
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Acids & Bases: Understanding Connections Between Descriptions if Weak Acid Dissociations
For a certain acid pka is 3.58. Calculate the pH at which an aqueous solution of this acid would be 6.5% dissociated. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.
*Photo included below
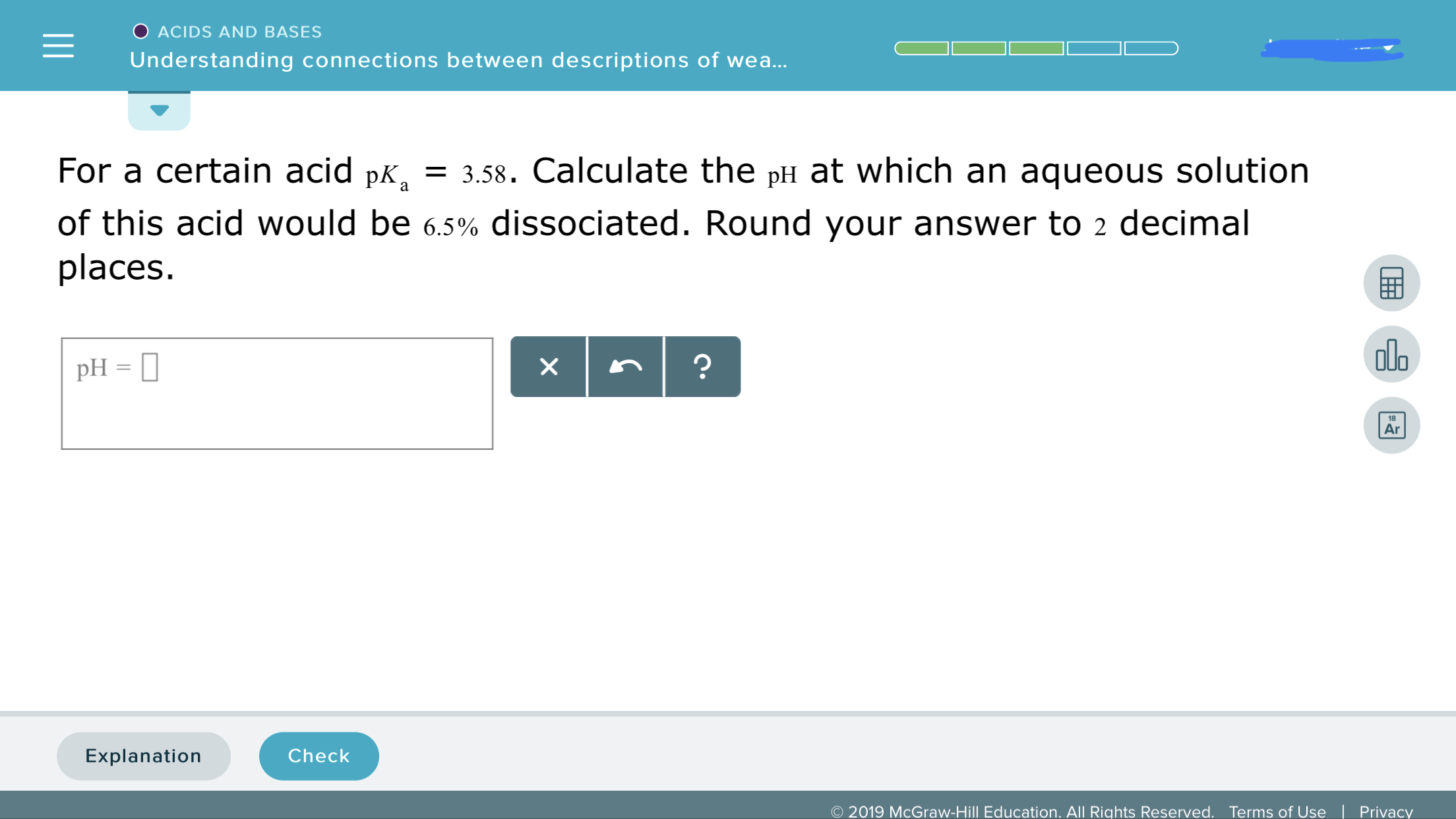
Transcribed Image Text:ACIDS AND BASES
Understanding connections between descriptions of wea
For a certain acid pK, 3.58. Calculate the pH at which an aqueous solution
of this acid would be 6.5% dissociated. Round your answer to 2 decimal
places
ala
18
Ar
Explanation
Check
© 2019 McGraw-Hill Education. All Rights Reserved.
Terms of Use
|
Privacy
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- lish United States (en_us) When a Lewis acid and a Lewis base combine, the product may be referred to as an acid-base BIEE 困| A Paragraph - US X x² EE 3 E E T T. 2 Ω Font family HCB Tx Font size Path: parrow_forwardA weak base has a Kb = 1.5 x 109. What is the value of the pKa for the conjugate acid? Enter your answer, rounded to the correct number of significant figures, into the box below. Do not use scientific notation. If your answer is a decimal, please include a 0 before the decimal point. pka = type your answer...arrow_forwardThe pH of a 1.0M solution of carbonic acid (H₂CO₂) is measured to be 3.17. Calculate the acid dissociation constant K of carbonic acid. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. a K.-O 0. X 5arrow_forward
- Solve itarrow_forwardThe acid dissociation constant K, of hypobromous acid (HB10) is 2.3 × 10 º. Calculate the pH of a 0.77M solution of hypobromous acid. Round your answer to 1 decimal place. pH = ?arrow_forwardConsider the following data on some weak acids and weak bases: formula hydrocyanic acid HCN hypochlorous acid HCIO name acid 01 M Nacio 0.1 MC₂NHBr 0.1 KBr 0.1 MKCN solution 49 10 10 3.0 10 Use this data to rank the following solutions in order of increasing pH. In other words, select a 'I' next to the solution that will have the lowest pH, a 2 next to the solution that will have the next lowest pH, and so on. PH choose one 8 choose one choose one 8 those base 3 K₂ formula pyridine CHN 17-10 ammonia NH, 18×105 name 腰国语。arrow_forward
- The pH of a 0.92M solution of hypobromous acid (HBRO) is measured to be 4.34. Calculate the acid dissociation constant K, of hypobromous acid. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K %3D a x10 Canti 2021 McGraw Hill LLC.arrow_forwardConstruct the expression for Ka for the weak acid, NH,. NH, (aq) + H,O(1)=H,0(aq) + NH,(aq) 1 Based on the definition of Ka, drag the tiles into the numerator or denominator to construct the expression for the given acid. Koarrow_forwardI need part D, E and F onlyarrow_forward
- In an aqueous solution of a certain acid with pKa = 2.73 the pH is 2.09. Calculate the percent of the acid that is dissociated in this solution. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.arrow_forwardUse the following table to predict the best acid / base pair for the desired pH/pOH value:pH = 5.00What is the best acid AND base pair? Name Acid Base pKa Hydrochloric acid HCl Cl- -7.00 Phosphoric acid H3PO4 H2PO4- 2.12 Hydrofluoric acid HF F- 3.18 Lactic acid Lactic acid Lactate 3.85 Acetic acid CH3COOH CH3COO- 4.74 Carbonic acid H2CO3 HCO3- 6.36 Dihydrogen phosphate H2PO4- HPO42- 7.21 Ammonium NH4+ NH3 9.25 Hydrocyanic acid HCN CN- 9.31 Bicarbonate HCO3- CO32- 10.25 Methylammonium ion CH3NH3+ CH3NH2 10.62 Hydrogen phosphate HPO42- PO43- 12.38arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY