
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
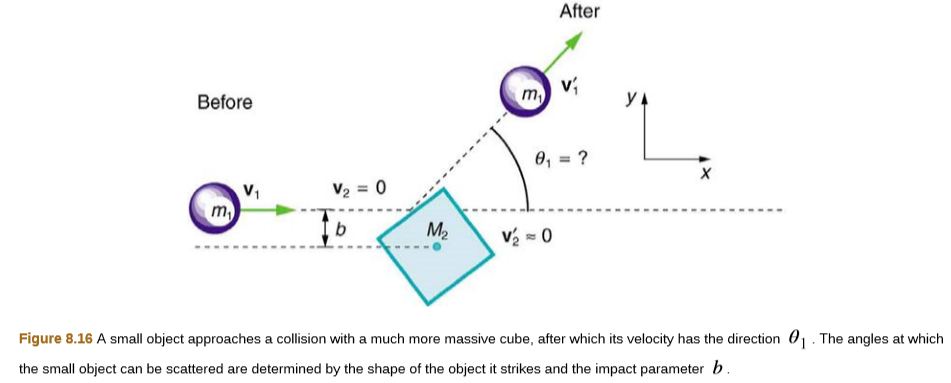
Shows a cube at rest and a small object heading toward it. (a) Describe the directions (angle θ1) at which the small object can emerge after colliding elastically with the cube. How does θ1 depend on b, the so-called impact parameter? Ignore any effects that might be due to rotation after the collision, and assume that the cube is much more massive than the small object. (b) Answer the same questions if the small object instead collides with a massive sphere.
Transcribed Image Text:After
v;
Before
m,
УА
0, = ?
х
V1
V2 = 0
m,
M2
V = 0
Figure 8.16 A small object approaches a collision with a much more massive cube, after which its velocity has the direction 01. The angles at which
the small object can be scattered are determined by the shape of the object it strikes and the impact parameter b.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Do I use the concept of elastic collision and its related linear momentum and velocity equations? That is how I've solved it and got 535 m/s. Ths velocity decreases because the potential energy is supplied to moving the cannon?arrow_forwardThree cubes, of side l0l0, 2l02l0, and 3l03l0 are placed next to one another (in contact) with their centers along a straight line as shown in the figure What is the position, along this line, of the CMCM of this system? Assume the cubes are made of the same uniform material. Express your answer in terms of l0l0. Express your answer using two significant figures.arrow_forwardA coordinate plane has a horizontal axis labeled t (s) and a vertical axis labeled Fx (N). A straight line is drawn from (0,0) to (2,4), then from (2,4) to (3,4), and from (3,4) to (5,0). (a) Find the impulse of the force. (Give your answer to one decimal place.)(b) Find the final velocity of the particle if it is initially at rest.(c) Find the final velocity of the particle if it is initially moving along the x-axis with a velocity of −2.55 m/s.arrow_forward
- A 0.00600 kg bullet traveling horizontally with speed 1.00 103 m/s strikes a 16.0 kg door, embedding itself 11.9 cm from the side opposite the hinges as shown in the figure below. The 1.00 m wide door is free to swing on its frictionless hinges. Imagine that the door is hanging vertically downward, hinged at the top, so that the figure is a side view of the door and bullet during the collision. What is the maximum height (in cm) that the bottom of the door will reach after the collision?arrow_forwardPlease Help!arrow_forwardA solid sphere of mass, M = 5.0 kg, and radius, R = 0.100 m is placed on two blocks so that it’s centre of mass lies at the origin as shown on the right. A bullet of mass, m = 0.100 kg, and with an x coordinate of b = 0.04 m strikes the sphere from below with a vertical velocity, v = 65 m/s and embeds in the sphere coming to rest at the location (-b,0) in the diagram below. Since there is no momentum in the horizontal direction, after the bullet hits the sphere , it will rise up to some maximum height and then fall back to its initial position on the two blocks. While the sphere is in the air it will rotate. What is the magnitude of the angle (in degrees) through which the sphere will rotate before it makes contact with the two blocks again?arrow_forward
- Hello, I need help finding the solution with a explanation for this question. Please and thank you.arrow_forwardA 0.12-kg ball is moving at 6 m/s when it is hit by a bat, causing it to reverse direction and have a speed of 14 m/s. What is the magnitude of the linear impulse experienced by the ball?arrow_forwardA 60-kg rocket is fired from O with an initial velocity v0 = 125 m/s along the indicated trajectory. The rocket explodes 7 seconds after launch and breaks into three pieces A, B, and C having masses of 10, 30, and 20 kg, respectively. Pieces B and C are recovered at the impact coordinates shown. Instrumentation records reveal that piece B reached a maximum altitude of 1500 m after the explosion and that piece C struck the ground 6 seconds after the explosion. What are the impact coordinates for piece A? Neglect air resistance.arrow_forward
- Sphere A of mass 0.9 kg travels with an initial velocity vA =11 m/s as shown and strikes the 2.8-kg sphere B which travels with a velocity VB =6 m/s. If the coefficient of restitution is 0.4, determine the speed of sphere B after impact. Give your answer in m/s. VA VB A Barrow_forwardCan you help me when this question . It is one question with three parts , I am struggling to solvearrow_forwardA 4-Kilogram object slides, on a smooth surface, towards the north at a velocity of 5 meters per second. The object hits a fixed pole and is deflected from north to east by an angle of 60° and has a velocity of 5 meters per second. The change in the magnitude of the northward component of the moment of the object is Select one: О а. —20Кg* (т/s) O b. -10K9 * (m/s) О с. 10Кg* (т/s) d. -30Kg * (m/s) OKg * (m/s) e.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON