
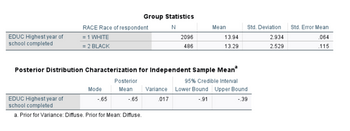
a. State the null and research hypotheses:
H0:
H1:
b. Is the F statistic for Levene’s test significant?
c. What is the alpha level for the t-test?
d. Obtained t-value:
e. Significance level for the t-test:
f. Decision rule:
If the significance level of the obtained t statistic is greater than ____ (alpha level), we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
If the significance level of the obtained t statistic is equal to or less than ____ (alpha level), we reject the null hypothesis.
g. Decision: Since the significance level of the obtained t statistic is _____ and it is __________(greater or less) than ____ (alpha level), we ________(reject or fail to reject) the null hypothesis.
h. Interpretation/conclusion:
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 11 images

- The test statistic of z = 2.05 is obtained when testing the claim that p > 0.4. Identify the hypothesis test as being two-tailed, left-tailed, or right-tailed. Find the P-value. Using a significance level of α = 0.10, should we reject H0 or should we fail to reject H0?arrow_forwardThe test statistic of z=2.77 is obtained when testing the claim that p≠0.684. a. Identify the hypothesis test as being two-tailed, left-tailed, or right-tailed. b. Find the P-value. c. Using a significance level of α=0.10, should we reject H0 or should we fail to reject H0?arrow_forwardTest the claim that the proportion of men who own cats is smaller than the proportion of women who own cats at the .05 significance level.The null and alternative hypothesis would be: H0:μM=μFH1:μM<μF H0:pM=pFH1:pM<pF H0:pM=pFH1:pM>pF H0:pM=pFH1:pM≠pF H0:μM=μFH1:μM≠μF H0:μM=μFH1:μM>μF The test is: right-tailed left-tailed two-tailed Based on a sample of 20 men, 40% owned catsBased on a sample of 60 women, 55% owned catsThe test statistic is: (to 2 decimals)The p-value is: (to 2 decimals)Based on this we: Fail to reject the null hypothesis Reject the null hypothesisarrow_forward
- Use the given information to find the P-value. Also, use a 0.05 significance level and state theconclusion about the null hypothesis (reject the null hypothesis or fail to reject the null hypothesis).With H1: p (does not equal) 3/5, the test statistic is z = 0.78arrow_forwardThis Question: 4 pts 1 of 9 (0 complete) This Quiz: 45 pts possible Assume a significance level of a = 0.05 and use the given information to complete parts (a) and (b) below. Original claim: More than 54% of adults would erase all of their personal information online if they could. The hypothesis test results in a P-value of 0.1661. a. State a conclusion about the null hypothesis. (Reject H, or fail to reject Ho.) Choose the correct answer below. A. Reject Ho because the P-value is greater than a. B. Reject Ho because the P-value is less than or equal to a. C. Fail to reject H, because the P-value is less than or equal to a. O D. Fail to reject H, because the P-value is greater than a. b. Without using technical terms, state a final conclusion that addresses the original claim. Which of the following is the correct conclusion? A. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that the percentage of adults that would erase all of their personal information online if they could is…arrow_forwardIarrow_forward
- Test the claim that the mean GPA of night students is larger than 2.1 at the 0.01 significance level. The null and alternative hypotheses would be: 0.525 Ho: u = 2.1 Ho: µ = 2.1 Ho:µ = 2.1 Ho:p 0.525 Ho:p 0.525 H:p> 0.525 H1:p+ 2.1 H:µ > 2.1 H:µ < 2.1 H1:p< 0.525 H :p + 0.525 The test is: left-tailed two-tailed right-tailed Based on a sample of 38 people, the sample mean GPA was 2.11 with a standard deviation of 0.2 The p-value is: (to 3 decimals) The significance level is: (to 2 decimals) Based on this we: O Fail to reject the null hypothesis O Reject the null hypothesis Question Help: Message instructor Submit Question N D archarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is true regarding the influence of a small alpha level in the context of hypothesis testing? a. A small alpha level reduces the likelihood of a Type I error. b. A small alpha level reduces the effect size. c. A small alpha level increases statistical power. d. A small alpha level increases the likelihood of detecting statistical significance.arrow_forwardState the Result: A hypothesis test was conducted at the alpha = 0.01 level of significance. The test resulted in a p-value of 0.044.arrow_forward
- Test the daim that the proportion of men who own cats is significan tly different than the proportion of women who own cats at the 0.02 significance level. The null and alternative hypothesis would be: Ho:PM = PF Ho:HM PF Ho:PM µp H1:µM PF H1:µM + HF The test is left-tailed two-tailed right-tailed Based on a sample of 80 men, 40% owned cats Based on a sample of 20 women, 50% owned cats positive Critical Value = [three decimal accuracy] Test Statistic = [three decimal accuracy] Based on this we: O Reject the null hypothesis O Fail to reject the null hypothesisarrow_forwardUse the given information to find the p-value. Also, use a 0.05 significance level and state the conclusion about the null hypothesis (reject the null hypothesis or fail to reject the null hypothesis). K The test statistic in a right-tailed test is z=0.52. OA. 0.6030; fail to reject the null hypothesis OB. 0.0195; reject the null hypothesis OC. 0.3015; reject the null hypothesis OD. 0.3015; fail to reject the null hypothesis I Z 7 s 7 S x H command E D с III T R F G B Y I H U N B I J M G K O 6 H Time Remaining: 01:02:48 P command E . ? option Nextarrow_forwardThe test statistic of z=2.26 is obtained when testing the claim that p≠0.659. a. Identify the hypothesis test as being two-tailed, left-tailed, or right-tailed. b. Find the P-value. c. Using a significance level of α=0.01, should we reject H0 or should we fail to reject H0?arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





