
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:a. What is the monopolist's profit-maximizing output and price?
Output:
Price: $
b. What will be the monopolist's total profit?
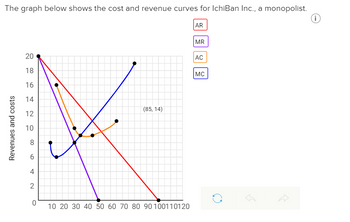
Transcribed Image Text:The graph below shows the cost and revenue curves for IchiBan Inc., a monopolist.
Revenues and costs
20
18
16
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
0
(85, 14)
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100110120
AR
MR
AC
MC
(i)
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1: Define profit maximization:-
If a firm wants to maximise its profits, it will produce the amount at which its marginal cost of production equals its marginal income from that production.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- a. what is the optimal quantity of goods for the firm to produce b. what is the optimal price for the quantity of goods for the firm to produce c. what is the total revenue for the firm d. what is the total cost for the firm e. what is profit/loss for the firmarrow_forwardQuestion 33 Suppose a monopolist faces the demand curve P = 200 – 2Q, has marginal cost curve MC = 2Q, and zero fixed costs. If the monopolist can perfectly price discriminate, which of the following is true? The monopolist sells 33 units at a profit of 3300. The monopolist sells 33 units at a profit of 1650. The monopolist sells 50 units at a profit of 5000. The monopolist sells 50 units at a profit of 2500.arrow_forwardWhat is the profit-maximizing (equilibrium) condition that a monopolist uses to set its quantity of output? Question 8Answer a. Marginal Cost = Marginal Revenue b. Price = Marginal Revenue c. Price = Average Cost d. Price = Marginal Cost e. Supply = Demandarrow_forward
- What is price discrimination? From the perspective of running a business, is this a good thing or bad thing for profits?arrow_forwardQUESTION 1 A. The total cost function for a monopolist is given by TC = 44,000 + 180Q + 0.03Q² and the demand function is P = 420 – 0.06Q per unit of output. i. What is the profit maximising level of output? ii. Calculate the profit maximizing price. iii. Calculate total profit at the profit maximising level of output.arrow_forwardb bMy Question X WMonop HW X Σ Σ G + f G Office Editing for Docs, Sheets & Slides chrome-extension://bpmcpldpdmajfigpchkicefoigmkfalc/... The quantity has been found for you by finding where MC-MR. The monopolist sets price by charging as high as demand will bear at that quantity. So once the quantity has been found, go upon the dotted is the price. Total Revenue is PxQ, Total costs are found by finding the average cost and multiplving by O. ATC AVC 100 100 MR What is the optimal quantity? What is the price? What is Total Revenue? What is Total Cost? What is Total Variable Cost? What is Total Fixed Cost? [Hint: Average fixed cost is the vertical distance between the ATC and AVC curves at the optimal Q.] Is there a profit or a loss? How much? 8 11:02arrow_forward
- Suppose that the monopolist's demand is: P = 8 – Q, and marginal revenue is: MR = 8 – 2Q. - The marginal cost is: MC = 2, and there is no fixed cost. a.Find out the profit maximizing output level. b.Specify the amount of economic profit or loss at the profit maximizing output. c.Calculate the price elasticity of demand at the profit maximizing point and explain it.arrow_forwardThe diagram below shows a monopolist’s marginal cost scheduleand the demand curve. Find and depict the following items within the diagram and briefly explainhow you found them: a) The efficient (i.e., total surplus maximising) quantity. b) The monopolist’s profit maximising quantity. c) The monopolist’s profit maximising price. d) The monopolist’s optimal profit. e) The deadweight loss.arrow_forwardIt is possible for a monopolist's to earn economic profits even in the long run due to: a. its barriers to the entry of other firms. b. the nature of the monopolist's product. c. its practice of third-degree price discrimination.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education