
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question

Transcribed Image Text:**Weighted Average Cost Method with Perpetual Inventory**
The beginning inventory at Midnight Supplies and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period ending March 31 are as follows:
| Date | Transaction | Number of Units | Per Unit | Total |
|------------|-------------|-----------------|----------|------------|
| Jan. 1 | Inventory | 9,000 | $60.00 | $540,000 |
| Jan. 10 | Purchase | 21,000 | 70.00 | 1,470,000 |
| Jan. 28 | Sale | 10,250 | 140.00 | 1,435,000 |
| Jan. 30 | Sale | 5,750 | 140.00 | 805,000 |
| Feb. 5 | Sale | 3,500 | 140.00 | 490,000 |
| Feb. 10 | Purchase | 39,500 | 75.00 | 2,962,500 |
| Feb. 16 | Sale | 15,000 | 150.00 | 2,250,000 |
| Feb. 28 | Sale | 10,000 | 150.00 | 1,500,000 |
| Mar. 5 | Purchase | 25,000 | 82.00 | 2,050,000 |
| Mar. 14 | Sale | 30,000 | 150.00 | 4,500,000 |
| Mar. 25 | Purchase | 10,000 | 88.40 | 884,000 |
| Mar. 30 | Sale | 19,000 | 150.00 | 2,850,000 |
This table provides an overview of the inventory transactions including sales and purchases for Midnight Supplies over the first quarter of the year. The data is organized by date and type of transaction, listing the number of units, cost per unit, and total transaction amount.
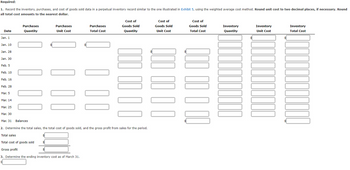
Transcribed Image Text:**Inventory Management Exercise**
**Objective:**
1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of goods sold data in a perpetual inventory record using the weighted average cost method. Round unit costs to two decimal places if necessary, and round all total costs to the nearest dollar.
**Table Overview:**
- **Columns**:
- **Date**
- **Purchases**:
- Quantity
- Unit Cost
- Total Cost
- **Cost of Goods Sold**:
- Quantity
- Unit Cost
- Total Cost
- **Inventory**:
- Quantity
- Unit Cost
- Total Cost
**Dates to Record:**
- **Jan. 1**
- **Jan. 10**
- **Jan. 28**
- **Jan. 30**
- **Feb. 5**
- **Feb. 10**
- **Feb. 16**
- **Feb. 28**
- **Mar. 5**
- **Mar. 14**
- **Mar. 25**
- **Mar. 30**
- **Mar. 31** (Balances)
**Instructions:**
2. Calculate the following for the period:
- Total Sales
- Total Cost of Goods Sold
- Gross Profit
3. Determine the ending inventory cost as of March 31.
**Explanation of Process:**
- For each transaction date, update the inventory records based on purchases and sales using the weighted average cost method.
- After each transaction, compute the new average cost per unit for inventory.
- On March 31, calculate and record the balance totals, total sales, cost of goods sold, gross profit, and ending inventory cost.
This exercise helps in understanding how to maintain a perpetual inventory system and apply the weighted average cost method to real-life data.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- pre.22arrow_forwardWeighted Average Cost Method with Perpetual Inventory The beginning inventory for Midnight Supplies and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period are as follows: Date Transaction Numberof Units Per Unit Total Jan. 1 Inventory 7,500 $79.00 $592,500 10 Purchase 22,500 89.00 2,002,500 28 Sale 11,250 158.00 1,777,500 30 Sale 3,750 158.00 592,500 Feb. 5 Sale 1,500 158.00 237,000 10 Purchase 54,000 91.50 4,941,000 16 Sale 27,000 168.00 4,536,000 28 Sale 25,500 168.00 4,284,000 Mar. 5 Purchase 45,000 93.50 4,207,500 14 Sale 30,000 168.00 5,040,000 25 Purchase 7,500 94.00 705,000 30 Sale 26,250 168.00 4,410,000 Required: 1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of goods sold data in a perpetual inventory record similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 5, using the weighted average cost method. Round unit cost to two decimal places, if necessary. Round…arrow_forwardPeriodic Inventory Using FIFO, LIFO, and Weighted Average Cost Methods The units of an item available for sale during the year were as follows: Jan. 1 Inventory 13 units at $3,800 $49,400 Aug. 7 Purchase 19 units at $3,900 74,100 Dec. 11 Purchase 13 units at $4,100 53,300 45 units $176,800 There are 18 units of the item in the physical inventory at December 31. The periodic inventory system is used. Determine the inventory cost using (a) the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method; (b) the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method; and (c) the weighted average cost method (Round per unit cost to two decimal places and your final answer to the nearest whole dollar).arrow_forward
- The inventory records for Radford Company reflected the following Beginning inventory on May 1 First purchase on May 7 second purchase on May 17 Third purchase on May 23 1,800 units @ $5.20 1,900 units @ $5.40 2,100 units @ $5.50 1,700 units @ $5.60 Sales on May 31 5,700 units @ $7.10 What is the weighted average cost per unit for May? Multiple Choice $5.37 $5.43arrow_forwardPeriodic inventory by three methods The beginning inventory at Midnight Supplies and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period ending March 31 are as follows: Number Date Transaction of Units Per Unit Total Jan. 1 Inventory Jan. 10 Purchase Jan. 28 Sale Jan. 30 Sale Feb. 5 Sale Feb. 10 Purchase Feb. 16 Sale Feb. 28 Sale Mar. 5 Purchase Mar. 14 Sale Mar. 25 Purchase Mar. 30 Sale 9,000 $60.00 $540,000 21,000 70.00 1,470,000 10,250 140.00 1,435,000 5,750 140.00 805,000 3,500 140.00 490,000 39,500 75.00 2,962,500 15,000 150.00 2,250,000 10,000 150.00 1,500,000 25,000 82.00 2,050,000 30,000 150.00 4,500,000 10,000 88.40 884,000 19,000 150.00 2,850,000 1. Determine the inventory on March 31 and the cost of goods sold for the three-month period, using the first-in, first-out method and the periodic inventory system. Inventory, March 31 $ 966,000 ✓ Cost of goods sold $ 6,940,500 2. Determine the inventory on March 31 and the cost of goods sold for the three-month period, using the…arrow_forwardFIFO Perpetual Inventory The beginning inventory of merchandise at Rhodes Co. and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period ending June 30 are as follows: Date Transaction Numberof Units Per Unit Total Apr. 3 Inventory 42 $375 $15,750 8 Purchase 84 450 37,800 11 Sale 56 1,250 70,000 30 Sale 35 1,250 43,750 May 8 Purchase 70 500 35,000 10 Sale 42 1,250 52,500 19 Sale 21 1,250 26,250 28 Purchase 70 550 38,500 June 5 Sale 42 1,315 55,230 16 Sale 56 1,315 73,640 21 Purchase 126 600 75,600 28 Sale 63 1,315 82,845 Required: 1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of merchandise sold data in a perpetual inventory record similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 3, using the first-in, first-out method. Under FIFO, if units are in inventory at two different costs, enter the units with the LOWER unit cost first in the Cost of Merchandise Sold Unit Cost…arrow_forward
- Periodic Inventory Using FIFO, LIFO, and Weighted Average Cost Methods The units of an item available for sale during the year were as follows: Jan. 1 Inventory 15 units at $5,000 $75,000 Aug. 7 Purchase 16 units at $5,100 81,600 Dec. 11 Purchase 11 units at $5,300 58,300 42 units $214,900 There are 17 units of the item in the physical inventory at December 31. The periodic inventory system is used. Determine the inventory cost using (a) the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method; (b) the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method; and (c) the weighted average cost method (Round per unit cost to two decimal places and your final answer to the nearest whole dollar). а. First-in, first-out (FIFO) $4 b. Last-in, first-out (LIFO) С. Weighted average costarrow_forwardThe beginning inventory at Midnight Supplies and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period ending March 31 are as follows: Date Jan. Feb. Mar. Transaction Number of Units 9,000 21,000 10,250 5,750 3,500 1 Inventory 10 Purchase 28 Sale 30 Sale 5 Sale 10 16 28 5 Purchase 14 25 30 Purchase Sale Sale Sale Purchase Sale 39,500 15,000 10,000 25,000 30,000 10,000 19,000 Per Unit $60.00 70.00 140.00 140.00 140.00 75.00 150.00 150.00 82.00 150.00 88.40 150.00 Total $540,000 1,470,000 1,435,000 805,000 490,000 2,962,500 2,250,000 1,500,000 2,050,000 4,500,000 884,000 2,850,000 Required: 1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of goods sold data in a perpetual inventory record similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 3, using the first-in, first-out method. 2. Determine the total sales and the total cost of goods sold for the period. Journalize summary entries for the sales and corresponding cost of goods sold for the period. Assume that all sales were on account and date your…arrow_forwardInventory by Three Methods The units of an item available for sale during the year were as follows: Jan.1 Inventory 27 units at $400 per unit Feb. 19 Purchase 55 units at $460 per unit June 8 Purchase 62 units at $540 per unit Oct. 7 Purchase 57 units at $550 per unit There are 46 units of the item in the physical inventory at December 31. The periodic inventory system is used. Determine the inventory cost under each of the following methods. a. Determine the inventory cost by the first-in, first-out method.$ b. Determine the inventory cost by the last-in, first-out method.$ c. Determine the inventory cost by the average cost method. Do not round intermediate calculation and round final answer to the nearest whole value.$arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education