
Concept explainers
Absenteeism: Absenteeism can be a serious employment problem. It is estimated that absenteeism reduces potential output by more than 10%. Two economists launched a research project to learn more about the problem. They randomly selected 100 organizations to participate in a 1-year study. For each organization, they recorded the average number of days absent per employee and several variables thought to affect absenteeism. The file ‘absenteeism FinEx’ contains the data on these selected 100 organizations.
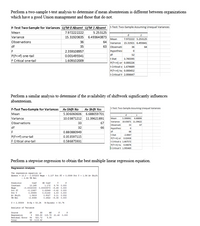
Question: How does the MLR analysis compare with the t-test for Av Shift in predicting absenteeism? Comment on the similarities and/or differences. (both MLR and t-test are provided below)
Data:
| Wage | Pct PT | Pct U | Av Shift | U/M Rel | Absent |
| 22477 | 8.5 | 57.1 | 1 | 1 | 5.4 |
| 29939 | 1.9 | 41.5 | 0 | 1 | 4.1 |
| 22957 | 12.2 | 52.6 | 1 | 0 | 11.5 |
| 18888 | 30.8 | 65.1 | 0 | 1 | 2.1 |
| 15078 | 6.8 | 68.8 | 0 | 1 | 5.9 |
| 15481 | 5.1 | 46.4 | 0 | 0 | 12.9 |
| 21481 | 25.3 | 38.9 | 0 | 1 | 3.5 |
| 29687 | 9.2 | 17.2 | 0 | 0 | 2.6 |
| 13603 | 8.4 | 12.9 | 0 | 0 | 8.6 |
| 18303 | 4.9 | 18.1 | 0 | 1 | 2.7 |
| 20832 | 23.8 | 64.4 | 1 | 1 | 6.6 |
| 22325 | 24.1 | 63.7 | 1 | 1 | 2.1 |
| 19964 | 8.6 | 12.2 | 0 | 1 | 3.8 |
| 32496 | 5.9 | 11.8 | 1 | 0 | 4.3 |
| 15795 | 2.9 | 25.8 | 0 | 1 | 4.3 |
| 21138 | 24.3 | 53.2 | 0 | 0 | 2.2 |
| 18859 | 20.6 | 22.8 | 1 | 1 | 8.6 |
| 12023 | 9 | 49.8 | 1 | 1 | 10.8 |
| 33272 | 24 | 39.1 | 1 | 0 | 2.9 |
| 22325 | 11.9 | 32.6 | 1 | 0 | 5.3 |
| 26147 | 0 | 67.7 | 1 | 0 | 8.2 |
| 33229 | 11.7 | 10.8 | 0 | 0 | 2.8 |
| 37970 | 14.6 | 25.5 | 1 | 1 | 2.4 |
| 15281 | 27.2 | 31.8 | 0 | 0 | 2.8 |
| 19423 | 17.2 | 35 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| 26587 | 13.9 | 41.9 | 1 | 1 | 9.5 |
| 22963 | 2.6 | 52.9 | 0 | 1 | 4.3 |
| 26404 | 6.4 | 64.4 | 0 | 1 | 8.9 |
| 16315 | 4.9 | 69.7 | 0 | 1 | 7.2 |
| 26759 | 23.2 | 61.8 | 1 | 1 | 5.6 |
| 30824 | 13.2 | 52.1 | 0 | 1 | 2.4 |
| 31979 | 27.7 | 57.4 | 1 | 1 | 2.7 |
| 23135 | 7 | 15.2 | 0 | 0 | 13.4 |
| 18014 | 0 | 38.7 | 1 | 0 | 14.8 |
| 18541 | 13.8 | 69.4 | 1 | 1 | 10.7 |
| 16747 | 9.9 | 67.2 | 1 | 0 | 10.3 |
| 13473 | 6.3 | 47.8 | 0 | 1 | 4.6 |
| 42986 | 13.4 | 24.5 | 1 | 0 | 3.9 |
| 23964 | 8.8 | 79.4 | 1 | 0 | 13.3 |
| 30794 | 0.4 | 12.1 | 1 | 0 | 2.2 |
| 21104 | 14.7 | 71 | 0 | 1 | 5.7 |
| 19137 | 7.7 | 28 | 1 | 0 | 11.8 |
| 26058 | 7.3 | 45.6 | 0 | 1 | 2.5 |
| 22085 | 6.8 | 25.4 | 0 | 1 | 2.1 |
| 29044 | 8.6 | 40.6 | 0 | 0 | 4.1 |
| 24205 | 19.6 | 25.1 | 1 | 1 | 4.9 |
| 17698 | 10.8 | 42.3 | 1 | 1 | 7.7 |
| 26399 | 4.5 | 63.3 | 1 | 1 | 6.3 |
| 40590 | 15.9 | 69.4 | 1 | 1 | 2.9 |
| 24805 | 5.7 | 17.7 | 1 | 1 | 2.6 |
| 18899 | 13.1 | 54.8 | 1 | 1 | 6.1 |
| 26802 | 15.5 | 46.5 | 0 | 1 | 6 |
| 30034 | 11.8 | 53.2 | 1 | 0 | 6.7 |
| 15713 | 16.6 | 41.2 | 1 | 0 | 11.9 |
| 18280 | 6.4 | 65 | 1 | 1 | 9.3 |
| 41009 | 6.7 | 54.9 | 0 | 1 | 3.6 |
| 24021 | 14 | 20.6 | 1 | 1 | 2.6 |
| 21836 | 27.6 | 29 | 0 | 1 | 2.1 |
| 21157 | 5.5 | 50.2 | 1 | 1 | 9 |
| 19529 | 14.5 | 56.6 | 1 | 0 | 11 |
| 31240 | 26.3 | 36.4 | 1 | 1 | 2.9 |
| 20963 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2.2 |
| 33826 | 8.2 | 87.9 | 0 | 1 | 3.3 |
| 23349 | 0 | 38.5 | 1 | 1 | 5.9 |
| 22695 | 25.4 | 47 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| 30475 | 0 | 69.3 | 1 | 0 | 10.8 |
| 16631 | 5.9 | 48.2 | 1 | 1 | 7.1 |
| 28996 | 18.6 | 29.3 | 1 | 1 | 2.9 |
| 15807 | 16.9 | 42.9 | 1 | 1 | 6.2 |
| 15585 | 0 | 59.4 | 1 | 0 | 10.3 |
| 18466 | 9 | 69.4 | 1 | 0 | 13.5 |
| 35140 | 21.1 | 37.1 | 1 | 1 | 6.7 |
| 33459 | 14.1 | 19.5 | 1 | 1 | 2.6 |
| 24357 | 0 | 21.5 | 1 | 1 | 5.2 |
| 19370 | 3.7 | 35 | 1 | 1 | 7.2 |
| 21820 | 6.3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3.5 |
| 23351 | 12.3 | 27.1 | 1 | 1 | 5.4 |
| 22938 | 6.8 | 68.5 | 1 | 1 | 5.8 |
| 16477 | 10 | 61.5 | 1 | 1 | 11.7 |
| 20790 | 28.5 | 59.9 | 1 | 0 | 5.6 |
| 20352 | 19.4 | 34.6 | 1 | 0 | 4.6 |
| 19743 | 14.3 | 39.7 | 1 | 0 | 8.6 |
| 22775 | 10.3 | 35.7 | 1 | 1 | 2.1 |
| 24229 | 0.9 | 26.7 | 1 | 0 | 9.6 |
| 41195 | 8.6 | 66.7 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| 23143 | 4.2 | 63.1 | 0 | 1 | 10.6 |
| 13400 | 28.1 | 46.7 | 0 | 0 | 5.8 |
| 21371 | 14.9 | 78.9 | 1 | 0 | 7.4 |
| 28675 | 7.7 | 63.4 | 0 | 0 | 10.3 |
| 18171 | 6.9 | 47.9 | 0 | 1 | 6.3 |
| 23670 | 20.5 | 46.3 | 1 | 1 | 6.7 |
| 29745 | 6.1 | 53.9 | 1 | 0 | 6.7 |
| 14672 | 13.9 | 46 | 1 | 0 | 13.3 |
| 20382 | 0 | 38.6 | 1 | 1 | 4.1 |
| 24952 | 14.6 | 53.8 | 0 | 1 | 4.6 |
| 28878 | 7.4 | 12.2 | 1 | 1 | 2.7 |
| 24558 | 24.5 | 37 | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| 20447 | 0.9 | 27.4 | 1 | 1 | 4.2 |
| 27714 | 8.7 | 58.1 | 0 | 0 | 9 |
| 18116 | 3.5 | 47.5 | 1 | 1 | 7.7 |

Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

- Dr. Watts is a pediatrician. His group did some research on the sleep habits of children less than 24 months old. They found a weak negative correlation between a child’s age and the number of hours per day he or she slept. What does this mean? As a child’s age increases, the hours of sleep decreases in a nearly perfect pattern. As a child’s age increases, the hours of sleep increases in a nearly perfect pattern. As a child’s age increases, the hours of sleep decreases but the relationship is not perfect. As a child’s age increases, the hours of sleep increases but the relationship is not perfect.arrow_forwardYou are a consultant to EAI and you have received the data on theannual salaries of 2500 managers. Some of these managers have alsoindicated that they have received some training. Conduct theappropriate descriptive analyses and present a report that willenable EAI to understand its operations. The link to the data is: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1KluyxHQdEsVNA38_EWPcEgKUJomm9b67/viewarrow_forwardAnterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries occur most frequently in planting and cutting sports such as basketball, soccer, and volleyball. National collegiate athletic association injury data show that female athletes injure the ACL more frequently than their male counterparts do. A sports medicine professor wants to test this claim. He surveyed 5 universities that had both men's and woman's basketball, soccer, and volleyball and asked them how many grade 3 ACL tears they had during the past 5 seasons. Using the following results, are women at greater risk than men for ACL injuries? (use a standard deviation of 0.01, one tail test). Women- 4,3, 5, 2,4 Men- 2, 0, 1 ,2, 1 What is the difference between a repeated measure study and a matched pairs study?arrow_forward
- A recent study revealed that the average weight of babies born in the United States is normally distributed with a mean of 7.5 pounds. This number is lower than recent years and so researchers are interested in determining what factors are associated with lower birth weights. One researcher decides to look at the age of the mother to determine if younger mothers have babies that are significantly heavier or lighter than average. To study this the researcher collects data from 87 babies who were born to mothers between the ages of 16 and 18. Only one baby was measured per mother. Twins and other multiple births were excluded. The average weight for these babies was 7.3 pounds with a standard deviation of .6 pounds. Was the average weight of babies of young mothers significantly different than babies in the general population? No, the difference was not significant Yes, they were lighter. Yes, they were heavierarrow_forwardAnterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries occur most frequently in planting and cutting sports such as basketball, soccer, and volleyball. National collegiate athletic association injury data show that female athletes injure the ACL more frequently than their male counterparts do. A sports medicine professor wants to test this claim. He surveyed 5 universities that had both men's and woman's basketball, soccer, and volleyball and asked them how many grade 3 ACL tears they had during the past 5 seasons. Using the following results, are women at greater risk than men for ACL injuries? (use a standard deviation of 0.01, one tail test). Women- 4,3, 5, 2,4 Men- 2, 0, 1 ,2, 1 Calcualte the sum of squares of injuries for men.arrow_forwardYour state is going to vote on becoming a "right to work" state in the next, and you wonder if there is there a relationship between salary levels and unionization. You find data on salary from the U.S. Census, which is split into three groups: Low; Moderate/About Average, and; High. To see if salary, measured in this way, is associated with unionization you find a variable in the same dataset called "UNION", which has two categories: the respondent has a unionized job and the respondent does not have a unionized job. Because you want to know if you should favor or oppose becoming a "right to work" state, you test these two variables to see if there is an association between salary level and unionized labor. What type of hypothesis test is most appropriate?arrow_forward
- Each year, marketing and information firm J.D. Power and Associates surveys new car owners 90 days after they have purchased their cars. The data collected are used to rate auto brands (Toyota, Ford, and others) on initial quality and initial customer satisfaction. USA Today reported both the number of manufacturing defects per 100 vehicles and a satisfaction score for all 33 brands sold in the United States.+ A research group decides to compare the mean number of defects for 2 specific models of cars, A and B, made this year by taking random samples of 100 cars of each model. USE SALT (a) After collecting the data, the research group calculates a 95% confidence interval to estimate the difference in population means. In this case, what is the population? O the defects O all cars made this year all cars for models A and B that were produced this year O the 100 cars from each model (b) Suppose the calculated confidence interval is (100, 104) number of defects. What is the value of the…arrow_forwardIn 2015, over 30,00030,000 Americans died from opioid overdoses, and the number of inpatient stays and emergency visits to hospitals related to opiods increased dramatically compared to previous years. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) have partnered with the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) to gather data on opioid-related deaths and hospitalizations. These data include information about inpatient stays, emergency department visits, age, sex, income, and opiod-related use. For a given patient admitted to a hopsital for an opioid-related event, identify which of these events are disjoint.arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





