
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780078807213
Author: Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
A 0.2 kgkg plastic cart and a 20 kgkg lead cart can both roll without friction on a horizontal surface. Equal forces are used to push both carts forward for a distance of 1 mm, starting from rest.
After traveling 1 mm, is the momentum of the plastic cart greater than, less than, or equal to the momentum of the lead cart?
Match the words in the left column to the appropriate blanks in the sentences on the right.
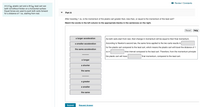
Transcribed Image Text:I Review I Constants
A 0.2 kg plastic cart and a 20 kg lead cart can
both roll without friction on a horizontal surface.
Equal forces are used to push both carts forward
for a distance of 1 m, starting from rest.
Part A
After traveling 1 m, is the momentum of the plastic cart greater than, less than, or equal to the momentum of the lead cart?
Match the words in the left column to the appropriate blanks in the sentences on the right.
Reset Help
a larger acceleration
As both carts start from rest, their change in momentum will be equal to their final momentum.
a smaller acceleration
According to Newton's second law, the same force applied to the two carts results in
for the plastic cart compared to the lead cart, which means the plastic cart will travel the distance of 1
the same acceleration
m in
time interval compared to the lead cart. Therefore, from the momentum principle
the plastic cart will have
final momentum, compared to the lead cart.
a longer
a shorter
the same
a greater
a smaller
the same
Submit
Request Answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The rocket sled shown below decelerates at a rate of 196m/s2 . What force is necessary to produce this deceleration? Assume that the rockets are off. The mass of the system is 2.10103kgarrow_forwardIf the rocket sled shown in the previous problem starts with only one rocket burning, what is the magnitude of this acceleration? Assume that the mass of the system is 2.10103kg , the thrust Tis 2.40104N , and the force of friction opposing the motion is 650.0 N. (b) Why is the acceleration n one-fourth of what it is with all rockets burning?arrow_forwardbetween points in a plane do not change when a coordinate system is rotated In other words, the magnitude of a vector Is invariant under rotations of the coordinate system. Suppose a coordinate system S is rotated about its origin by angle to become a new coordinate system S’, as shown in the following figure. A point in a plane has coordinates (x,y)in S and coordinates (x,y) in S’. (a) Show that, during the transformation of rotation, the coordinates in S are expressed in terms of the coordinates in S by the following relations: {x=xcos+ysiny=xsin+ycos (b) Show that the distance of point Pto the origin is invariant under rotations of the coordinate system. Here, you have to show that x2+y2=x2+y2. (c) Show that the distance between points Pand Q is invariant under rotations of the coordinate system. Here, you have to show that ( xP =xQ )2+( yP yQ )2=( xP =xQ )2+( yP yQ )2 .arrow_forward
- Express your weight in newtons. From this determine your mass in kilograms.arrow_forwardA 100-kg astronaut finds himself separated from his spaceship by 10 m and moving away from the spaceship at 0.1 m/s. To get back to the spaceship, he throws a 10-kg tool bag away from the spaceship at 5.0 m/s. How long will he take to return to the spaceship?arrow_forwardCheck Your Understanding Suppose that Balto in Example 2.10 leaves the game to attend to more important matter, but Astro Clifford and Dug continue playing. Astro and Clifford’s pull on the toy does not change, but Dug rims around and bites on the toy in a different place. With how big a force and in what direction must Dug pull on the toy now to balance out the combined pulls from Clifford and Astro? Illustrate this situation by drawing a vector diagram indicating all forces involved.arrow_forward
- Two cars of the same mass approach an extremely icy four-way perpendicular intersection. Car A travels northward at 30 m/s and car B is travelling eastward. They collide and stick together, traveling at 28 north of east. What was the initial velocity of car B?arrow_forwardThe velocity of a 10-kg object is given by v=5t2i(7t+2t3)j, where if t is in seconds, then v will be in meters per second. a. What is the net force on the object as a function of time? b. What is the momentum of the object when t = 15.0 s?arrow_forwardAstronauts in orbit are apparently weightless. This means that a clever method of measuring the mass of astronauts is needed to monitor their mass gains or losses, and adjust their diet. One way to do this is to exert a known force on an astronaut and measure the acceleration produced. Suppose a net external force of 50.0 N is exerted, and an astronaut’s acceleration is measured to be 0.893m/s2 . (a) Calculate her mass. (b) By exerting a force on the astronaut, the vehicle in which she orbits experiences an equal and opposite force. Use this knowledge to find an equation for the acceleration of the system (astronaut and spaceship) that would be measured by a nearby observer. (c) Discuss how this would affect the measurement of the astronaut’s acceleration. Propose a method by which recoil of the vehicle is avoided.arrow_forward
- An object that has a small mass and an object that has a large mass have the same kinetic energy. Which mass has the largest momentum?arrow_forwardA woman was transporting an open box of cupcakes to a school party. The car in front of her stopped suddenly; she applied her brakes immediately. She was wearing her seat belt and suffered no physical harm (just a great deal of embarrassment), but the cupcakes flew into the dashboard and became “smushcakes.” Explain what happened.arrow_forwardA load of gravel is dumped straight down into a 30000-kg freight car coasting at 2.2 m/s on a straight section of a railroad. If the freight car’s speed after receiving the gravel is 1.5 m/s, what mass of gravel did it receive?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9781938168284
Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. Wolff
Publisher:OpenStax