
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
ALL 3 and last part posted in writing !
Compute
|
|
|
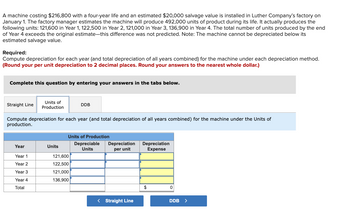
Transcribed Image Text:A machine costing $216,800 with a four-year life and an estimated $20,000 salvage value is installed in Luther Company’s factory on January 1. The factory manager estimates the machine will produce 492,000 units of product during its life. It actually produces the following units: 121,600 in Year 1, 122,500 in Year 2, 121,000 in Year 3, 136,900 in Year 4. The total number of units produced by the end of Year 4 exceeds the original estimate—this difference was not predicted. Note: The machine cannot be depreciated below its estimated salvage value.
**Required:**
Compute depreciation for each year (and total depreciation of all years combined) for the machine under each depreciation method. *(Round your per unit depreciation to 2 decimal places. Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar.)*
**Instructions:**
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
- **Straight Line**
- **Units of Production**
- **DDB (Double Declining Balance)**
### Units of Production
Compute depreciation for each year (and total depreciation of all years combined) for the machine under the Units of Production method.
| Year | Units | Depreciable Units | Depreciation per unit | Depreciation Expense |
|-------|--------|-------------------|-----------------------|----------------------|
| Year 1| 121,600| | | |
| Year 2| 122,500| | | |
| Year 3| 121,000| | | |
| Year 4| 136,900| | | |
| Total | | | | $0 |
_Navigate using the buttons_: `< Straight Line` | `DDB >`
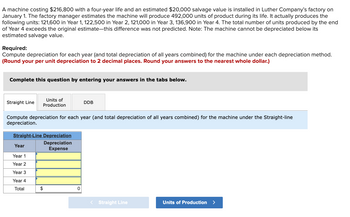
Transcribed Image Text:### Depreciation Calculation for a Machine
A machine costing $216,800 with a four-year life and an estimated $20,000 salvage value is installed in Luther Company’s factory on January 1. The factory manager estimates the machine will produce 492,000 units of product during its life. It actually produces the following units:
- 121,600 in Year 1
- 122,500 in Year 2
- 121,000 in Year 3
- 136,900 in Year 4
The total number of units produced by the end of Year 4 exceeds the original estimate—this difference was not predicted. Note: The machine cannot be depreciated below its estimated salvage value.
#### Required:
Compute depreciation for each year (and total depreciation for all years combined) for the machine under each depreciation method. (Round per unit depreciation to 2 decimal places. Round answers to the nearest whole dollar.)
#### Instructions:
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
### Depreciation Methods:
1. Straight Line
2. Units of Production
3. Double Declining Balance (DDB)
#### Straight-Line Depreciation Table
| Year | Depreciation Expense |
|--------|----------------------|
| Year 1 | |
| Year 2 | |
| Year 3 | |
| Year 4 | |
| Total | $0 |
Use the navigation to switch between different depreciation methods.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Required: State the effect (higher, lower, no effect) of accelerated depreciation relative to straight-line depreciation on a. Depreciation expense in the first year. b. The asset's net book value after two years. Cash flows from operations (excluding income taxes). с.arrow_forwardThe Annual Depreciation Expense be using straight-line depreciation will be $6250, the accounts would be used in the adjusting entry for a full year of depreciation will be Debit - Depreciation Expense, Truck</> Credit - Accumulated Depreciation, Truck. 13) Under the Fixed assets section of the balance sheet, what number would we put in the "Accumulated Depreciation, Truck" section for Year # 4 if depreciation is calculated ANNUALLY (assume Jan 1st, 2019 to Dec 31st, 2019 is Year #1).arrow_forward4arrow_forward
- On January 1, 2023, a machine was purchased for $105,000. The machine has an estimated salvage value of $6,420 and an estimated useful life of 5 years. The machine can operate for 106,000 hours before it needs to be replaced. The company closed its books on December 31 and operates the machine as follows: 2023, 21,200 hours; 2024, 26,500 hours; 2025, 15,900 hours: 2026, 31,800 hours; and 2027, 10,600 hours. Compute the annual depreciation charges over the machine's life assuming a December 31 year-end for each of the following depreciation methods. (Round rate per hour to 2 decimal places, e.g. 15.25 and final answers to 0 decimal places, e.g. 45,892.) 1. Straight-line Methodi $ 2. Activity Method Year 2023 2024 2025 $ 19,716 19,716 24,645 14,787arrow_forward1. Determine the annual depreciation expense for each of the estimated 5 years of use, the accumulated depreciation at the end of each year, and the book value of the equipment at the end of each year by (a) the straight-line method and (b) the double-declining-balance method. a. Straight-line method Additional Instruction Accumulated Depreciation, Year Depreciation Expense End of Year Book Value, End of Year 1 2 3 4 5 b. Double-declining-balance method Accumulated Depreciation, Year Depreciation Expense End of Year Book Value, End of Year 1 2 3 4 5 New lithographic equipment, acquired at a cost of $859,200 on March 1 at the beginning of a fiscal year, has an estimated useful life of 5 years and an estimated residual value of $96,660. The manager requested…arrow_forwardYour staff person has provided you with the following journal entry for January 20x1 depreciation. The monthly deprecation is supposed to be $100.00. What is wrong with this entry?arrow_forward
- Original Cost POST. ... Accumulated Depreciation for Previous Years DATE DESCRIPTION REF. DEBIT CREDIT ... Book Value, Beginning Year 4 1 20xx ... Salvage Value 2 2. ... Revised Remaining Depreciation Cost 3 ... 4 Revised Useful Life 15 YEARS Revised Depreciation, Total Revised Depreciation, Per Year ...arrow_forwardPharoah Company purchases equipment on January 1, Year 1, at a cost of $267,000. The asset is expected to have a service life of 5 years and a salvage value of $20,000.arrow_forwardH1.arrow_forward
- Using the following information, create a Double declining, depreciation schedule. Van cost:34,440 Residual value: 1,722 Useful Life: 3 Years Example: Straight-line depreciation Schedule. Years Value at the beginning of the year Depreciation End of year Value 1 34,440 10,906 23,535 2 23,535 10,906 12,628 3 12,628 10,906 1,722arrow_forwardsubject; accountingarrow_forwardPartial-year depreciation Equipment acquired at a cost of $74,000 has an estimated residual value of $4,000 and an estimated useful life of 10 years. It was placed in service on April 1 of the current fiscal year, which ends on December 31. When required, round your answers to two decimal places. a. Determine the depreciation for the current fiscal year and for the following fiscal year by the straight-line method. Year 1 $ Year 2 $ Depreciation b. Determine the depreciation for the current fiscal year and for the following fiscal year by the double-declining-balance method. Year 1 Year 2 Depreciationarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education