
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
7
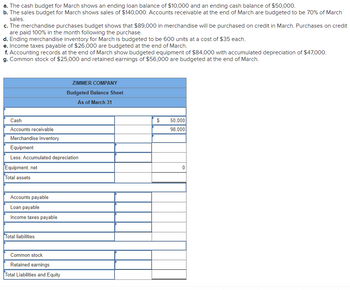
Transcribed Image Text:a. The cash budget for March shows an ending loan balance of $10,000 and an ending cash balance of $50,000.
b. The sales budget for March shows sales of $140,000. Accounts receivable at the end of March are budgeted to be 70% of March
sales.
c. The merchandise purchases budget shows that $89,000 in merchandise will be purchased on credit in March. Purchases on credit
are paid 100% in the month following the purchase.
d. Ending merchandise inventory for March is budgeted to be 600 units at a cost of $35 each.
e. Income taxes payable of $26,000 are budgeted at the end of March.
f. Accounting records at the end of March show budgeted equipment of $84,000 with accumulated depreciation of $47,000.
g. Common stock of $25,000 and retained earnings of $56,000 are budgeted at the end of March.
Cash
Accounts receivable
Merchandise Inventory
Equipment
Less: Accumulated depreciation
Equipment, net
Total assets
Accounts payable
Loan payable
Income taxes payable
Total liabilities
ZIMMER COMPANY
Budgeted Balance Sheet
As of March 31
Common stock
Retained earnings
Total Liabilities and Equity
$
50,000
98,000
0
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education