
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134753119
Author: Sheldon Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
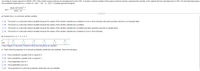
Transcribed Image Text:According to recent research by NASA, 34% of the world's space products are manufactured in the USA. Consider a random sample of five space products and let x represent the number in the sample that are manufactured in USA. The formula below gives
the probability distribution for x, where n! = (n)(n – 1)(n - 2)...(2)(1). Complete parts a through d.
(5!)(0.34)*(0.66)5 - x
p(x) =
(x1)(5 - х)!
a. Explain why x is a discrete random variable.
O A. The event x is a discrete random variable because the values of the random variable are contained in one or more intervals and each possible outcome is not equally likely.
O B. The event x is a discrete random variable because the values of the random variable are countable.
OC. The event x is a discrete random variable because the values of the random variable are countable and each possible outcome is equally likely.
O D. The event x is a discrete random variable because the values of the random variable are contained in one or more intervals.
b. Find p(x) for x = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5.
1
3
4
p(x)
(Type integers or decimals rounded to three decimal places as needed.)
c. Check that the properties for a discrete probability distribution are satisfied. Select all that apply.
O A. Each probability is greater than or equal to 0.
O B. Each probability is greater than or equal to 1
O C. The probabilities sum to 1.
O D. The probabilities sum to 0.
O E. The properties for a discrete probability distribution are not satisfied.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Consider two events A and B. The probability for event A is P(A) = 0.52. Suppose P(B|A) = 0.65 and P(B|AC) = 0.45. a. Find P(AC). b. Find P(An B). c. Find P(An B). d. Construct a probability tree diagram. See the diagram on pages 50 and 52 of the course packet. Find P(B). Find P(A/B). Are A and B mutually exclusive? Why or why not? Are A and B independent? Why or why not? U e. f. g. h.arrow_forwardFlip two fair coins. Then the sample space is {HH, HT, TH, TT} where T = tails and H = heads. The outcomes HT and TH are different and the HT means that the first coin showed heads and the second coin showed tails. The TH means that the first coin showed tails and the second coin showed heads. Let A = the event of getting at least one tail while letting B = the event of getting all tails. What is the probability of event A ∩ B? a. 0.66 b. 0.50 c. 0.25 d. 0.75arrow_forwardA box of 50 remote control devices contains 3 that have a defective power button. If devices are randomly sampled from the box and inspected one at a? time, determine the following probabilities. a. The probability that the first control device is defective. b. The probability that the first control device is good and the second control device is defective. c. The probability that the first three sampled devices are all good.arrow_forward
- Suppose D and C are independent events in the same sample space. If we know that Pr [D] = ½ and Pr[C] = ½, Pr[DUC] determine Pr DUC A. 8 35 26 B. 35 9 C. 35 6 D. E. 27 35arrow_forwardLet E and F be mutually exclusive events in a sample space S. The odds that E occurs are 3:5 and the odds F occurs are 2:8. If it is known that either E or F occurred, what are the odds that the event was E? The odds that E occurred areDO (Type whole numbers. Simpity your answer.)arrow_forwardK What is the difference between an outcome and an event? (...) Choose the correct answer below. O A. An event is the result of a single probability experiment. An outcome is the set of all possible events. OB. An event is the result of a single probability experiment. An outcome is a set of one or more possible events. OC. An outcome is the result of a single probability experiment. An event is a set of one or more possible outcomes. O D. An outcome is the result of a single probability experiment. An event is the set of all possible outcomes.arrow_forward
- A coin with a 0.80 probability for a tail is flipped six times. a. Find the probability of obtaining exactly five tails. b. Find the probability of obtaining exactly one head. c. True or false? The probabilities in parts a and b must be equal to each other.arrow_forwardL American Airlines' flights from Chicago to Atlanta are on time 60 % of the time. Suppose 14 flights are randomly selected, and the number on-time flights is recorded. 1.The probability that at least 2 flights are on time is %3D 2.The probability that at most 2 flights are on time is 3.The probability that exactly 7 flights are on time is = > Next Question MacBook Pro %23 & 24 3.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON

A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:9780134753119
Author:Sheldon Ross
Publisher:PEARSON
