
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
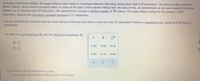
Transcribed Image Text:According to previous studies, the mean distance each visitor in Greenspan National Park hikes during their visit is 27 kilometers. The park recently closed its
shuttle system, which used to transport hikers to many of the park's most popular hiking trails. Because of this, an administrator at the park suspects the mean
distance, u, is now less than 27 kilometers. The administrator chooses a random sample of 78 visitors. The mean distance hiked for the sample is 25.6
kilometers. Assume the population standard deviation is 7.1 kilometers.
Can the administrator conclude that the mean distance hiked by each visitor is now less than 27 kilometers? Perform a hypothesis test, using the 0.05 level of
significance.
(a) State the null hypothesis H, and the alternative hypothesis H,.
O<O O$O D>O
H:
D=D D<O
(b) Perform a Z-test and find the p-value.
Here is some information to help you with your Z-test.
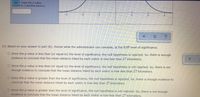
Transcribed Image Text:V Enter the p-value.
(Kound to 3 decimal places.)
-3
-2
-1
1.
(c) Based on your answer to part (b), choose what the administrator can conclude, at the 0.05 level of significance.
LEGO
O Since the p-value is less than (or equal to) the level of significance, the null hypothesis is rejected. So, there is enough
evidence to conclude that the mean distance hiked by each visitor is now less than 27 kilometers.
O Since the p-value is less than (or equal to) the level of significance, the null hypothesis is not rejected. So, there is not
enough evidence to conclude that the mean distance hiked by each visitor is now less than 27 kilometers.
O Since the p-value is greater than the level of significance, the null hypothesis is rejected. So, there is enough evidence to
conclude that the mean distance hiked by each visitor is now less than 27 kilometers.
O Since the p-value is greater than the level of significance, the null hypothesis is not rejected. So, there is not enough
evidence to conclude that the mean distance hiked by each visitor is now less than 27 kilometers.
3.
2.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A study was conducted in which students were asked to estimate the number of calories in a cheeseburger. One group was asked to do this after thinking about a calorie-laden cheesecake. A second group was asked to do this after thinking about an organic fruit salad. The mean number of calories estimated was 798 for the group that thought about the cheesecake and 1013 for the group that thought about the organic fruit salad. Suppose that the study was based on a sample of 20 students in each group, and the standard deviation of the number of calories estimated was 124 for the people who thought about the cheesecake first and 143 for the people who thought about the organic fruit salad first. Complete parts (a) through (e) below. a. State the null and alternative hypotheses if you want to determine whether the mean estimated number of calories in the cheeseburger is lower for the people who thought about the cheesecake first than for the people who thought about the organic fruit salad…arrow_forwardThe blue catfish (Ictalurus Furcatus) is the largest species of North Amercian catfish. The current world record stands at 143 pounds, which was caught in the John H. Kerr Reservoir (Bugg's Island Lake) located in Virginia. According to Amercian Expedition, the average weight of a blue catfish is between 20 to 40 pounds. Given that the largest blue catfish ever caught was at the John H. Kerr Reservoir, you believe that the mean weight of the fish in this reservoir is greater than 40 pounds.a) If you going to test this claim at the 0.05 significance level, what would be your null and alternative hypotheses?H0H0: H1H1: b) What type of hypothesis test should you conduct (left-, right-, or two-tailed)? left-tailed right-tailed two-tailedarrow_forwardHellen has just started a new years competition for her local climbing gym. There are two categories for this competition: singles and group (18 people). The rules are simple, put in the most hours in one months time and you get a guided tour to climb Ten Sleep canyon. She knows from running this competition over the years that the number of hours climbers at her gym spend training during this competiton is approximately normal and their mean competition hours per month in the gym are 24 hrs with a standard devaition of 6 hrs. Singles Distribution: X~N( , ) Group Distribution: x̄~N( , ) The winning single participant last year was in the 97 th percentile.... how many hours did the winner accumulate over the month? One of Hellan's friends Dave put in 27.12 hours on the wall. What is the probablity that another individual will beat his time? If someone puts in between 25.5-32.1 hours on the wall they get a Mountain Goat shirt. What percent of the singles competitors is expected to…arrow_forward
- The blue catfish (Ictalurus Furcatus) is the largest species of North Amercian catfish. The current world record stands at 143 pounds, which was caught in the John H. Kerr Reservoir (Bugg's Island Lake) located in Virginia. According to Amercian Expedition, the average weight of a blue catfish is between 20 to 40 pounds. Given that the largest blue catfish ever caught was at the John H. Kerr Reservoir, you believe that the mean weight of the fish in this reservoir is greater than 40 pounds. Use the data below, which represents the summary statistics for 50 blue catfish caught at this reservoir, and a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that the mean weight of the fish in the John H. Kerr Reservoir is greater than 40 pounds. n=50; ¯x=40.72 pounds; s=5.03pounds Calculate your test statistic. Write the result below, and be sure to round your final answer to two decimal places.e) Calculate your p-value. Write the result below, and be sure to round your final answer to four decimal…arrow_forwardThe state Government gives grants to low-income undergraduate students. According to the National Postsecondary Student Aid Study conducted by the U.S. Department of Education in 2008, the average Pell grant award for 2007-2008 was $2,600. We wonder if the mean amount is different this year for Pell grant recipients at San Jose State University. Suppose that we randomly select 50 Pell grant recipients from San Jose State University. For these 50 students, the mean Pell grant award is $2,450 with a standard deviation of $600. Let µ = the mean amount of Pell grant awards received by San Jose State University Pell grant recipients this year. We test the hypotheses: H0: μ = 2,600 , Ha: μ ≠ 2,600. The sample size is greater than 30, so a t-model is a good fit for the sampling distribution. What is the t-test statistic? What is the P-value?arrow_forwardStudents in a representative sample of 65 first-year students selected from a large university in England participated in a study of academic procrastination. Each student in the sample completed the Tuckman Procrastination Scale, which measures procrastination tendencies. Scores on this scale can range from 16 to 64, with scores over 40 indicating higher levels of procrastination. For the 65 first-year students in this study, the mean score on the procrastination scale was 37.2 and the standard deviation was 6.41. USE SALT (a) Construct a 95% confidence interval estimate of μ, the mean procrastination scale for first-year students at this college. (Round your answers to three decimal places.) (b) Based on your interval, is 40 a plausible value for the population mean score? O Yes O No What does this imply about the population of first-year students? O This implies that on average, students at this university do have high levels of procrastination. O This implies that students at this…arrow_forward
- The sample data here is the cholesterol levels for 10 men diagnosed with high cholesterol. The first row represents levels from 10 men who did not use the drug and the second row from 10 different men who did use the drug. If we want to test the claim that the mean level for all men who use the drug is less than the mean for all men who do not use it, what is the appropriate alternative hypothesis? The mean cholesterol level of males who take the medicine is higher than the mean cholesterol levels of men who do not take it. There is a significant difference between males who use the medicine and men who do not use the drug in terms of mean cholesterol levels. The mean cholesterol level of males who take the medicine is lower than the mean cholesterol levels of men who do not take it. There is no significant difference between males who use the medicine and men who do not use the drug in terms of mean cholesterol levels.arrow_forwardThe blue catfish (Ictalurus Furcatus) is the largest species of North Amercian catfish. The current world record stands at 143 pounds, which was caught in the John H. Kerr Reservoir (Bugg's Island Lake) located in Virginia. According to Amercian Expedition, the average weight of a blue catfish is between 20 to 40 pounds. Given that the largest blue catfish ever caught was at the John H. Kerr Reservoir, you believe that the mean weight of the fish in this reservoir is greater than 40 pounds. If you are going to test this claim, what would be your null and alternative hypotheses? Но: (? На: (?arrow_forwardA study was undertaken to see how accurate food labeling for calories on food that is considered reduced calorie. The group measured the amount of calories for each item of food and then found the percent difference between the measured and labeled amount of calories. The group also looked at food that was nationally advertised, regionally distributed, or locally prepared. Do the data indicate that at least one of the mean percent differences between the three groups is different from the others? The data summarized in the table below. National 3.15 Regional 36.75 Local Mean Standard Deviation Source Between Within 151 Total Fill in the hypotheses below: Ho: All the means are equal. Ha: At least one mean is different from the others. 7.4359 14.1558 SS 70.0204 Part 2 of 3 Complete the following ANOVA summary table (a 0.10). Round your answers to three decimal places, if necessary, and round any interim calculations to four decimal places. Sample Size df 20 12 8 MS - F P-valuearrow_forward
- Suppose we want to know the mean number of shurikens thrown each night by ninjas in Konoha village. Getting this information from every ninja in the village would take forever. Instead, we randomly select 20 ninjas from the ninja school that is closest to us. a. Identify the population of interest in this survey b. Describe the parameter of interest in this survey. c. Identify the sample of interest in this survey.arrow_forwardA study was undertaken to see how accurate food labeling for calories on food that is considered reduced calorie. The group measured the amount of calories for each item of food and then found the percent difference between the measured and labeled amount of calories. The group also looked at food that was nationally advertised, regionally distributed, or locally prepared. Do the data indicate that at least one of the mean percent differences between the three groups is different from the others? The data is summarized in the table below. National Mean Standard Deviation Sample Size Local -2.1 Regional 27.1667 143.125 Fill in the hypotheses below: Ho: Select an answer Ha: Select an answer 10.3257 20.797 53.5922 20 12 8arrow_forwardA nationwide job recruiting firm wants to compare the annual incomes for childcare workers in Utah and Oregon. Due to recent trends in the childcare industry, the firm suspects that the mean annual income of childcare workers in Utah is less than the mean annual income of childcare workers in Oregon. To see if this is true, the firm selected a random sample of 20 childcare workers from Utah and an independent random sample of 20 childcare workers from Oregon and asked them to report their mean annual income. The data obtained were as follows. Annual income in dollars 27060 , 42320 , 36445 , 37895, 44564 , 35325 , 30313 , 28698, 33706 , 48365 , 26946 , 25063 , 28339 , 29265 , 40051 , 37026 , 40150 , 42753 , 27820, 39471 Utah 29769 , 48859 , 32480 , 36288,45102 , 46219 ,51098 , 45516 , 38834 , 44659 , 40755 , 38006 , 39947 , 29801 , 32200, 38731 , 41370 , 28059 , 33753 , 35271 Oregon Send data to calc... v Send data to Excel The population standard deviation for the annual incomes of…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman