
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
“Alcohol and the Brain”
How widely do you think this information is known to the general public? Explain.
Article:
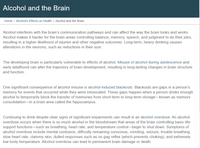
Transcribed Image Text:Alcohol and the Brain
Home / Alcohol's Effects on Health / Alcohol and the Brain
Alcohol interferes with the brain's communication pathways and can affect the way the brain looks and works.
Alcohol makes it harder for the brain areas controlling balance, memory, speech, and judgment to do their jobs,
resulting in a higher likelihood of injuries and other negative outcomes. Long-term, heavy drinking causes
alterations in the neurons, such as reductions in their size.
The developing brain is particularly vulnerable to effects of alcohol. Misuse of alcohol during adolescence and
early adulthood can alter the trajectory of brain development, resulting in long-lasting changes in brain structure
and function.
One significant consequence of alcohol misuse is alcohol-induced blackouts. Blackouts are gaps in a person's
memory for events that occurred while they were intoxicated. These gaps happen when a person drinks enough
alcohol to temporarily block the transfer of memories from short-term to long-term storage-known as memory
consolidation-in a brain area called the hippocampus.
Continuing to drink despite clear signs of significant impairments can result in an alcohol overdose. An alcohol
overdose occurs when there is so much alcohol in the bloodstream that areas of the brain controlling basic life-
support functions–such as breathing, heart rate, and temperature control-begin to shut down. Symptoms of
alcohol overdose include mental confusion, difficulty remaining conscious, vomiting, seizure, trouble breathing,
slow heart rate, clammy skin, dulled responses such as no gag reflex (which prevents choking), and extremely
low body temperature. Alcohol overdose can lead to permanent brain damage or death.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Applications like Sleep Cycle (https://www.sleepcycle.com/) monitor sleep cycles to improve answered users' health. Discuss their benefits for end users. out of Paragraph BIEE question Path: parrow_forwardGive a brief note on Thalamic and Hypothalamic hormones? Answer should include all pharmacological studies, everything which are related to pharmacology? Please answer at your own words.arrow_forwardWhy is experimental design the best study for fentanyl exposure in the brain.arrow_forward
- Please help me, idk if my answer is correct and I am trying to use this to study!!arrow_forwardSubjective changes in body functions that are not apparent to an observer such as headache nausea and anxiety are referred to asarrow_forwardThe expression "can't see the forest for the trees" implies an over-reliance on the parts/details of a problem instead of considering the whole. Based on what we covered in lecture, it might also describe someone who has an overactive relative to their parietal cortex; premotor cortex left hemisphere; right hemisphere right hemisphere; left hemisphere premotor cortex; parietal cortexarrow_forward
- please answer asaparrow_forwardcontemporary drug use, as related to legislative changes, the synthetic opioid fentanyl being used alone or mixed with heroin, and societal norms and/or acceptance of drug use. pharmacology and psychopharmacology as related to the complexity of human drug consumption on biological, psychological and social levels choose two illegal drugs opioids and cocaine, - compare with alcohol, nicotine or caffeine -discuss in terms of the effects on the body, mind and society. -discuss also in terms of the legalities and treatment perspectives when doing comparisons. -include a discuss about marijuana depending on the state of colorado or Caribbean region. - present at least two journal articles to support your perspectives and reasoning.arrow_forwardA victim may experience a(n)_____ prior to a seizure, which may indicate only that something abnormal or unusal.arrow_forward
- 26. Prozac and related drugs appear to work to elevate mood, relieve depression and reduce irritability (at least for some users) by elevating the levels of ________________ available at the synapses.arrow_forwardTrue or False: Epilepsy, a disorder of recurrent seizures, can be effectively managed in most patients with antiepileptic drugs.arrow_forwardAlcoholism is a state of altered cellular physiology caused by chronic consumption of alcohol that manifests in physical disturbances called ______ when alcohol use is suspended. hallucinations delusions dependency withdrawalarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education