
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
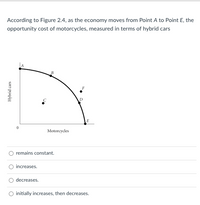
Transcribed Image Text:According to Figure 2.4, as the economy moves from Point A to Point E, the
opportunity cost of motorcycles, measured in terms of hybrid cars
B
F
E
Motorcycles
O remains constant.
O increases.
decreases.
O initially increases, then decreases.
Hybrid cars

Transcribed Image Text:SCENARIO 1.2: A scientist wants to understand the relationship between
automobile emissions and the level of global warming. The scientist collects
data on the volume of automobile emissions and the levels of global
warming over time. The scientist concludes that a 1% increase in automobile
emissions causes a 0.0003% increase in average global temperatures. From
this information he concludes that the automobile emissions are harmful to
the environment and should be reduced to stop the increase in global
temperatures.
Refer to Scenario 1.2. The statement that a 1% increase in the automobile
emissions causes a 0.0003% increase in average global temperatures is an
example of
normative economics.
marginal economics.
the fallacy of logic.
O positive economics.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Ethanol is again viewed as one part of a solution to the problem of shortages of petroleum products. Ethanol is made from a blend of gasoline and alcohol derived from corn or sugarcane. This program can be expected to Show Transcribed Text 3. Exercise 10.4 the price of sugarcane. Ethanol is again viewed as one pa alcohol derived from corn or suga This program can be expected to J not change C increase n to the problem of shortages of petroleum products. decrease the price of sugarcane.arrow_forwardPlease no written by hand Budget Selections to Build Demand As a commuter you have a budget of $250 to spend on gasoline each month. You drive a car that gets 20 miles per gallon (MPG). You can purchase 100 gallons of gasoline per month at the current price of $2.50 per gallon. Demand Schedule Price Quantity Commuting Errands Mp Social Activities Vacations $2.50 97.5 Drive Alone (700 miles) Small Trips as Needed (550 miles) Trips to City (350 miles) Out-of-State (350 miles) $3.00 Current price: $3.00/gallon Car Pool (425 miles) 2x per week (300 miles) Trips to Local Park (120 miles) In-State (200 miles) Add to schedule Previous $3.50 Public Transportation (60 miles) Next 1 Trip per Week (150 miles) Stay in Neighborhood (40 miles) > Stay-cation (50 miles) $4.00 QUANTITY 35 27.5 17.5 17.5 97.5 gallons Keynote $4.50 COST $105.00 $82.50 $52.50 $52.50 $292.50 of $250arrow_forward13) Suppose a certain change will generate £5,000 of benefits and £3,000 of costs.This change can best be described as(a) a potential Pareto improvement.(b) inefficient.(c) Pareto efficient.(d) equitable.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education