the organic starting material. Separate multiple products using the + sign from the drop-down menu.arrow_forwardThe compound below is treated with chlorine in the presence of light. CH3 CH3 [References] CH₂ Draw the structure for the organic radical species produced by reaction of the compound with a chlorine atom. Assume reaction occurs at the weakest C-H bond.arrow_forward5. Using curved arrows show the mechanism for the hydrohalogenation for the following reaction. Show how the two possible intermediate products are formed and explain why only one product proceeds to form the product. Clearly indicate attack of electrons and full and partial (8) charges. H-Br Br H-Br Product Intermediate Productsarrow_forward
- Complete the equation for the following proton-transfer reaction by using curved arrows to show the flow of electron pairs and drawing the products of the reaction. • Draw all atoms, including hydrogen atoms. Apply formal charges where appropriate. Assign lone pairs and radical electrons where appropriate. • Use the "starting points" menu to revert to the original molecule(s) shown. Draw the appropriate electron-flow arrows. . Omit + signs between structures. ● ● ● H H ││ H-C-C-0: T I H H == starting points == C H-Cl: در ? ChemDoodlearrow_forwardRank the following (in image one, the one with the chlorines) from most to least reactive in SN 1 reactions. How about ranking reactivity in nucleophilic addition (for example, Grignard) reactions in the second image?arrow_forwardHO HO H3O+, heat Select to Draw OH OH Please select a drawing or reagent from the question area Incorrect, 1 attempt remaining Your structure contains too many cyclic (ring) compounds. Review the reaction conditions including starting materials and/or intermediate structures and recount the number of carbon atoms in your structure. Retryarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY