
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
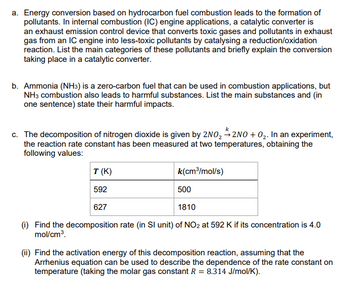
Transcribed Image Text:a. Energy conversion based on hydrocarbon fuel combustion leads to the formation of
pollutants. In internal combustion (IC) engine applications, a catalytic converter is
an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust
gas from an IC engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalysing a reduction/oxidation
reaction. List the main categories of these pollutants and briefly explain the conversion
taking place in a catalytic converter.
b. Ammonia (NH3) is a zero-carbon fuel that can be used in combustion applications, but
NH3 combustion also leads to harmful substances. List the main substances and (in
one sentence) state their harmful impacts.
c. The decomposition of nitrogen dioxide is given by 2NO₂2NO+O₂. In an experiment,
the reaction rate constant has been measured at two temperatures, obtaining the
following values:
T (K)
592
627
k(cm³/mol/s)
500
1810
(i) Find the decomposition rate (in SI unit) of NO₂ at 592 K if its concentration is 4.0
mol/cm³.
(ii) Find the activation energy of this decomposition reaction, assuming that the
Arrhenius equation can be used to describe the dependence of the rate constant on
temperature (taking the molar gas constant R = 8.314 J/mol/K).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 13 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Problem #1: The art of being a good chemical engineer is being able to quickly understand relationships between various phenomena. We oftentimes compare process variables (flow rate, temperature, pressure, etc.) to develop a mathematical understanding of a particular situation. Reactant concentration versus time, distillation pressure versus distillate (or bottoms) composition, and inlet flow rate versus outlet stream temperature of a heat exchanger are just a few of these. In gas chromatograph (GC), the GC converts a signal output (usually in mV) into a peak area. Calibration curves are made by testing the peak areas for different concentrations of a mixture and then fitting those areas to a linear expression. Using linear regression, develop the calibration curve for this dataset of various concentrations for monoethanolamine in toluene. Peak Area Conc, mg/L 0.05 0.03 5 0.13 7.5 0.25 10 0.33 12.5 0.35 15 0.44arrow_forwardI need to find volumectric flow rate. I attached my work as well as the question. I feel like my process is correct, but maybe I got lost in a math step.arrow_forwardThe gas phase reaction A → 2R + ½S is carried out in a tubular reactor with the following reaction and reactor conditions:(i) Reaction = First Order;(ii) Reactor Dimensions: diameter = 50 cm and length = 6 m;(iii) Power is made from the introduction of a single power currentwith 60% by weight of A and 40% by weight of aggregate;(iv) Global feeding of 400 mol/hour;(v) Feed current conditions: temperature of 25°C and pressure of 4 atm;(vi) Reactor temperature = 200 °C;(vii) Conversion obtained: 75%;(viii) Molecular Weights: Reagent A = 38 g/gmol; inert = 28 g/gmol.What is the volume of a mixing reactor operating under the same feed conditions as the tubular reactor and at the same conversion?arrow_forward
- 0 O file:///C:/Users/MEGA/Downloads/Cengel.%20Heat%20and%20mass%20Transfer%20F FIGURE P10-20 10-21 Water is boiled at sea level in a coffeemaker equipped with a 30-cm-long, 0.4-cm-diameter immersion-type electric heating element made of mechanically polished stainless steel. The coffeemaker initially contains 1 L of water at 14°C. Once boiling starts, it is observed that half of the water in the cof- feemaker evaporates in 32 min. Determine the power rating of the electric heating element immersed in water and the surface temperature of the heating element. Also determine how long it will take for this heater to raise the temperature of 1 L of cold water from 14°C to the boiling temperature. I atm St Coffee maker FIGURE P10-21 IL b ar th in 10 Со 0.5 atu she the occ han belo stair beloarrow_forwardQ3: Ethyl ether is made by dehydration of ethyl alcohol in the presence of sulfuric acid at 140 °C 2C2₂H5OH →→C4H₁0O+H₂O A simplified process is shown in figure below. If 87% conversion of the alcohol fed to reactor occurs per pass stream in reactor. 1- Write the equations that simulate above process. 2- Perform the degree of freedom for the overall and sub processes (List your answer in table). Pure ethyl ether (1200 kg/hr) 93% H₂SO4 7% H₂0 Alcohol separation Dilute H₂SO4 solution Fresh feed 95% alcohol Reactor Ether separation Recycle 92% alcohol 8% water Waste Sulfuric acid and waterarrow_forwardThe following reaction takes place in a catalytic reactor: NO2+O2 → NO3 In the process 1000 mol/s of NO3 are produced. The reaction has 90% conversion and air with 20% excess is supplied. Calculate the flow rates of the system.arrow_forward
- Using RCRA procedures, determine if the following are classified as hazardous wastes. State the reason why or why not is is hazardous. If it is a hazardous waste, state the RCRA waste category number. Assume that the industry porducing the waste is a RCRA hazardous waste generator. 1. Sawdust in a warehouse contaminated by a spill of pentachlorobenzene. 2. Sludge from the treatment of water from the chemical conversion coating of aluminum. 3. An aqueous industrial waste stream from a plastic manufacturing plant that is discharged to a river.arrow_forwardPowerplant cooling water with a temperature of 35 °C and a flowrate of 10 m3/s is discharged into a river with a temperature of 10 °C and a flowrate of 50 m3/s.a) What will the new temperature of the river be downstream of the mixing point? Draw and label your figure and state any assumptions.b) Using your knowledge of Henry’s law to justify your answer, how will this change in river temperature influence the amount of oxygen gas dissolved in the water?arrow_forwardA coal-fired 700 MW Power Plant has an efficiency of 35%, burns coal with an energy content of 10,000 BTU/lb, with 60% carbon content, 1.5% sulfur content. The coal burned produces 10% ash, and of the ash, 70% is fly ash.What are the particulate emissions released if a 99% efficient scrubber is used (in lb Fly Ash/hr)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The