
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
a. Calculate the total molar amount and mole fractions of methanol, air (N2+O2)
and water fed to the reactor.
b. Determine the extents of reaction, ??̇1and ??̇2.
c. Calculate the fractional conversion of methanol.
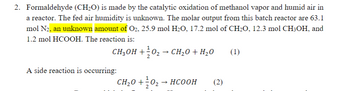
Transcribed Image Text:2. Formaldehyde (CH₂O) is made by the catalytic oxidation of methanol vapor and humid air in
a reactor. The fed air humidity is unknown. The molar output from this batch reactor are 63.1
mol N2, an unknown amount of O2, 25.9 mol H₂O, 17.2 mol of CH₂O, 12.3 mol CH3OH, and
1.2 mol HCOOH. The reaction is:
CH3OH +0₂ → CH₂O + H₂O
(1)
A side reaction is occurring:
CH,O +}0 → HCOOH
(2)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 7 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Solve correctly please, (Gpt/Ai wrong answer not allowed)arrow_forwardI only need help with the highlighted one please :)arrow_forwardDecomposition of sulfuryl chloride The reaction shown below is first order with regards to SO2Cl2 concentration and has a half-life of 7.40 h at 629 K. SO2Cl2 → SO2 + Cl2 What is the rate constant for the reaction at 218 K if the activation energy is 14.5 kJ/mol?arrow_forward
- 1. A house needs 200,000 Btu per day so that its temperature remanins at 68oF. How much CaCl26H2O(s) needs to be used to save enough energy for one day use? The process contains the heating of CaCl26H2O(s) from 68oF to 86oF and the reaction CaCl26H2O(s) = CaCl22H2O(s) + 4H2O(g). The water from the dehydration evaporates during the process. CaCl26H2O(s): ΔHof=-2607.89kJ/gmol, Cp=1.34J/g(oC) CaCl22H2O(s): ΔHof=-1402.90kJ/gmol, Cp=0.97J/g(oC)arrow_forwardREACTION ENGINEERING Consider a heterogeneous gas-phase catalytic reaction:AB(g)→A(g)+B(g) (Catalyst) The surface reaction mechanism follows three steps: AB(g) +S <----> AB*S (Adsorption)AB*S<----> B*S+A(g) (Surface reaction)B*S <---> B(g) + S (Desorption) a) Derive the initial rates (AR) of the reaction, assuming there is no product (ie., A and B) in the feed (ie., PA Pao=0), assuming adsorption is the rate determining step. Use initial pressure of AB (ie., PARA), total number of sites on the surface (C), and the rate and equilibrium constants in the expressions.Hint: Based on the reaction mechanism, only AB and B are adsorbed on the surface, i.e., there is no evidence that A alone can be adsorbed on the surface.arrow_forwardPrepare a material flowsheet similar to Figure 6.1 (shown below) for production of 2400 lb-mol/hr of Vinyl Chloride (VC) based on the reaction path #5 with the operating parameters provided below. You MUST show the Molar flow rates of ALL compounds in ALL streams in your flowsheet. Reaction Path #5. Balanced process for Chlorination of Ethylene C2H4 + Cl2--> C2H4CI2 (C) Ileat Liberated Ileat Absorbed y Reactinn 150 x 10 Blutr duriag Reaction = 52 x 10 Bluhr C2H4 + 2HCI + 1/2 O2--> C2H4CI2 + H2O 2C2H4CI2 --> 2C;H3CI + 2HCI (E) (D) 58.300 Ibhr 2C2H4 + Cl2 +1/2 O2 --> 2C2H3CI + H2O (C) 100% Conv. of Cl2 at 80°C and 150 kPa with 15% (G) Direct Chlorination YƯ C, 15 atm Pyrolysis Sorc +CH,CI- 26 ata HCI CH.CI, CAL 11.3,4KI hr 158,I Ihyhr CH,CI, C1,CI 4,900 Ihhr CH, -a CH,CI, excess C2H4 CH,ClCH,CI + HCI (E) 100% Conv. of HCl at 275°C and 150 kPa with 5% 105,500 Ib'hr excess C2Н4 (D) 75% Conv. At 500 °C and 3000 kPa. Water is separated from the mixture before entering Figure 6.1 reactor D.arrow_forward
- (a) Consider the mass transfer-limited reaction: A → 2B DAB = 0.01 cm²s-1 What would your concentration (mole fraction) profile look like as a function of distance (i.e. z/8)? What is the flux of A?arrow_forwardStart with the general mass balance relationship In – Out + Rxn = Accum and derive a formula that allows you to calculate the value of the first order reaction rate constant, k, given the half-life of a compound. Use the equation to determine the value of k for carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) given that CCl4 has a half-life of 8,030 days in air.arrow_forwardCalculate the solubility of Zn(OH)2 in a 0.0300M K2SO4 solution using activities and concentration. Determine the % error when using only concentrations (assuming that the actual solubility is the determined with the activity). The Kps of Zn(OH)2 is 1.2 x 10-17arrow_forward
- please quickly thanks !!!!arrow_forwardREACTION ENGINEERING Consider a heterogeneous gas-phase catalytic reaction:AB(g)→A(g)+B(g) (Catalyst) The surface reaction mechanism follows three steps: AB(g) +S <----> AB*S (Adsorption)AB*S<----> B*S+A(g) (Surface reaction)B*S <---> B(g) + S (Desorption) (a) Derive the rate law assuming desorption is rate-limiting. Express the overall reaction rate (- rab) in terms of total number of sites on the surface, C. partial pressures of the gas species (ie., Pab, Pa and Pb), rate constants of adsorption, the surface reaction, and desorption (ka,ks, and kd), and the equilibrium constants of adsorption, the surface reaction, and desorption (ie., K. Ks and Kd). Hint: Based on the reaction mechanism, only AB and B are adsorbed on the surface, i.e., there is no evidence that A alone can be adsorbed on the surface.arrow_forward2. Find the AH for the reaction below, given the following reactions and subsequent AH values: 2C2(g) + H2O(g) – C2H2(g) + /2 02(g) C2H2(g) + 2H2(g) C2He(g) AH = -94.5 kJ H20(g) - H2(g) + % O2 (g) AH =71.2 kJ C2H6(g) + /2 Oz(g) - 2 CO2(9) + 3 H2O(g) AH = -283 Kjarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The