
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
For the section shown in the figure below:
(a) Determine the coordinates of the centroid with respect to point “O”.
(b) Find the second moment of area of the section about “x” axis (Ix).
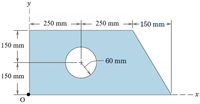
Transcribed Image Text:y
250 mm
250 mm 150 mm
150 mm
60 mm
150 mm
-- x
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3) The T shaped cross-section of a beam is made of a flange (the upper horizontal area A1 = 2000 mm2) and a web (the lower vertical area A2 = 3200 mm?) as shown in the figure. 20 mm If you want to compute the vertical distance C, of the centroid of this cross-section from the bottom most point of this cross- а. section then give the expression in terms of some numbers from which Cy can be computed. No need to carry out the calculation. b. From part (a) if you get Cy = 114.6 mm then give the final expression of the area moment of inertia Ix (about the x-axis going through the centroid of the T-section). Your expression should only contain some numbers. No need to finish the calculation. Give the final expression of the area moment of inertia ly (about the y-axis going through the centroid). Your expression should only contain some numbers. No need to finish the calculation. d. If you drill a circular hole of 15 mm diameter with its center 160 mm С. 20 mm 100 mm coinciding with the…arrow_forwardThe cross sectional area of the members of the truss shown is 500 mm² and E = 200 GPa. Solve the horizontal displacement of joint C due to external loadings in mm. AB 1.5 m O 0.1875 O 0.075 O 11.25 O 18.75 C 2 m D 10 kN 5 kNarrow_forwardDetermine the centroids and the second moment of the area for the figures shown below abouttheir centroidal axes.arrow_forward
- Consider the beam's cross-sectional area shown in (Figure 1). Suppose that a = 210 mm, b = 280 mm, c = 140 mm. Determine the location y¯ of the centroid for the beam's cross-sectional area.arrow_forwardFor the area shown, do the following: a. Determine the centroid with respect to the indicated X and Y axes of the area shown. If centroid is zero, show proof that it is zero. b. Determine the moment of inertia with respect to the centroidal X and Y axes c. Determine the product of inertia with respect to the indicated X and Y axes. d. Determine the polar moment of inertia with respect to the centroidal X and Y axes. вотт BE 80mm 60 mm 60 mmarrow_forwardQ2 / The cross sectional area of each member of the truss as shown in the figure below 1.75 in and E = 29(10')ksi , determine the vertical displacement at joint D due to radiant heating of member FD is subjected to an increase in temperature from 20° F C to 110° F, take a = 0.75(10³)/F , and member CD would be decreased 0.2 in use Method of Virtual Work. (P in k) P=9 VP F E 4 m А D B C 3 m 3 m 3 m +arrow_forward
- PLease show all of your workarrow_forwardFor the image at the right, the coordinate angle, y = 55°, and the angle in the x-y plan, e = 47°, (-23 i + 26 j+ 44 k) lbs. What is the magnitude of the force, F, acting along and the force along a-a is, F = the line b-b? а-а b-b F X yarrow_forwardSOLVE STEP BY STEP IN DIGITAL FORMAT Determine by the method of nodes the forces at which all the members of the following truss work. 5.5 K 8 pies 10 pies D 6 pies 3.5 K 8 pies 10 pies 40° A Earrow_forward
- F3=30N F2=80N Express each of the three forces acting on the support in Cartesian vector form and determine the magnitude of the resultant force and its direction, measured clockwise from positive x axis.arrow_forwardFor the truss structure shown, express the position vector r AC from point A topoint C in terms of its components in x and y. Determine the length of truss member AC usingvector operations (i.e., do not simply use the Pythagorean Theorem). Calculate the unit vector forr ACarrow_forwardDetermine by integration the centroid (?̅) of theshape in the figure (to the right).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning