
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
A boy stands on a bridge 13.3 m above the water, and he drops a water balloon on a boat of unsuspecting tourists. The boat is traveling at a constant speed of 15.3 m/s (toward the bridge), and the boy manages to hit a tourist on the boat with the balloon. How far away from the base of the bridge was the boat when the boy released the balloon?
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Given:
The speed of boat = 15.3 m/s
Distance between the bridge and water = 13.3 m
arrow_forward
Step 2
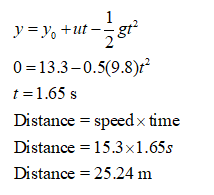
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A car drives straight off of a horizontal cliff with a speed of 45.3 m/s. If it is in the air for 4.43 s, how far from the base of the cliff does the car land? And what is the height of the cliff?arrow_forwardA stunt car traveling at 20 m/s flies horizontally off a cliff and lands 39.2 m from the base of the cliff. How tall is the cliff?arrow_forwardA projectile is shot perfectly horizontally with a speed of 7.02 m/s, and a height of 6.14 m. How far off the ground will it be after 0.459 s? Express your answer in meters to 3 significant figures. Use g=9.81 m/s².arrow_forward
- A person is standing on top of a building. While standing at the edge of the building the person throws a water balloon downward with a speed of 14 m/s and at an angle of 44° below the horizontal. It takes 2.9 s for the water balloon to hit the person's friend. (a) How high is the building in meters? (b) How fast is the water balloon moving when it hits the friend on the ground? Give your answer in m/s. (c) What was the horizontal distance between the friend on the ground and the building in meters?arrow_forwardA baseball player hits a homerun during a game. The ball leaves his bat at 27 degrees with a speed of 17 m/s. The ball soars into the upper deck 200 m from home plate. The ball takes 3.5 s to reach the upper deck. How high above the ground did the ball land?arrow_forwardA single-engine air plain starts its engine at one end of the runway. It accelerates at a constant rate and takes off at 38 m/s after 20 seconds on the runway, just as it is running out of runway. How long is the runway? Your Answer:arrow_forward
- A male volleyball player performs a jump serve and hits the ball 2 meters right above the end line. A volleyball court is 18 meters long, with the net situated right at the middle. The player's serve barely touches the top of the net at exactly 0.5 s.arrow_forwardgarden hose sprays a burst of water horizontally from 1.6 m above level ground. It hits a fence 2.1 m away, horizontally, at a height 0.93 m above the ground. What was the initial speed of the burst of water?arrow_forwardYou are traveling in a convertible with the top down. The car is moving at a constant velocity of 13.6 m/s, due east along flat ground. You throw a tomato straight upward at a speed of 9.17 m/s. How far has the car moved when you get a chance to catch the tomato?arrow_forward
- A player passes a basketball to another player who catches it at the same level from which it was thrown. The initial speed of the ball is 8.1 m/s , and it travels a distance of 4.2 m . What was the initial direction of the ball? What was its time of flight?arrow_forwardA drop tower of an amusement park rises at 5 m/s and is 45 m above theground when one of the riders drops her phone. How long does it take for the phone to fall to the ground?arrow_forwardA piano has been pushed to the top of the ramp at the back of a moving van. The workers think it is safe, but as they walk away, it begins to roll down the ramp. If the back of the truck is 1.0 m above the ground and the ramp is inclined at 20°, how much time do the workers have to get to the piano before it reaches the bottom of the ramp?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON