
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Solve for all parts a-e for the question in the image below.
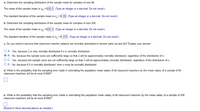
Transcribed Image Text:a. Determine the sampling distribution of the sample mean for samples of size 64.
The mean of the sample mean is µ = $ 56.3. (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.)
The standard deviation of the sample mean is; =S.95. (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.)
b. Determine the sampling distribution of the sample mean for samples of size 256.
The mean of the sample mean is µ; = $ 56.3. Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.)
The standard deviation of the sample mean is o; =S .475|. (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.)
c. Do you need to assume that classroom teacher salaries are normally distributed to answer parts (a) and (b)? Explain your answer.
O A. Yes, because x is only normally distributed if x is normally distributed.
O B. No, because the sample sizes are sufficiently large so that x will be approximately normally distributed, regardless of the distribution of x.
O C. Yes, because the sample sizes are not sufficiently large so that x will be approximately normally distributed, regardless of the distribution of x.
O D. No, because if x is normally distributed, then x must be normally distributed.
d. What is the probability that the sampling error made in estimating the population mean salary of all classroom teachers by the mean salary of a sample of 64
classroom teachers will be at most $1000?
e. What is the probability that the sampling error made in estimating the population mean salary of all classroom teachers by the mean salary of a sample of 256
classroom teachers will be at most $1000?
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
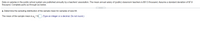
Transcribed Image Text:Data on salaries in the public school system are published annually by a teachers' association. The mean annual salary of (public) classroom teachers is $51.5 thousand. Assume a standard deviation of $7.6
thousand. Complete parts (a) through (e) below.
.....
a. Determine the sampling distribution of the sample mean for samples of size 64.
The mean of the sample mean is µ, = $ . (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Solve. Bill and Ted earned a total of $65 babysitting during the month of November. Bill earned $5 more than 1/2 of what Ted earned. How much did they each earn? Bill $ Ted $arrow_forwardSolve. 1 5 8 5x + 20 x - 16 X- 4 Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete youarrow_forwardWill you solve for the following?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman