
Concept explainers
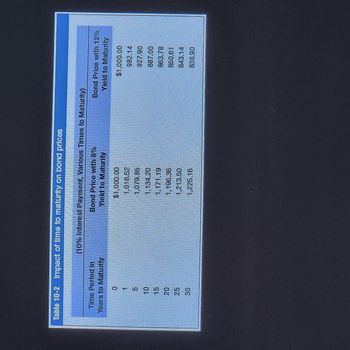
Refer to Table 10-2.
a. Assume the interest rate in the market (yield to maturity) goes down to 8 percent for the 10 percent bonds. Using column 2, indicate what the
b. Assume the interest rate in the market (yield to maturity) goes up to 12 percent for the 10 percent bonds. Using column 3, indicate what the bond price will be with a 10-year, a 20-year, and a 25-year period.
c. Assume the interest rate in the market (yield to maturity) goes down to 8 percent for the 10 percent bonds. If interest rates in the market are going down, which bond would you choose to own?
multiple choice 1
-
10 Years
-
20 Years
-
25 Years
d. Assume the interest rate in the market (yield to maturity) goes up to 12 percent for the 10 percent bonds. If interest rates in the market are going up, which bond would you choose to own?
multiple choice 2
-
10 Years
-
20 Years
-
25 Years
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

- Please answer 6D.arrow_forward12. Suppose that 1-year bonds currently offer a nominal yield to maturity of 4% (1,0 = 0.04), otherwise comparable 2-year bonds currently offer a yield to maturity of 4.5% (12,0 = 0.045), and 3 year bonds currently offer a yield to maturity of 4.8% (13,0 = 0.048). a. Draw the current yield curve. b. Based on the Expectations Theory of Term Structure, what yield to maturity do investors expect next year's 1 year bonds to earn (i.e. - what is it,1)? c. What do investors expect the yield to be on 1 year bonds in two years (11,2 = ?)? d. What do investors expect the yield to be on 2 year bonds next year (i2,1 =?)?arrow_forwardThe following table summarizes prices of various default-free zero-coupon bonds (expressed as a percentage of the face value): a. Compute the yield to maturity for each bond. b. Plot the zero-coupon yield curve (for the first five years). c. Is the yield curve upward sloping, downward sloping, or flat? a. Compute the yield to maturity for each bond. The yield on the 1-year bond is 3.92 %. (Round to two decimal places.) Data table (Click on the following icon in order to copy its contents into a spreadsheet.) Maturity (years) Price (per $100 face value) 1 $95.51 2 3 $91.10 $86.55 $81.69 $76.45 Print Dondayarrow_forward
- A Treasury bond that matures in 10 years has a yield of 4.25%. A 10-year corporate bond has a yield of 9.00%. Assume that the liquidity premium on the corporate bond is 0.70%. What is the default risk premium on the corporate bond? Round your answer to two decimal places.arrow_forwardAssume that the real, risk-free rate of interest is expected to be constant over time at 3 percent, and that the annual yield on a 6-year corporate bond is 8.00 percent, while the annual yield on a 10-year corporate bond is 7.75 percent: you may assume that the default risk and liquidity premium are the same for both bonds. Also assume that the maturity risk premium for all securities can be estimated as MRP, (0.1%) *(t-1), where t is the number of periods until maturity. Finally assume that inflation is expected to be constant at 3 percent for Years 1-6, and then constant at some rate for Years 7-10 (4 years). Given this information, determine what the market must anticipate the average annual rate of inflation will be for Years 7-10. 2.583% O 1979% 2.281% 1.375 % O 1.677 % 4arrow_forwardPlease see attached. Definitions: Yield to maturity (YTM) is the return the bond holder receives on the bond if held to maturity. Treasury note is a U.S. government bond with a maturity of between two and ten years. Current yield is the annual bond coupon payment divided by the current price.arrow_forward
- Suppose the term structure of interest rate is flat. Consider the following four bonds: Bond Term to Maturity (year) Coupon rate YTM 1 5 10% 7% 2 3 7 7 10% O a. 2,3,4,1 O b. 2,1,4,3 O c. 1,2,3,4 O d. 4,3,2,1 3% 3% 7% 4 7 If the yield-to-maturity for all bonds changes by 1%, rank the bonds from the lowest percentage change in price to the largest percentage change in price based on duration approximation. 7% 5%arrow_forwardConsider the following: Price Yield to maturity Periods to maturity Modified duration Fixed-rate Bond Fixed-rate Note 107.18 5.00% 18 6.9848 100.00 5.00% 8 3.5851 a. For an increase in interest rates of 100 basis points, determine the change in value for the fixed-rate note. Show your work. b. For an increase in interest rates of 100 basis points, determine the change in value for the fixed-rate bond. Show your work. c. Which of the two fixed-rate securities are more sensitive to increases interest rates? Why? d. What would be the most appropriate course of action to take given interest rates are expected to rise? Explain carefully.arrow_forwardAssume that a $10,000.00 bond paying 8.5% interest is currently selling at 106. What is the current selling price of the bond? What is the current yield of this bond? a. b. (arrow_forward
- Show all workings. Complete the following table and draw a graph showing how bond pricefor each bond changes over time as they move towards their maturitydates. Describe the relationship between bond prices and timeremaining for maturity.YearsreminingtomaturityBOND ACoupon rate = 8% p.a.Market interest rate =6% p.a.BOND BCoupon rate = 6% p.a.Market interest rate =6% p.a.BOND CCoupon rate = 4% p.a.Market interest rate =6% p.a.109876543210arrow_forwardCalculate the total annual interest, total cost, and current yield for the bond. (Round the "Current yield" to the nearest tenth percent and other answers to the nearest whole dollar.) Number of bonds Total annual Bond Selling price Total cost Current yield purchased interest Wang 6 1/2% 26 4. 68.125 % 96 Prev 9 of 18 Next > Marrow_forward(Related to Checkpoint 9.2 and Checkpoint 9.3) (Bond valuation) The 15-year $1,000 par bonds of Vail Inc. pay 9 percent interest. The market's required yield to maturity on a comparable-risk bond is 6 percent. The current market price for the bond is $1,100. a. Determine the yield to maturity. b. What is the value of the bonds to you given the yield to maturity on a comparable-risk bond? c. Should you purchase the bond at the current market price? ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- a. What is your yield to maturity on the Vail bonds given the current market price of the bonds? % (Round to two decimal places.)arrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





