
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
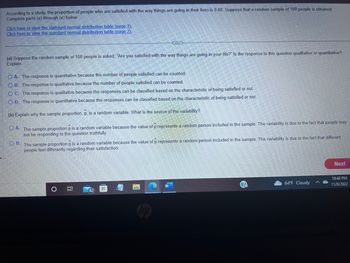
According to a study, the proportion of people who are satisfied with the way things are going in their lives is 0.80. Suppose that a random sample of 100 people is obtained
![According to a study, the proportion of people who are satisfied with the way things are going in their lives is 0.80. Suppose that a random sample of 100 people is obtained. Complete parts (a) through (c) below.
*Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 1).*
*Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 2).*
---
**(b) Explain why the sample proportion, p̂, is a random variable. What is the source of the variability?**
- **O A.** The sample proportion p̂ is a random variable because the value of p̂ represents a random person included in the sample. The variability is due to the fact that people may not be responding to the question truthfully.
- **O B.** The sample proportion p̂ is a random variable because the value of p̂ represents a random person included in the sample. The variability is due to the fact that different people feel differently regarding their satisfaction.
- **O C.** The sample proportion p̂ is a random variable because the value of p̂ varies from sample to sample. The variability is due to the fact that different people feel differently regarding their satisfaction.
- **O D.** The sample proportion p̂ is a random variable because the value of p̂ varies from sample to sample. The variability is due to the fact that people may not be responding to the question truthfully.
---
**(c) Describe the sampling distribution of p̂, the proportion of people who are satisfied with the way things are going in their life. Be sure to verify the model requirements.**
Since the sample size is no less than 5% of the population size and np(1 - p) ≥ 10, the distribution of p̂ is [normal distribution symbol] with μᵖ̂ = [0.80] and σᵖ̂ = [0.040].
[Next Button]](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/04eb1062-54d0-416c-ad3c-f2b55c6eff31/71eae64c-b2bd-409d-8c05-ed09b56a7e1d/91svn7k_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:According to a study, the proportion of people who are satisfied with the way things are going in their lives is 0.80. Suppose that a random sample of 100 people is obtained. Complete parts (a) through (c) below.
*Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 1).*
*Click here to view the standard normal distribution table (page 2).*
---
**(b) Explain why the sample proportion, p̂, is a random variable. What is the source of the variability?**
- **O A.** The sample proportion p̂ is a random variable because the value of p̂ represents a random person included in the sample. The variability is due to the fact that people may not be responding to the question truthfully.
- **O B.** The sample proportion p̂ is a random variable because the value of p̂ represents a random person included in the sample. The variability is due to the fact that different people feel differently regarding their satisfaction.
- **O C.** The sample proportion p̂ is a random variable because the value of p̂ varies from sample to sample. The variability is due to the fact that different people feel differently regarding their satisfaction.
- **O D.** The sample proportion p̂ is a random variable because the value of p̂ varies from sample to sample. The variability is due to the fact that people may not be responding to the question truthfully.
---
**(c) Describe the sampling distribution of p̂, the proportion of people who are satisfied with the way things are going in their life. Be sure to verify the model requirements.**
Since the sample size is no less than 5% of the population size and np(1 - p) ≥ 10, the distribution of p̂ is [normal distribution symbol] with μᵖ̂ = [0.80] and σᵖ̂ = [0.040].
[Next Button]
Transcribed Image Text:**Study on Satisfaction Rates**
According to a study, 80% (0.80) of people are satisfied with the way things are going in their lives. Suppose a random sample of 100 people is obtained.
**Tasks:**
- **View Standard Normal Distribution Tables:**
- Page 1
- Page 2
**Question (a):**
If a random sample of 100 people is asked, "Are you satisfied with the way things are going in your life?" Is the response to this question qualitative or quantitative? Explain.
- **Options:**
- **A.** The response is quantitative because the number of people satisfied can be counted.
- **B.** The response is qualitative because the number of people satisfied can be counted.
- **C.** The response is qualitative because the responses can be classified based on the characteristic of being satisfied or not.
- **D.** The response is quantitative because the responses can be classified based on the characteristic of being satisfied or not.
**Question (b):**
Explain why the sample proportion, \( \hat{p} \), is a random variable. What is the source of variability?
- **Options:**
- **A.** The sample proportion \( \hat{p} \) is a random variable because the value of \( \hat{p} \) represents a random person included in the sample. The variability is due to the fact that people may not be responding to the question truthfully.
- **B.** The sample proportion \( \hat{p} \) is a random variable because the value of \( \hat{p} \) represents a random person included in the sample. The variability is due to the fact that different people feel differently regarding their satisfaction.
**Instructions:**
- Review the options carefully.
- Consider the nature of qualitative versus quantitative data.
- Understand the concept of sample proportion as a random variable.
- Reflect on the sources of variability in survey responses.
Finally, select the most appropriate response before proceeding to the next step.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A magazine reports that women trust recommendations from a particular social networking site more than recommendations from any other social network platform. But does trust in this social networking site differ by gender? The following sample data show the number of women and men who stated in a recent sample that they trust recommendations made on this particular social networking site. Women Men Sample 150 170 Trust RecommendationsMade on the social networking site 117 102 (a) What is the point estimate of the proportion of women who trust recommendations made on this particular social networking site? (b) What is the point estimate of the proportion of men who trust recommendations made on this particular social networking site? (c) Provide a 95% confidence interval estimate of the difference between the proportion of women and men who trust recommendations made on this particular social networking site. (Round your answers to four decimal places.) toarrow_forwardIS IT REASONABLE TO ASSUME THIS SAMPLE CAME FROM A NORMAL POPULATION?arrow_forwardA recent Gallup Poll interviewed a random sample of 1523 adults. Of these, 868 bought a lottery tickets in the past year. Suppose that in fact (unknown to Gallup) exactly 60% of all adults bought a lottery ticket in the past year. If Gallup took many simple random samples of 1,523 people, the sample proportion who bought a ticket would vary from sample to sample. The sampling distribution would be close to normal with a mean of 0.6 and a standard deviation of___ A)0.4899 B)0.0251 C)0.00016 D)0.0126arrow_forward
- when a population distribution is symmetric, unimodal, without outliers?arrow_forwardAny basketball fan knows that Shaquille O'Neal, one of the NBA's most dominant centers of the last twenty years, always had difficulty shooting free throws. Over the course of his career, his overall made free-throw percentage was 53.3%. During one off- season, Shag had been working with an assistant coach on his free-throw technique. During the next season, a simple random sample showed that Shaq made 26 of 39 free-throw attempts. Test the claim that Shaq has significantly improved his free-throw shooting using a 0.05 significance level. Check the conditions of the Central Limit Theorem for this scenario. Calculate the number of expected successes.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman