
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
A 4.10-kg steel ball strikes a wall with a speed of 13.0 m/s at an angle of ? = 60.0° with the surface. It bounces off with the same speed and angle (see figure below). If the ball is in contact with the wall for 0.200 s, what is the average force exerted by the wall on the ball? (Assume right and up are the positive directions.)
| Fx = | N |
| Fy = | N |
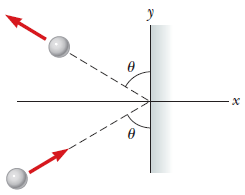
Transcribed Image Text:This diagram illustrates the reflection of a projectile off a surface. It features an axis with the x-axis horizontal and the y-axis vertical. A vertical line represents a reflecting surface positioned along the y-axis.
Two spheres are shown:
1. The first sphere approaches the reflecting surface at an angle \(\theta\) with respect to the horizontal x-axis. A dashed line indicates the path taken by the sphere toward the surface, and an arrow represents the direction of motion.
2. Upon reflection, the second sphere moves away from the surface at the same angle \(\theta\), forming a symmetrical path. The outgoing path is also represented by a dashed line, with an arrow showing the direction.
The angle \(\theta\) is the angle of incidence and is equal to the angle of reflection, illustrating the law of reflection. The diagram effectively demonstrates how the angle between the incident path and the normal (perpendicular to the surface) is equal to the angle between the reflected path and the normal.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 3.30-kg steel ball strikes a wall with a speed of 11.0 m/s at an angle of 0 = 60.0° with the surface. It bounces off with the same speed and angle (see figure below). If the ball is in contact with the wall for 0.200 s, what is the average force exerted by the wall on the ball? (Assume right and up are the positive directions.) Fx N Fy yarrow_forwardA 0.25-kg ball, initially at reston a tee, is hit with a bat in the x-direction while 1.00 meter above the ground. If the ball hits the ground 20 meters away and was in contact with the bat for 0.10-s, what average force was exerted on the ball during the contact time? Answer: 111 Narrow_forwardA 142g baseball is moving at 17.0 m / s in the + x direction. When hit with a bat by a baseball player, its final velocity is 21.0 m / s in the -x direction. The bat acts on the ball for 6.0 x 10⁻² s. What is the magnitude of the average force exerted by the bat on the ball?arrow_forward
- A car of mass 1,907 kg collides with a wall. The initial speed of the car is 18.2 m/s. After collision, the car bounced in the opposite direction at a speed of 2.9 m/s. If the collision lasted for 172 ms, what was the average force in newtons exerted on the car by the wall? Express your answer in two decimal places with units of Newton.arrow_forwardA 4.10-kg steel ball strikes a wall with a speed of 11.0 m/s at an angle of ? = 60.0° with the surface. It bounces off with the same speed and angle (see figure below). If the ball is in contact with the wall for 0.200 s, what is the average force exerted by the wall on the ball? (Assume right and up are the positive directions.) Fx = Fy =arrow_forwardA 59.5 kg man standing on a frictionless surface pushes two large boxes in opposite directions as shown. Initially everything is a rest. If the left box has mass 41.5 kg and final speed 3.25 m/s, and the right box has mass 27.0 kg and final speed 2.00 m/s, what is the final velocity (magnitude and direction) of the man? Let the positive direction be to the right.arrow_forward
- A 340-g ball B is hanging from an inextensible cord attached to a support C . A 170-g ball A strikes B with a velocity v0 with a magnitude of 1.5 m/s at an angle of 60° with the vertical. Assuming perfectly elastic impact (e= 1) and no friction, determine the height h reached by ball B.arrow_forwardA 3.90-kg steel ball strikes a wall with a speed of 9.0 m/s at an angle of 0= 60.0° with the surface. It bounces off with the same speed and angle (see figure below). If the ball is in contact with the wall for 0.200 s, what is the average force exerted by the wall on the ball? (Assume right and up are the positive directions.) F₁ = N F₂ Submit Answer Ⓡ a deletearrow_forwardA 2.72-kg steel ball strikes a massive wall at 10.0 m/s at an angle of 0 = 60.0° with the plane of the wall. It bounces off the wall with the same speed and angle (see the figure below). If the ball is in contact with the wall for 0.198 s, what is the average force exerted by the wall on the ball? -237.93 magnitude The response you submitted has the wrong sign. N -y-direction e X direction y Need Help? Watch It Read Itarrow_forward
- A baseball (m= 150 g) approaches a bat horizontally at a speed of 43.9 m/s (98.2 mi/h) and is hit straight back at a speed of 52.6 m/s (118 mi/h). If the ball is in contact with the bat for a time of 1.27 ms, what is the average force exerted on the ball by the bat? Neglect the weight of the bat, since it is so much less than the force of the bat. Choose the direction of the incoming ball as the positive direction. Number i Units VO Vfarrow_forwardA 3.00-kg steel ball strikes a wall with a speed of 10.0 m/s at an angle of 60.0° with the surface. It bounces off with the same speed and angle. If the ball is in contact with the wall for 0.300 s, what is the average force exerted by the wall on the ball in Newtons? 60.0 --X 60.0 Lütfen birini seçin: O A. -173 O B. -120 O C. -240 O D. -260 O E. -150arrow_forwardTreat the collision as elastic. A moving billiard ball hits an identical (except for color) stationary ball. After the collision, the orange ball always goes off in the positive x-direction. The final speeds are v and V. Calculate the angle θ that the green ball goes off in. (θ should be positive.) V0 = the initial green body's speed = 6 m/s M = the mass of both balls = 6 kg φ = the incoming green ball's angle = 70o It's always a good idea to check your answer with the momentum-conservation and energy-conservation equations.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON